Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States and worldwide. Unfortunately, standard therapies remain inadequate. An increased
understanding of the molecular biology of lung cancer biology is required to develop more effective new therapies. In this report, we show that the Wnt pathway is activated through
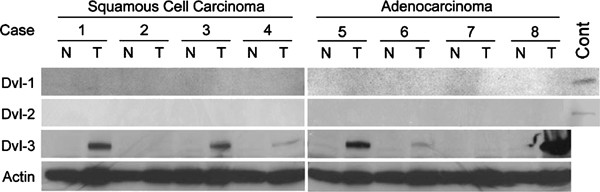
Dishevelled (Dvl) overexpression in NSCLC. Analysis of freshly resected tumors and lung cancer cell lines demonstrate that Dvl-3, a critical mediator of Wnt signaling, is overexpressed.
Specifically, Dvl-3 was overexpressed significantly in 75% of fresh NSCLC microdissected samples compared to control paired matched normal lung samples. To evaluate the biological
significance of Wnt signaling and, in particular, Dvl function in lung cancer, we transfected siRNA (designed to inhibit selectively human Dvl-1, -2, and -3), to the NSCLC cell line H1703,
which is known to have _β_-catenin-mediated Tcf-dependent transcriptional activity. Here, we demonstrate that Dvl-specific siRNA treatment in H1703 decreases significantly Dvl and
_β_-catenin expression, resulting in reduction of Tcf-dependent transcriptional activity, and, importantly, growth inhibition. Taken together, these data support the novel hypothesis that
Dvl overexpression is critical to Wnt signaling activation and cell growth in NSCLC. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via
your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 50 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $5.18 per issue Learn more Buy this
article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in
* Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS AJUBA PROMOTES THE PROLIFERATION, INVASION AND MIGRATION OF NSCLC
CELLS BY ACTIVATING THE ERK/Β-CATENIN PATHWAY Article Open access 16 April 2025 SIRT1 SILENCING AMELIORATES MALIGNANCY OF NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER VIA ACTIVATING FOXO1 Article Open access
28 August 2024 BUB1 INDUCES AKT/MTOR PATHWAY ACTIVITY TO PROMOTE EMT INDUCTION IN HUMAN SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Article Open access 04 September 2024 REFERENCES * Brantjes H, Barker N, van Es
J and Clevers H . (2002). _Biol. Chem._, 383, 255–261. * Brognard J and Dennis PA . (2002). _Cell Death Differ._, 9, 893–904. * Cagatay T and Ozturk M . (2002). _Oncogene_, 21, 7971–7980. *
Hommura F, Furuuchi K, Yamazaki K, Ogura S, Kinoshita I, Shimizu M, Moriuchi T, Katoh H, Nishimura M and Dosaka-Akita H . (2002). _Cancer_, 94, 752–758. * Li L, Mao J, Sun L, Liu W and Wu D
. (2002). _J. Biol. Chem._, 277, 5977–5981. * Liu J, Stevens J, Rote CA, Yost HJ, Hu Y, Neufeld KL, White RL and Matsunami N . (2001). _Mol. Cell_, 7, 927–936. * Matsuzawa SI and Reed JC .
(2001). _Mol. Cell_, 7, 915–926. * Minna JD . (1998). _Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine_ VOL. 14. Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Isselbacher KJ, Martin JB (eds). McGraw-Hill: New
York, pp. 522–562. Google Scholar * Morin PJ . (1999). _BioEssays_, 21, 1021–1030. * Polakis P . (2000). _Genes Dev._, 14, 1837–1851. * Sekido Y, Fong KM and Minna JD . (1998). _Biochim.
Biophys. Acta_, 1378, F21–F59. * Shimizu H, Julius MA, Giarre M, Zheng Z, Brown AM and Kitajewski J . (1997). _Cell Growth Differ._, 8, 1349–1358. * Sunaga N, Kohno T, Kolligs FT, Fearon ER,
Saito R and Yokota J . (2001). _Genes Chromosom. Cancer_, 30, 316–321. * Ueda M, Gemmill RM, West J, Winn R, Sugita M, Tanaka N, Ueki M and Drabkin HA . (2001). _Br. J. Cancer_, 85, 64–68.
* Wang J, Shou J and Chen X . (2000). _Oncogene_, 19, 1843–1848. * Wharton Jr KA . (2003). _Dev. Biol._, 253, 1–17. * Winn RA, Bremnes RM, Bemis L, Franklin WA, Miller YE, Cool C and Heasley
LE . (2002). _Oncogene_, 21, 7497–7506. * You L, Uematsu K, McBrine MJ, McCormick F and Jablons DM . (2001). _Proc. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res._, 42, 609. Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION
AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Thoracic Oncology Laboratory, UCSF Cancer Center, University of California at San Francisco, San Francisco, 94115, CA, USA Kazutsugu Uematsu, Biao He, Liang You,
Zhidong Xu, Frank McCormick & David Mark Jablons * The Fourth Department of Internal Medicine, Nippon Medical School, Tokyo, 113-8602, Japan Kazutsugu Uematsu Authors * Kazutsugu Uematsu
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Biao He View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Liang
You View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Zhidong Xu View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Frank McCormick View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * David Mark Jablons View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to David Mark Jablons. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Uematsu, K., He, B.,
You, L. _et al._ Activation of the Wnt pathway in non small cell lung cancer: evidence of dishevelled overexpression. _Oncogene_ 22, 7218–7221 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206817
Download citation * Received: 04 April 2003 * Revised: 08 May 2003 * Accepted: 15 May 2003 * Published: 16 October 2003 * Issue Date: 16 October 2003 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206817 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * Dishevelled (Dvl) * Wnt signaling * non small cell lung
cancer * siRNA