Play all audios:
ABSTRACT SAP (or SH2D1A), an adaptor-like molecule expressed in immune cells, is composed almost exclusively of a Src homology 2 (SH2) domain1,2,3,4. In humans, SAP is mutated and either
absent or non-functional in X-linked lymphoproliferative (XLP) syndrome, a disease characterized by an inappropriate response to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection5. Through its SH2 domain,
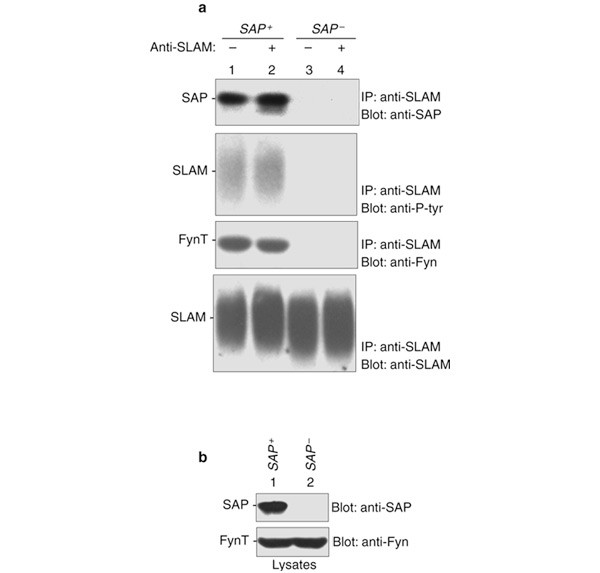
SAP associates with tyrosines in the cytoplasmic domain of the SLAM family of immune cell receptors, and is absolutely required for the function of these receptors1,6,7,8,9,10. This property
results from the ability of SAP to promote the selective recruitment and activation of FynT, a cytoplasmic Src-related protein tyrosine kinase (PTK)8. Here, we demonstrate that SAP operates
in this pathway by binding to the SH3 domain of FynT, through a second region in the SAP SH2 domain distinct from the phosphotyrosine-binding motif. We demonstrate that this interaction is
essential for SAP-mediated signalling in T cells, and for the capacity of SAP to modulate immune cell function. These observations characterize a biologically important signalling mechanism
in which an adaptor molecule composed only of an SH2 domain links a receptor devoid of intrinsic catalytic activity to the kinase required for its function. Access through your institution
Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and
online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes
which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY
OTHERS STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS OF TARGET RECOGNITION BY THE LYMPHOCYTE ADAPTOR PROTEIN LNK Article Open access 20 October 2021 HACS1 SIGNALING ADAPTOR PROTEIN RECOGNIZES A MOTIF
IN THE PAIRED IMMUNOGLOBULIN RECEPTOR B CYTOPLASMIC DOMAIN Article Open access 13 November 2020 SH3-DOMAIN MUTATIONS SELECTIVELY DISRUPT CSK HOMODIMERIZATION OR PTPN22 BINDING Article Open
access 07 April 2022 REFERENCES * Sayos, J. et al. The X-linked lymphoproliferative-disease gene product SAP regulates signals induced through the co-receptor SLAM. _Nature_ 395, 462–469
(1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Coffey, A.ˇJ. et al. Host response to EBV infection in X-linked lymphoproliferative disease results from mutations in an SH2-domain encoding gene.
_Nature Genet._ 20, 129–135 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Nichols, K.ˇE. et al. Inactivating mutations in an SH2 domain-encoding gene in X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome.
_Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 95, 13765–13770 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Veillette, A. The SAP family: a new class of adaptor-like molecules that regulates immune cell functions.
_Sci. STKE._ 2002, E8 (2002). Google Scholar * Morra, M. et al. X-linked lymphoproliferative disease: a progressive immunodeficiency. _Annu. Rev. Immunol._ 19, 657–682 (2001). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Parolini, S. et al. X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. 2B4 molecules displaying inhibitory rather than activating function are responsible for the inability of natural
killer cells to kill Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells. _J. Exp. Med._ 192, 337–346 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Bottino, C. et al. NTB-A, a novel SH2D1A-associated surface
molecule contributing to the inability of natural killer cells to kill Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells in X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. _J. Exp. Med._ 194, 235–246 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Latour, S. et al. Regulation of SLAM-mediated signal transduction by SAP, the X-linked lymphoproliferative gene product. _Nature Immunol._ 2, 681–690 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Tangye, S.ˇG., Phillips, J.ˇH., Lanier, L.ˇL. & Nichols, K.ˇE. Functional requirement for SAP in 2B4-mediated activation of human natural killer cells as
revealed by the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. _J. Immunol._ 165, 2932–2936 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Tangye, S.ˇG. et al. Cutting edge: human 2B4, an activating NK
cell receptor, recruits the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 and the adaptor signaling protein SAP. _J. Immunol._ 162, 6981–6985 (1999). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wu, C. et al. SAP
controls T cell responses to virus and terminal differentiation of TH2 cells. _Nature Immunol._ 2, 410–414 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Czar, M.ˇJ. et al. Altered lymphocyte
responses and cytokine production in mice deficient in the X-linked lymphoproliferative disease gene _SH2D1A_/_DSHP_/_SAP_. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 98, 7449–7454 (2001). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Mikhalap, S.ˇV. et al. CDw150 associates with src-homology 2-containing inositol phosphatase and modulates CD95-mediated apoptosis. _J. Immunol._ 162, 5719–5727 (1999). CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Sicheri, F. & Kuriyan, J. Structures of Src-family tyrosine kinases. _Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol._ 7, 777–785 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Thompson,
A.ˇD. et al. EAT-2 is a novel SH2 domain containing protein that is up regulated by Ewing's sarcoma _EWS_/_FLI1_ fusion gene. _Oncogene_ 13, 2649–2658 (1996). CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Poy, F. et al. Crystal structures of the XLP protein SAP reveal a class of SH2 domains with extended, phosphotyrosine-independent sequence recognition. _Mol. Cell_ 4, 555–561
