Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Extensive studies have shown that p53 is important in tumour prevention1. However, little is known about its normal physiological function. Here we show that p53 is important in
reproduction, in a gender-specific manner. Significant decreases in embryonic implantation, pregnancy rate and litter size were observed in matings with _p53_-/- female mice but not with
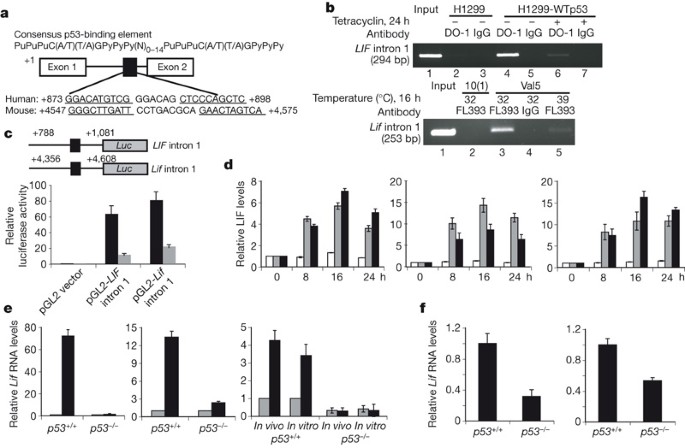
_p53_-/- male mice. The gene encoding leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF), a cytokine critical for implantation2, was identified as a p53-regulated gene that functions as the downstream
mediator of this effect. p53 can regulate both basal and inducible transcription of LIF. Loss of p53 decreased both the level and function of LIF in uteri. Lower LIF levels were observed in
the uteri of _p53_-/- mice than in those of _p53_+/+ mice, particularly at day 4 of pregnancy, when transiently induced high levels of LIF were crucial for embryonic implantation. This
observation probably accounts for the impaired implantation of embryos in _p53_-/- female mice. Administration of LIF to pregnant _p53_-/- mice restored maternal reproduction by improving
implantation. These results demonstrate a function for p53 in maternal reproduction through the regulation of LIF. Evidence is accumulating that p53 may have a similar function in humans.
Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this
journal Receive 51 print issues and online access $199.00 per year only $3.90 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer
support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS CORE BINDING FACTORS ARE ESSENTIAL FOR OVULATION, LUTEINIZATION, AND FEMALE FERTILITY IN MICE Article Open access 18 June 2020 TOLL-LIKE
RECEPTOR-4 NULL MUTATION CAUSES FETAL LOSS AND FETAL GROWTH RESTRICTION ASSOCIATED WITH IMPAIRED MATERNAL IMMUNE TOLERANCE IN MICE Article Open access 16 August 2021 UTERINE EPITHELIAL GP130
ORCHESTRATES HORMONE RESPONSE AND EPITHELIAL REMODELING FOR SUCCESSFUL EMBRYO ATTACHMENT IN MICE Article Open access 16 January 2023 REFERENCES * Vogelstein, B., Lane, D. & Levine, A.
J. Surfing the p53 network. _Nature_ 408, 307–310 (2000) Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Stewart, C. L. et al. Blastocyst implantation depends on maternal expression of
leukaemia inhibitory factor. _Nature_ 359, 76–79 (1992) Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Atwal, G. S. et al. Haplotype structure and selection of the _MDM2_ oncogene in humans.
_Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 104, 4524–4529 (2007) Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Murphy, M. E. Polymorphic variants in the p53 pathway. _Cell Death Differ._ 13,
916–920 (2006) Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * el-Deiry, W. S., Kern, S. E., Pietenpol, J. A., Kinzler, K. W. & Vogelstein, B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53.
_Nature Genet._ 1, 45–49 (1992) Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hoh, J. et al. The p53MH algorithm and its application in detecting p53-responsive genes. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_
99, 8467–8472 (2002) Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chen, J. R. et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor can substitute for nidatory estrogen and is essential to
inducing a receptive uterus for implantation but is not essential for subsequent embryogenesis. _Endocrinology_ 141, 4365–4372 (2000) Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Song, H., Lim,
H., Das, S. K., Paria, B. C. & Dey, S. K. Dysregulation of EGF family of growth factors and COX-2 in the uterus during the preattachment and attachment reactions of the blastocyst with
the luminal epithelium correlates with implantation failure in LIF-deficient mice. _Mol. Endocrinol._ 14, 1147–1161 (2000) Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cullinan, E. B. et al.
Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and LIF receptor expression in human endometrium suggests a potential autocrine/paracrine function in regulating embryo implantation. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci.
USA_ 93, 3115–3120 (1996) Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Armstrong, J. F., Kaufman, M. H., Harrison, D. J. & Clarke, A. R. High-frequency developmental
abnormalities in p53-deficient mice. _Curr. Biol._ 5, 931–936 (1995) Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kay, C., Jeyendran, R. S. & Coulam, C. B. p53 tumour suppressor gene
polymorphism is associated with recurrent implantation failure. _Reprod. Biomed. Online_ 13, 492–496 (2006) Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hambartsoumian, E. Endometrial leukemia
inhibitory factor (LIF) as a possible cause of unexplained infertility and multiple failures of implantation. _Am. J. Reprod. Immunol._ 39, 137–143 (1998) Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Bond, G. L. et al. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the _MDM2_ promoter attenuates the p53 tumor suppressor pathway and accelerates tumor formation in humans. _Cell_ 119,
591–602 (2004) Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Harvey, D. & Levine, A. J. p53 alteration is a common event in the spontaneous immortalization of primary BALB/c murine embryo
fibroblasts. _Genes Dev._ 5, 2375–2385 (1991) Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pochampally, R., Fodera, B., Chen, L., Lu, W. & Chen, J. Activation of an MDM2-specific caspase by
p53 in the absence of apoptosis. _J. Biol. Chem._ 274, 15271–15277 (1999) Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wu, X. & Levine, A. J. p53 and E2F-1 cooperate to mediate apoptosis.
_Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 91, 3602–3606 (1994) Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Radhakrishnan, S. K., Gierut, J. & Gartel, A. L. Multiple alternate p21
transcripts are regulated by p53 in human cells. _Oncogene_ 25, 1812–1815 (2006) Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Chen, X., Ko, L. J., Jayaraman, L. & Prives, C. p53 levels,
functional domains, and DNA damage determine the extent of the apoptotic response of tumor cells. _Genes Dev._ 10, 2438–2451 (1996) Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Nagy, A.,
Gertsenstein, M., Vintersten, K. & Behringer, R. _Manipulating the Mouse Embryo, a Laboratory Manual_ 3rd edn (Cold Spring Harbor Press, New York, 2003) Google Scholar Download
references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank S. Christen for critical review of the manuscript, and I. Snyder and the staff of the University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey animal facility
for providing animal care. This research was supported by grants from the Breast Cancer Research Foundation and the National Cancer Institute. AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS W.H., Z.F. and A.J.L.
designed the research. W.H., Z.F. and A.K.T. performed the research. W.H., Z.F. and A.J.L. analysed data and wrote the paper. AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * Wenwei Hu and Zhaohui Feng:
These authors contributed equally to this work. AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Cancer Institute of New Jersey, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, New Brunswick, New Jersey
08903, USA , Wenwei Hu, Zhaohui Feng, Angelika K. Teresky & Arnold J. Levine * The Simons Center for Systems Biology, The Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, New Jersey 08540, USA ,
Arnold J. Levine Authors * Wenwei Hu View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Zhaohui Feng View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Angelika K. Teresky View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Arnold J. Levine View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Arnold J. Levine. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES This file contains
Supplementary Figures S1-S5 with Legends. (PDF 1115 kb) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Hu, W., Feng, Z., Teresky, A. _et al._ p53
regulates maternal reproduction through LIF. _Nature_ 450, 721–724 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05993 Download citation * Received: 24 July 2007 * Accepted: 10 October 2007 *
Published: 29 November 2007 * Issue Date: 29 November 2007 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05993 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this
content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative