Play all audios:
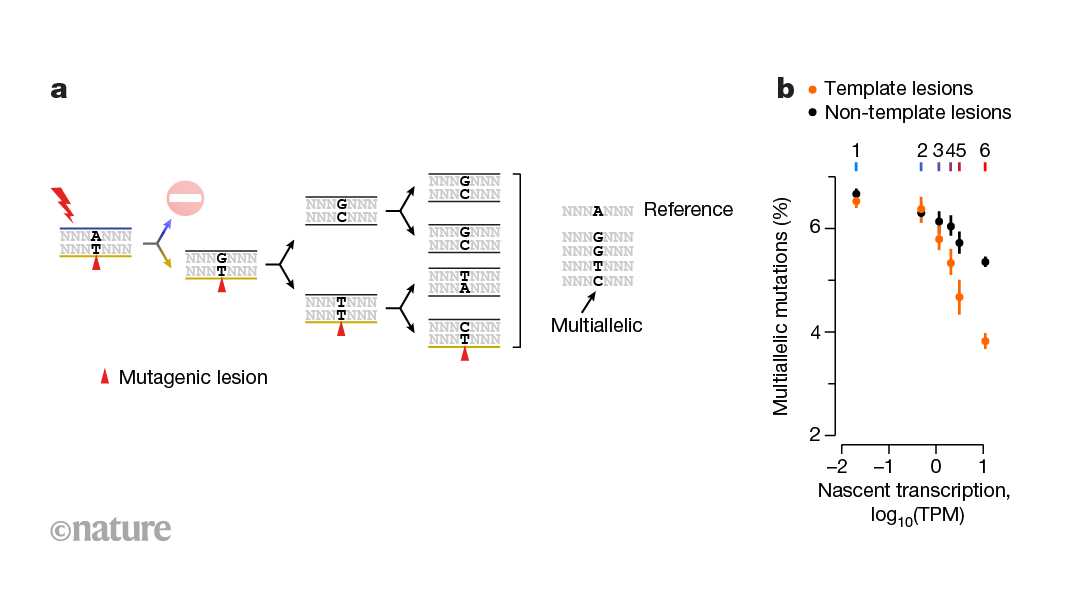
* RESEARCH BRIEFINGS * 07 August 2024 The two strands of DNA, although chemically equivalent, are replicated and repaired asymmetrically. Insights into the persistence of DNA damage show how
strand-specific interactions shape the genome-wide distribution of mutations, including the unexpected symmetry of mutations arising in the DNA strands during replication.