Play all audios:
Access through your institution Buy or subscribe Somatic hyperpointmutation of antibody variable-region genes was the first mechanism of receptor modification to be discovered. It operates
in T-cell-dependent antibody responses during proliferative expansion of the responding B cells in a particular microenvironment, the germinal centre. From the newly arising antibody
mutants, those that show a high affinity for the immunizing antigen are selected into the ‘memory’ B-cell pool10. A second process by which B cells can change receptor specificity is based
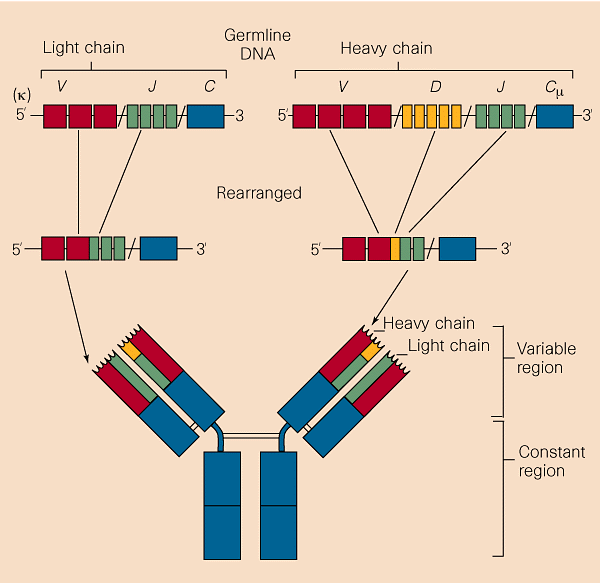
on ‘secondary’ _V_ (_D_ )_J_ rearrangements. Each newborn B cell expresses a distinct antigen receptor, with a distinct combination of a _V_ H, a _D_ Hand a _J_ Hgene segment for the
variable region of the antibody heavy chain, and a _V_ Land a _J_ Lsegment for that of the light chain (_V_ κ and _J_ κ or _V_ λ and _J_ λ, depending on whether the cell expresses a light
chain of class κ or λ)2. However, any B cell that expresses a particular κ chain can continue, or reinitiate, rearrangements of the variable-region genes to get rid of the _V_ κ_J_ κ gene
segment initially expressed. It can then express a new κ chain, or switch to expression of a λ chain. This is achieved either by rearrangements of upstream (non-rearranged) _V_ κ genes to
downstream (non-rearranged) _J_ κ segments (Fig. 1), or by elimination of the _V_ κ_J_ κ rearrangement carried by the cell, together with the κ constant-region gene on the same chromosome.
Even in the case of the heavy chain, B cells can change specificity by rearranging a (non-rearranged) upstream _V_ Hgene into the _V_ H _D_ H _J_ Hcomplex that was initially assembled and
expressed10. This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 51 print issues and
online access $199.00 per year only $3.90 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes
which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support REFERENCES * Burnet, F. M. _The
Clonal Selection Theory of Acquired Immunity_ (University Press, Cambridge, 1959). * Tonegawa, S. _Nature_ 302, 575–581 (1983). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Han, S. _et al._
_Science_ 274, 2094–2097 (1996). Google Scholar * Hikada, M. _et al._ _Science_ 274, 2092–2094 (1996). Google Scholar * Han, S. _et al._ _Science_ 278, 301–305 (1997). Google Scholar *
Papavasiliou, F. _et al._ _Science_ 278, 298–301 (1997). Google Scholar * Hikida, M. & Ohmori, H. _J. Exp. Med._ 187, 795–799 (1998). Google Scholar * Hertz, M., Kouskoff, V.,
Nakamura, T. & Nemazee, D. _Nature_ 394, 292–295 (1998). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Meffre, E. et al. (in the press). * Rajewsky, K. _Nature_ 381, 751–758 (1996). Article ADS
CAS Google Scholar * Tiegs, S. L. _et al._ _J. Exp. Med._ 177, 1009–1020 (1993). Google Scholar * Gay, D. T. _et al._ _J. Exp. Med._ 177, 999–1008 (1993). Google Scholar * Davis, M. M.
_et al._ _Annu. Rev. Immunol._ 16, 523–544 (1998). Google Scholar * Arakawa, H., Furusawa, S., Ekino, S. & Yamagishi, H. _EMBO J._ 15, 2540–2546 (1996). Google Scholar Download
references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Institute for Genetics, University of Köln, Weyertal 121, D-50931, Köln, Germany Klaus Rajewsky * EMBL Mouse Biology Programme, Via
Ramarini 32, I-00016, Monterotondo-Scalo (Rome), Italy Klaus Rajewsky Authors * Klaus Rajewsky View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar RIGHTS AND
PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Rajewsky, K. Burnet's unhappy hybrid. _Nature_ 394, 624–625 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/29187 Download
citation * Issue Date: 13 August 1998 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/29187 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative