Play all audios:
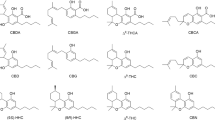
THERE have been few reports concerning the chemistry and pharmacology of marijuana and its constituents1,2, and most investigators have studied the natural product or a crude extract.
Mechoulam and co-workers3 isolated Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, which is believed to be the most active constituent of marijuana and has been shown to have marijuana-like activity in man4.
Subsequently, Δ8-tetrahydrocannabinol was purified and now both isomers have been prepared synthetically and are available in small quantities for pharmacological experimentation. These
substances are somewhat unique in that there are few agents which have such a profound effect on the central nervous system yet do not contain either a sulphur or nitrogen atom in the
molecule. We report here some preliminary pharmacological results with pure synthetic Δ8 and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), and also describe the effect of the insertion of a heterocyclic
atom in ring C on the pharmacology of these agents. The nitrogen analogue of Δ9-THC (I in Fig. 1) was synthesized by Pars and co-workers5 and the sulphur analogue (II) by R. K. R.
(unpublished data).
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
