Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Graphene oxide, a two-dimensional aromatic scaffold decorated by oxygen-containing functional groups, possesses rich chemical properties and may present a green alternative to
precious metal catalysts. Graphene oxide-based carbocatalysis has recently been demonstrated for aerobic oxidative reactions. However, its widespread application is hindered by the need for
high catalyst loadings. Here we report a simple chemical treatment that can create and enlarge the defects in graphene oxide and impart on it enhanced catalytic activities for the oxidative
coupling of amines to imines (up to 98% yield at 5 wt% catalyst loading, under solvent-free, open-air conditions). This study examines the origin of the enhanced catalytic activity, which
can be linked to the synergistic effect of carboxylic acid groups and unpaired electrons at the edge defects. The discovery of a simple chemical processing step to synthesize highly active
graphene oxide allows the premise of industrial-scale carbocatalysis to be explored. You have full access to this article via your institution. Download PDF SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY
OTHERS CONTROLLING COVALENT CHEMISTRY ON GRAPHENE OXIDE Article 18 February 2022 GRAPHSENE AS A NOVEL POROUS TWO-DIMENSIONAL CARBON MATERIAL FOR ENHANCED OXYGEN REDUCTION ELECTROCATALYSIS
Article Open access 21 April 2024 FACILELY SYNTHESIZED NITROGEN-DOPED REDUCED GRAPHENE OXIDE FUNCTIONALIZED WITH COPPER IONS AS ELECTROCATALYST FOR OXYGEN REDUCTION Article Open access 04
January 2021 INTRODUCTION In the drive towards green and sustainable chemistry, a constant refrain is the use of non-toxic, sustainable catalysts with minimal environmental footprint1,2,3.
The use of carbon catalysts is attractive in this regard because of their low cost and natural abundance4,5,6,7,8. Carbocatalysis is well established in the oxidative dehydrogenation of
ethylbenzene to produce styrene4. Oxidative aromatization involving a molecular oxygen and activated carbon system has also been used to prepare aromatic compounds such as pyrazoles,
pyridine, indoles and so on8. Although the detailed mechanism of these reactions is not yet well understood, it is believed that the multiplier effect of the surface area and the dynamic
exchange of oxygen functionalities in the mesopores of nanostructured carbon have important roles in promoting efficient catalysis. In this regard, graphene oxide (GO)9,10,11,12,13,14
produced by the exfoliation of graphite oxide, is emerging as a versatile mediator of synthetic transformation. In many reactions, it can serve both as a supporting scaffold for various
catalytically active species15 as well as a ‘carbocatalyst’ in its own right6. The ability of GO to facilitate synthetic transformations stems from several intrinsic features. First, the
presence of oxygen-containing functional groups allows GO to function as an oxidant for the oxidation of sulphides,16 olefins and various hydrocarbons17. In addition, the acidic nature of GO
allows GO to act as a solid acid for hydration,18 Friedel–Crafts reaction,19 Aza–Michael additions,20 condensation21 and ring-opening polymerization22. Therefore, it is attractive to
develop GO-based carbocatalysts as an alternative to dwindling precious metal resources6,23. The only drawback is that the efficiency of GO is low, requiring high loading (60–400 wt%) for
typical oxidative reactions16,17,18. In addition, the non-stoichiometric and inhomogeneous nature of GO24,25 presents considerable challenges for understanding the detailed mechanism of
catalysis. Here we present a detailed, systematic study to probe the catalytic activity and origin of aerobic oxidation in porous GO. Highly catalytic porous GO with enhanced catalytic
activity is generated by a sequential base and an acid treatment, and yields up to 98% can be achieved with unprecedentedly low catalyst loading (5 wt %) for the oxidative coupling of amines
to imines under mild conditions. Our studies suggest that carboxylic acid functionalities and spin-electrons at the edge sites are most likely involved in the aerobic oxidation of amines.
RESULTS PROBING THE CATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF GO MATERIALS GO consists of both acidic and basic oxygenated groups that are solvated by water molecules. Owing to its amphiphilic nature, the
chemical nature of GO sheets is influenced by the base or the acid treatments. To examine the catalytic effects of GO, several factors need to be explored. Owing to the harsh oxidation and
sonication processes during its synthesis, GO sheets are usually coated by debris made of highly oxidized, and acidic molecular fragments26,27. Without a careful washing step to remove these
debris, it is not clear whether the catalysis effects originate from this oxidative debris or from the intrinsic oxygen functional groups in GO. Second, contributions from metallic
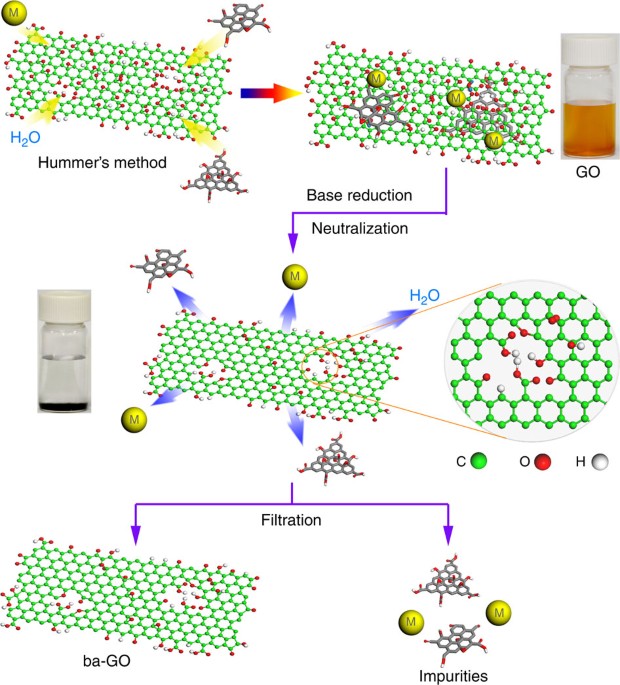
contaminations cannot be excluded28 unless the GO is well purified. Therefore, as-synthesized GO sheets were subjected to the sequential base and acid treatments to eliminate acidic debris
and metallic contamination (Fig. 1 and Supplementary Fig. S1). To check whether metallic impurities were removed after the purification steps, modified GO (abbreviated as ba-GO) and its
precursor graphite were analysed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (Supplementary Table S1). As shown, the concentrations of all metal impurities in ba-GO are much lower than
the graphite precursor and as-prepared GO. Aerobic oxidative coupling of primary amines, which often requires the use of precious metal catalyst,29,30,31,32 was chosen as a model reaction,
where GO and ba-GO were used as the substitute for the metal catalysts. Performing the reaction with GO and oxygen in CH3CN at 80 °C for 5 h results in a 44% gas chromatography (GC) yield
(Supplementary Methods) for _N_-benzylidene benzylamine 2A (Supplementary Table S2, entry 4). Interestingly, ba-GO shows dramatically improved conversion. The optimized reaction was
conducted at 80 °C with 25 mg of ba-GO and 0.5 mmol of benzylamine. The reaction was performed with continuous stirring and bubbling with oxygen for 5 h. As a result, the oxidative coupling
product could be obtained with 89% GC yield (Supplementary Table S2, entry 8), remarkably higher than that for GO (Supplementary Table S2, entries 4–6). For longer times, around 6% of 2A was
also converted to benzylaldehyde _via_ hydrolysis (Supplementary Table S2, entry 7). Control experiments using graphite or oxidized debris recovered from the purification process produced
<2% yield (Supplementary Table S2, entries 10–11). Control experiments were also carried out using alternative carbon catalysts similar to oxidized nanodiamond and carbon black for
comparison, which all showed low activity (Supplementary Table S2, entries 12–13). These results prove that observed catalytic activity is unique to ba-GO, and the oxidative debris and metal
contaminants do not have any significant role. In small-scale reactions, ba-GO has demonstrated its effectiveness in the oxidative coupling of various primary amines (Supplementary Table
S3). The applicability of this carbon catalyst has been further extended to cross-dehydrogenative coupling33,34,35,36 of tetrahydroisoquinoline 3 and carbon nucleophiles 4, yielding 67–89%
of coupling products 5 (Supplementary Fig. S2). As GO-based materials can be readily scaled up in large quantities37, it is important to determine whether the scale of the catalytic process
can be increased. Therefore, a 1-g scale reaction for oxidative coupling of benzylamine (9.3 mmol, 1.0 g) was investigated. We find that only 20 wt% of the catalyst loading is required for a
large-scale reaction in 50 ml CH3CN, yielding 98% of _N_-benzylidene benzylamine (Supplementary Table S2, entry 14). We have also verified that the catalysis can be carried out in open air
and similar conversion and yield can be achieved (Supplementary Table S2, entry 15). Performing the reaction in anaerobic conditions (glove box, oxygen<0.2 ppm) reduced the yield to 5%,
