Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Inherited symbionts which selectively cause the death of male hosts are found widely across the Insecta. Previous studies have shown a single, but different micro-organism to be
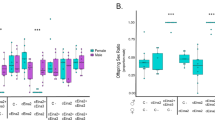
responsible for male-killing in each taxonomic group studied. We here produce evidence that within a group of insects, the Coccinellidae, there is more than one causal agent of male
lethality. We report a novel observation of a male-killing trait in the species _Coleomegilla maculata_. Six of 26 crosses were found to produce a female-biased sex ratio associated with a
low egg hatch-rate. The trait was matrilinearly inherited and was observed to be tetracycline-sensitive. However, tests which indicate the presence of a _Rickettsia_, previously found to
cause male-killing in another member of the Coccinellidae, _Adalia bipunctata_, proved negative. We therefore conclude that the phenomenon of male-killing is multicausal, within, as well as
between, taxonomic groups of the Insecta. SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS QUALITY OVER QUANTITY: UNRAVELING THE CONTRIBUTIONS TO CYTOPLASMIC INCOMPATIBILITY CAUSED BY TWO COINFECTING
_CARDINIUM_ SYMBIONTS Article 05 February 2022 A MALE-KILLING GENE ENCODED BY A SYMBIOTIC VIRUS OF _DROSOPHILA_ Article Open access 13 March 2023 INTRACELLULAR SYMBIONTS DRIVE SEX RATIO IN
THE WHITEFLY BY FACILITATING FERTILIZATION AND PROVISIONING OF B VITAMINS Article 20 July 2020 ARTICLE PDF REFERENCES * Balayeva, N M, Eremeeva, M E, Tissot-Dupont, H, Zakharov, I A, and
Raoult, D. 1995. Genotype characterization of the bacterium expressing the male-killing trait in the ladybird beetle _Adalia bipunctata_ with specific Rickettsial molecular tools. _Appl Env
Microbiol_, 61, 1431–1437. CAS Google Scholar * Breeuwer, J A J, and Werren, J H. 1990. Microorganisms associated with chromosome destruction and reproductive isolation between two insect
species. _Nature_, 346, 558–560. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Breeuwer, J A J, and Werren, J H. 1993. Effect Of genotype on cytoplasmic incompatibility between two species of
_Nasonia_. _Heredity_, 70, 428–436. Article Google Scholar * Gherna, R L, Werren, J H, Weisburg, W, Cote, R, Woese, C R, Mandelco, L, and Brenner, D J. 1991. _Arsenophonus nasoniae_
gen.-nov., sp.-nov., the causative agent of the son killer trait in the parasitic wasp _Nasonia vitripennis_. _Int J Syst Bact_, 41, 563–565. Article Google Scholar * Hu, K. 1979.
Maternally inherited ‘sonless’ abnormal SR condition in the ladybeetle _Harmonia axyridis_. _Acta Genet Sinica_, 6, 296–304. Google Scholar * Hurst, G D D, and Majerus, M E N. 1993. Why do
maternally inherited microorganisms kill males? _Heredity_, 71, 81–95. Article Google Scholar * Hurst, G D D, Majerus, M E N, and Walker, L E. 1992. Cytoplasmic male killing elements in
_Adalia bipunctata_ (Linnaeus) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). _Heredity_, 69, 84–91. Article Google Scholar * Hurst, L D. 1991. The incidences and evolution of cytoplasmic male killers.
_Proc R Soc B_, 244, 91–99. Article Google Scholar * Hurst, L D. 1993. The incidences, mechanisms and evolution of cytoplasmic sex ratio distorters in animals. _Biol Rev_, 68, 121–193.
Article Google Scholar * Matsuka, M, Hashi, H, and Okada, I. 1975. Abnormal sex-ratio found in the lady beetle, _Harmonia axyridis_ Pallas (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). _Appl Ent Zool_, 10,
84–89. Article Google Scholar * Moran, N A, Munson, M A, Baumann, P, and Ishikawa, H. 1993. A molecular clock in endosymbiotic bacteria is callibrated using the insect hosts. _Proc R Soc
B_, 253, 167–171. Article Google Scholar * Niuima, K, and Nakajima, K. 1981. Abnormal sex ratio in _Menochilius sexmaculatus_ (Fabricius). _Bull Fac Agric Tamagawa Univ_, 21, 59–67. Google
Scholar * O'Neill, S L, Giordano, R, Colbert, A M E, Karr, T L, and Robertson, H M. 1992. 16S rRNA phylogenetic analysis of the bacterial endosymbionts associated with cytoplasmic
incompatibility in insects. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_, 89, 2699–2702. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Pienkowski, R L. 1965. The incidence and effect of egg
cannibalism in first instar _Coleomegilla maculata lengi_ (Coccinellidae). _Ann Entomol Soc Am_, 58, 150–153. Article Google Scholar * Rigaud, T, and Juchault, P. 1992. Genetic control of
the vertical transmission of a cytoplasmic sex factor in _Armadillidium vulgare_. _Heredity_, 68, 47–52. Article Google Scholar * Rousset, F, Bouchon, D, Pintureau, B, Juchault, P, and
Solignac, M. 1992. _Wolbachia_ endosymbionts responsible for various alterations of sexuality in arthropods. _Proc R Soc B_, 250, 91–98. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Shull, H F.
1948. An all-female strain of lady beetles with reversion to normal sex ratios. _Am Nat_, 82, 241–251. Article Google Scholar * Skinner, S W. 1985. Son-killer: a third extrachromosomal
factor affecting sex ratios in the parasitoid wasp _Nasonia vitripennis_. _Genetics_, 109, 745–754. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Smith, B C. 1961. Influence of water and
previous food on the longevity of unfed larvae of _Coleomegilla maculata lengi_. _J Econ Entomol_, 54, 194–195. Article Google Scholar * Stouthamer, R, Breeuwer, J A J, Luck, R F, and
Werren, J H. 1993. Molecular identification of organisms associated with parthenogenesis. _Nature_, 361, 66–68. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Werren, J H. 1987. The coevolution of
autosomal and cytoplasmic sex ratio factors. _J Theor Biol_, 124, 317–334. Article Google Scholar * Werren, J H, Skinner, S W, and Huger, A M. 1986. Male-killing bacteria in a parasitic
wasp. _Science_, 231, 990–992. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Werren, J H, Hurst, G D D, Zhang, W, Breeuwer, J A J, Stouthamer, R, and Majerus, M E N. 1994. Rickettsial relative
associated with male killing in the ladybird beetle (_Adalia bipunctata_). _J Bacteriol_, 176, 388–394. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Werren, J H, Zhang, W, and
Guo, L R. 1995. Evolution and phylogeny of _Wolbachia_: reproductive parasites of arthropods. _Proc R Soc B_, 261, 55–71. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Williams, S G, Sacci, J B J,
Schriefer, M E, Andersen, E M, Fujioka, K K, Sorvillo, F J, Barr, A R, and Azad, A F. 1992. Typhus and typhuslike rickettsiae associated with opposums and their fleas in Los Angeles. _J
Clin Microbiol_, 30, 1758–1762. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Williamson, D L, and Poulson, D F. 1979. Sex ratio organisms (Spiroplasmas) of _Drosophila_. In: Whitcomb, R.
F. and Tully, J. G. (eds) _The Mycoplasmas_, pp. 175–208. Academic Press, New York. Chapter Google Scholar Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of
Genetics, Downing Street, Cambridge, CB2 3EH, UK Gregory D D Hurst, Tansy C Hammarton, Tamsin M O Majerus, Linda E Walker, Dominique Bertrand & Michael E N Majerus * Department of
Entomology, Iowa State University, Ames, IA 50011, USA John J Obrycki Authors * Gregory D D Hurst View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Tansy
C Hammarton View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * John J Obrycki View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * Tamsin M O Majerus View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Linda E Walker View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Dominique Bertrand View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Michael E N Majerus View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Hurst, G., Hammarton, T., Obrycki, J. _et
al._ Male-killing bacterium in a fifth ladybird beetle, _Coleomegilla maculata_ (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). _Heredity_ 77, 177–185 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1996.122 Download
citation * Received: 30 October 1995 * Issue Date: 01 August 1996 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1996.122 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read
this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
KEYWORDS * _Coleomegilla maculata_ * female-biased sex ratio * inherited symbiont * male-killing