(1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Li, S.ˇC. et al. Novel mode of ligand binding by the SH2 domain of the human XLP disease gene product SAP/SH2D1A. _Curr. Biol._ 9, 1355–1362 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Hwang, P.ˇM. et al. A “three-pronged” binding mechanism for the SAP/SH2D1A SH2 domain: structural basis and relevance to the XLP syndrome. _EMBO J._ 21,
314–323 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Rotin, D. et al. SH2 domains prevent tyrosine dephosphorylation of the EGF receptor: identification of Tyr992 as the high-affinity binding
site for SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma. _EMBO J._ 11, 559–567 (1992). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yu, J. et al. Synergistic regulation of immunoreceptor signaling by
slp-76-related adaptor clnk and serine/threonine protein kinase hpk-1. _Mol. Cell Biol._ 21, 6102–6112 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Moarefi, I. et al. Activation of the Src-family
tyrosine kinase Hck by SH3 domain displacement. _Nature_ 385, 650–653 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lerner, E.ˇC. & Smithgall, T.ˇE. SH3-dependent stimulation of Src-family
kinase autophosphorylation without tail release from the SH2 domain _in vivo_. _Nature Struct. Biol._ 9, 365–369 (2002). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Anafi, M., Rosen, M.ˇK., Gish, G.ˇD.,
Kay, L.ˇE. & Pawson, T. A potential SH3 domain-binding site in the Crk SH2 domain. _J. Biol. Chem._ 271, 21365–21374 (1996). Article CAS Google Scholar * Abraham, N., Miceli, M.ˇC.,
Parnes, J.ˇR. & Veillette, A. Enhancement of T-cell responsiveness by the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase p56lck. _Nature_ 350, 62–66 (1991). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Latour, S., Fournel, M. & Veillette, A. Regulation of T-cell antigen receptor signalling by Syk tyrosine protein kinase. _Mol. Cell. Biol._ 17, 4434–4441 (1997). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Davidson, D., Chow, L.ˇM., Fournel, M. & Veillette, A. Differential regulation of T cell antigen responsiveness by isoforms of the src-related tyrosine protein kinase p59fyn.
_J. Exp. Med._ 175, 1483–1492 (1992). Article CAS Google Scholar * Cloutier, J.ˇF. & Veillette, A. Cooperative inhibition of T-cell antigen receptor signaling by a complex between a
kinase and a phosphatase. _J. Exp. Med._ 189, 111–121 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Gregorieff, A., Pyronnet, S., Sonenberg, N. & Veillette, A. Regulation of SOCS-1 expression
by translational repression. _J. Biol. Chem._ 275, 21596–21604 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Veillette, A., Bookman, M.ˇA., Horak, E.ˇM. & Bolen, J.ˇB. The CD4 and CD8 T cell
surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. _Cell_ 55, 301–308 (1988). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Supported by grants from the CANVAC National Centre of Excellence, the National Cancer Institute of Canada and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (to A.V.), the Institut National de
la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale and the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (France) (to S.L.). S.L. held a Fellowship from the Medical Research Council of Canada. He is now a
Scientist from the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (France). A.V. is a Senior Investigator of the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and holds a Canada Research Chair.
AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Laboratory of Molecular Oncology, Clinical Research Institute of Montreal, Montréal, H2W 1R7, Québec, Canada Sylvain Latour, Romain Roncagalli,
Riyan Chen, Marcin Bakinowski, Xiaochu Shi, Dominique Davidson & André Veillette * Unité INSERM U429, Hôpital Necker Enfants-Malades, Paris, France Sylvain Latour * Program in Molecular
Biology, University of Montréal, Montréal, H2W 1R7, Québec, Canada Romain Roncagalli & André Veillette * Department of Medicine, University of Montréal, Montréal, H2W 1R7, Québec, Canada
André Veillette * National Human Genome Research Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, 20892, MD, USA Pamela L. Schwartzberg * Department of Biochemistry, McGill University,
Montréal, H3G 1Y6, Québec, Canada André Veillette * Departments of Microbiology and Immunology, McGill University, Montréal, H3G 1Y6, Québec, Canada André Veillette * Department of Medicine,
McGill University, Montréal, H3G 1Y6, Québec, Canada André Veillette Authors * Sylvain Latour View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Romain
Roncagalli View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Riyan Chen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Marcin Bakinowski View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Xiaochu Shi View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Pamela L. Schwartzberg View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Dominique Davidson View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * André Veillette View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence
to André Veillette. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE
THIS ARTICLE Latour, S., Roncagalli, R., Chen, R. _et al._ Binding of SAP SH2 domain to FynT SH3 domain reveals a novel mechanism of receptor signalling in immune regulation. _Nat Cell Biol_
5, 149–154 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb919 Download citation * Received: 03 September 2002 * Revised: 09 October 2002 * Accepted: 28 October 2002 * Published: 27 January 2003 * Issue
Date: 01 February 2003 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb919 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a
shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative