Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Multiple myeloma (MM) is an incurable B-cell malignancy characterized by accumulation of malignant plasma cells in bone marrow (BM) and recurrent or persistent infections. Toll-like
receptors (TLRs) are essential in the host defense against infections and today 10 human TLRs (TLR1-TLR10) and one TLR-homolog (RP105) have been characterized. B cells express several TLRs
(mainly TLR1, 6, 7, 9, 10 and RP105) and TLR-initiated responses in B cells include proliferation, anti-apoptosis effect and plasma cell (PC) differentiation. The present study was designed
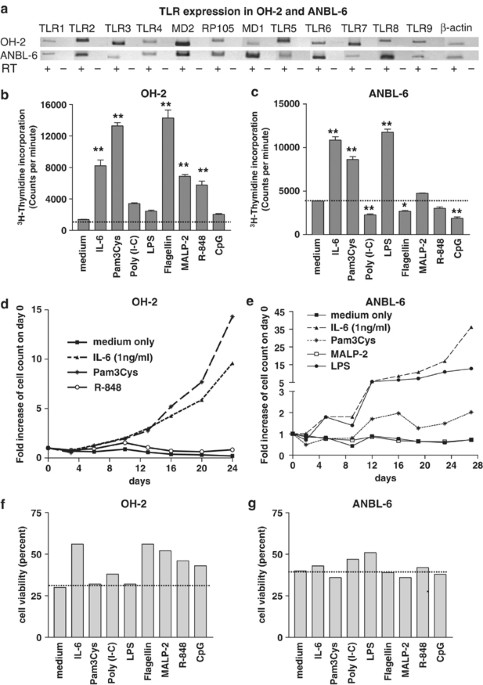
to analyze the role of TLRs in MM. We show that frequent expressions of TLRs were detected in cell lines from MM patients (minimum six TLRs in each). In comparison, only few TLRs (mainly
TLR1 and or RP105) were found expressed in PCs from BM of healthy donors. In addition, TLR-specific ligands induce increased proliferation and survival of the MM cell lines, partially due to
an autocrine interleukin-6 production. Importantly, we demonstrate that also PC from MM patients proliferates in response to TLR-specific ligands. In conclusion, TLR-ligands may contribute
to increased growth and survival of MM cells in MM patients. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS
OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on
SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about
institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS LILRB4 REGULATES MULTIPLE MYELOMA DEVELOPMENT THROUGH STAT3-PFKFB1 PATHWAY
Article Open access 18 July 2024 IDENTIFICATION AND VALIDATION OF ECTO-5' NUCLEOTIDASE AS AN IMMUNOTHERAPEUTIC TARGET IN MULTIPLE MYELOMA Article Open access 01 April 2022 JUST
SCRATCHING THE SURFACE: NOVEL TREATMENT APPROACHES FOR MULTIPLE MYELOMA TARGETING CELL MEMBRANE PROTEINS Article 03 July 2024 REFERENCES * O'Connor BP, Gleeson MW, Noelle RJ, Erickson
LD . The rise and fall of long-lived humoral immunity: terminal differentiation of plasma cells in health and disease. _Immunol Rev_ 2003; 194: 61–76. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Shapiro-Shelef M, Calame K . Plasma cell differentiation and multiple myeloma. _Curr Opin Immunol_ 2004; 16: 226–234. Article CAS Google Scholar * Hideshima T, Richardson P, Anderson KC .
Novel therapeutic approaches for multiple myeloma. _Immunol Rev_ 2003; 194: 164–176. Article CAS Google Scholar * Seidl S, Kaufmann H, Drach J . New insights into the pathophysiology of
multiple myeloma. _Lancet Oncol_ 2003; 4: 557–564. Article CAS Google Scholar * Anderson KC, Shaughnessy Jr JD, Barlogie B, Harousseau JL, Roodman GD . Multiple myeloma. _Hematology (Am
Soc Hematol Educ Program)_ 2002, 214–240. * Brenne AT, Baade RT, Waage A, Sundan A, Borset M, Hjorth-Hansen H . Interleukin-21 is a growth and survival factor for human myeloma cells.
_Blood_ 2002; 99: 3756–3762. Article CAS Google Scholar * Lauta VM . A review of the cytokine network in multiple myeloma: diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic implications. _Cancer_
2003; 97: 2440–2452. Article CAS Google Scholar * Jacobson DR, Zolla-Pazner S . Immunosuppression and infection in multiple myeloma. _Semin Oncol_ 1986; 13: 282–290. CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Oken MM, Pomeroy C, Weisdorf D, Bennett JM . Prophylactic antibiotics for the prevention of early infection in multiple myeloma. _Am J Med_ 1996; 100: 624–628. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Akira S, Hemmi H . Recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by TLR family. _Immunol Lett_ 2003; 85: 85–95. Article CAS Google Scholar * Akira S . Mammalian
Toll-like receptors. _Curr Opin Immunol_ 2003; 15: 238. Article CAS Google Scholar * Bernasconi NL, Traggiai E, Lanzavecchia A . Maintenance of serological memory by polyclonal activation
of human memory B cells. _Science_ 2002; 298: 2199–2202. Article CAS Google Scholar * Bernasconi NL, Onai N, Lanzavecchia A . A role for Toll-like receptors in acquired immunity:
upregulation of TLR9 by BCR triggering in naive B cells and constitutive expression in memory B cells. _Blood_ 2003; 101: 4500–4504. Article CAS Google Scholar * Hornung V, Rothenfusser
S, Britsch S, Krug A, Jahrsdorfer B, Giese T _et al_. Quantitative expression of Toll-like receptor 1-10 mRNA in cellular subsets of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and sensitivity
to CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. _J Immunol_ 2002; 168: 4531–4537. Article CAS Google Scholar * Jung J, Yi AK, Zhang X, Choe J, Li L, Choi YS . Distinct response of human B cell
subpopulations in recognition of an innate immune signal, CpG DNA. _J Immunol_ 2002; 169: 2368–2373. Article CAS Google Scholar * Krieg AM . CpG motifs in bacterial DNA and their immune
effects. _Annu Rev Immunol_ 2002; 20: 709–760. Article CAS Google Scholar * Bourke E, Bosisio D, Golay J, Polentarutti N, Mantovani A . The Toll-like receptor repertoire of human B
lymphocytes: inducible and selective expression of TLR9 and TLR10 in normal and transformed cells. _Blood_ 2003; 102: 956–963. Article Google Scholar * Bishop GA, Ramirez LM, Baccam M,
Busch LK, Pederson LK, Tomai MA . The immune response modifier resiquimod mimics CD40-induced B cell activation. _Cellular Immunol_ 2001; 208: 9–17. Article CAS Google Scholar * Jurk M,
Heil F, Vollmer J, Schetter C, Krieg AM, Wagner H _et al_. Human TLR7 or TLR8 independently confer responsiveness to the antiviral compound R-848. _Nat Immunol_ 2002; 3: 499. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Peng SL . Signaling in B cells via Toll-like receptors. _Curr Opin Immunol_ 2005; 17: 230–236. Article CAS Google Scholar * Borset M, Waage A, Brekke OL, Helseth E . TNF
and IL-6 are potent growth factors for OH-2, a novel human myeloma cell line. _Eur J Haematol_ 1994; 53: 31–37. Article CAS Google Scholar * Jarrossay D, Napolitani G, Colonna M,
Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A . Specialization and complementarity in microbial molecule recognition by human myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. _Eur J Immunol_ 2001; 11: 3388–3393.
Article Google Scholar * Scheel B, Teufel R, Probst J, Carralot JP, Geginat J, Radsak M _et al_. Toll-like receptor-dependent activation of several human blood cell types by
protamine-condensed mRNA. _Eur J Immunol_ 2005; 35: 1557–1566. Article CAS Google Scholar * Rasmussen T, Theilgaard-Monch K, Hudlebusch HR, Lodahl M, Johnsen HE, Dahl IMS . Occurrence of
dysregulated oncogenes in primary plasma cells representing consecutive stages of myeloma pathogenesis: indications for different disease entities. _Br J Haematol_ 2003; 123: 253–262.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Rasmussen T, Jensen L, Honore L, Andersen H, Johnsen HE . Circulating clonal cells in multiple myeloma do not express CD34 mRNA, as measured by single-cell
and real-time RT-PCR assays. _Br J Haematol_ 1999; 107: 818–824. Article CAS Google Scholar * Durie BG, Salmon SE . A clinical staging system for multiple myeloma. Correlation of measured
myeloma cell mass with presenting clinical features, response to treatment, and survival. _Cancer_ 1975; 36: 842–854. Article CAS Google Scholar * Greipp PR, San MJ, Durie BG, Crowley
JJ, Barlogie B, Blade J _et al_. International staging system for multiple myeloma. _J Clin Oncol_ 2005; 23: 3412–3420. Article Google Scholar * Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R,
Flavell RA . Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. _Nature_ 2001; 413: 732–738. Article CAS Google Scholar * Hirschfeld M, Ma Y, Weis JH,
Vogel SN, Weis JJ . Cutting edge: repurification of lipopolysaccharide eliminates signaling through both human and murine Toll-like receptor 2. _J Immunol_ 2000; 165: 618–622. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Hayashi F, Smith KD, Ozinsky A, Hawn TR, Yi EC, Goodlett DR _et al_. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. _Nature_ 2001;
410: 1099–1103. Article CAS Google Scholar * Mita Y, Dobashi K, Endou K, Kawata T, Shimizu Y, Nakazawa T _et al_. Toll-like receptor 4 surface expression on human monocytes and B cells
is modulated by IL-2 and IL-4. _Immunol Lett_ 2002; 81: 71–75. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zarember KA, Godowski PJ . Tissue expression of human Toll-like receptors and differential
regulation of Toll-like receptor mRNAs in leukocytes in response to microbes, their products, and cytokines. _J Immunol_ 2002; 168: 554–561. Article CAS Google Scholar * Chen W, Wang J,
An H, Zhou J, Zhang L, Cao X . Heat shock up-regulates TLR9 expression in human B cells through activation of ERK and NF-kappaB signal pathways. _Immunol Lett_ 2005; 98: 153–159. Article
CAS Google Scholar * Gado K, Domjan C, Hegyesi H, Falus A . Role of interleukin-6 in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma. _Cell Biol Int_ 2000; 24: 195–209. Article CAS Google Scholar
* Borset M, Helseth E, Naume B, Waage A . Lack of IL-1 secretion from human myeloma cells highly purified by immunomagnetic separation. _Br J Haematol_ 1993; 85: 446–451. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Wagner M, Poeck H, Jahrsdoerfer B, Rothenfusser S, Prell D, Bohle B _et al_. IL-12p70-dependent Th1 induction by human B cells requires combined activation with CD40L and
CpG DNA. _J Immunol_ 2004; 172: 954–963. Article CAS Google Scholar * Divanovic S, Trompette A, Atabani SF, Madan R, Golenbock DT, Visintin A _et al_. Negative regulation of Toll-like
receptor 4 signaling by the Toll-like receptor homolog RP105. _Nat Immunol_ 2005; 6: 571–578. Article CAS Google Scholar * Ogata H, Su I, Miyake K, Nagai Y, Akashi S, Mecklenbrauker I _et
al_. The Toll-like receptor protein RP105 regulates lipopolysaccharide signaling in B cells. _J Exp Med_ 2000; 192: 23–29. Article CAS Google Scholar * Jahrsdorfer B, Muhlenhoff L,
Blackwell SE, Wagner M, Poeck H, Hartmann E _et al_. B-cell lymphomas differ in their responsiveness to CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. _Clin Cancer Res_ 2005; 11: 1490–1499. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Jahrsdorfer B, Wooldridge JE, Blackwell SE, Taylor CM, Griffith TS, Link BK _et al_. Immunostimulatory oligodeoxynucleotides induce apoptosis of B cell chronic lymphocytic
leukemia cells. _J Leukoc Biol_ 2005; 77: 378–387. Article Google Scholar * Zhong S, Yeo W, Tang M, Liu CL, Lin XR, Ho WM _et al_. Frequent detection of the replicative form of TT virus
DNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and bone marrow cells in cancer patients. _J Med Virol_ 2002; 66: 428–434. Article CAS Google Scholar * Beg AA . Endogenous ligands of Toll-like
receptors: implications for regulating inflammatory and immune responses. _Trends Immunol_ 2002; 23: 509–512. Article CAS Google Scholar * Kariko K, Ni HP, Capodici J, Lamphier M,
Weissman D . mRNA is an endogenous ligand for Toll-like receptor 3. _J Biol Chem_ 2004; 279: 12542–12550. Article CAS Google Scholar * Tsan MF, Gao B . Endogenous ligands of Toll-like
receptors. _J Leukoc Biol_ 2004; 76: 514–519. Article CAS Google Scholar * Rifkin IR, Leadbetter EA, Busconi L, Viglianti G, Marshak-Rothstein A . Toll-like receptors, endogenous ligands,
and systemic autoimmune disease. _Immunol Rev_ 2005; 204: 27–42. Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank Marianne Lodahl at Herlev Hospital, University
of Copenhagen, Denmark for technical assistance and Dr med. Anders Waage at St Olavs Hospital, Trondheim University Hospital, Norway for providing some of the patient material. This work was
supported by grants from the Central Norway Regional Health Authority, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, the Norwegian Cancer Society and the Norwegian Research Council.
AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Cancer Research and Molecular Medicine, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway J Bohnhorst, S H Moen, M
Fløttum, M Børset, T Espevik & A Sundan * Department of Hematology L54P4, Herlev Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Herlev, Denmark T Rasmussen & L Knudsen Authors * J Bohnhorst
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * T Rasmussen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * S H
Moen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M Fløttum View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * L
Knudsen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M Børset View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
* T Espevik View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A Sundan View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to J Bohnhorst. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES 1 AND 2 (DOC 69 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 (JPG 70 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 2 (JPG 205 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 3 (JPG 47 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY
FIGURE LEGENDS (DOC 25 KB) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Bohnhorst, J., Rasmussen, T., Moen, S. _et al._ Toll-like receptors mediate
proliferation and survival of multiple myeloma cells. _Leukemia_ 20, 1138–1144 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404225 Download citation * Received: 06 September 2005 * Revised: 02
January 2006 * Accepted: 05 January 2006 * Published: 13 April 2006 * Issue Date: 01 June 2006 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404225 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following
link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature
SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * Toll-like rfeceptor * multiple myeloma * plasma cells * proliferation * survival