thus indicating that oxygen is the terminal oxidant (Supplementary Table S2, entry 16). The dramatically enhanced activity of ba-GO in large-scale reaction suggests that higher concentration
of substrate significantly contributes to better performance. To prove this hypothesis, we carried out the reaction under solvent-free and open-air condition, the results show that only 5
wt% of the catalyst loading is sufficient to achieve a 100% conversion with yields up to 98% (Table 1, entry 1). With these optimized conditions, the effectiveness of ba-GO for oxidative
coupling of various primary amines in a large scale was assessed (Table 1). The electronic effects of the substituents on the phenyl ring are found to be well tolerated under mild reaction
conditions (Table 1, entries 3–7). Moreover, para-, meta- and ortho-substituted benzylamine prove to be suitable substrates, revealing that the steric hindrance effect of the aryl ring has
little impact on the efficiency of the coupling process (Table 1, entries 5–7). Catalysis of 2-thiophenemethylamine, a representative of the heterocyclic amines, can also be achieved by
ba-GO with 92% yield of the corresponding product (Table 1, entry 8). However, when alkyl amine was subjected to the coupling reaction, much lower yield was observed by NMR, this is probably
due to the inactive _α_-hydrogen of amine (Table 1, entry 9). More impressively, the ba-GO catalyst shows good recyclability and can be reused by simple filtration and rinsing in
acetonitrile. There is little difference in both relative activity and selectivity (Fig. 2) up to the sixth cycle tested. Above all, the performance of ba-GO is comparable or even superior
to that of metal catalysts29,30,31. The low catalyst loading is unprecedented compared with previous catalysis reaction using GO16,17,18. The combination of solvent-free and metal-free
catalysis using low catalyst loading is a good model for practical application. PROBING THE ORIGINS OF THE OBSERVED CATALYSIS It is instructive to ask this question. Why does sequential base
and acid treatment (ba-GO) improve the catalytic properties of GO so significantly? (refer to Supplementary Table S2 for a comparison of the catalytic performance of ba-GO versus GO). To
correlate the catalytic activity of GO with variation in its chemical structure following sequential base and acid treatments, thermal gravimetry analysis (TGA) and solid state 13C NMR
studies were performed. Figure 3a displays TGA thermograms of GO and ba-GO recorded in nitrogen atmosphere. A much lower weight loss between 150 and 300 °C is shown by the ba-GO sample
compared with GO itself. This result indicates that the oxygen functional groups of ba-GO are largely removed after the base–acid treatment. 13C NMR spectra reveal a significant decrease in
the concentration of oxygen functionalities at 71.0 ppm (C-OH) and 61.9 ppm (C-O-C), which are assignable to the hydroxyl and epoxide groups. The broad resonance peak at 122.0 ppm suggests
that sp2 conjugation is partly recovered with the loss of oxygenated groups (Fig. 3b). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis (Fig. 3c and Supplementary Fig. S3a) also confirms that the
populations of hydroxyl and epoxide groups become significantly reduced after stepwise base and acid treatments. According to the recent studies on the mechanism of base reduction of
GO,26,27 the removal of oxygen functionalities is attributed to the effective removal of oxidative fragments and to a dehydration reaction driven by the base reflux conditions38. Our
purification process as well as its subsequent characterizations has excluded the role of impurities arising from debris or metallic impurities, thus the intrinsic oxygen functional groups
in ba-GO should have an important role in the carbocatalysis. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) absorption spectroscopy was performed _in-situ_ (in a vacuum environment, see the
Supplementary Methods for details) at room temperature (RT) to analyse the functional groups in base-treated GO (b-GO) and ba-GO (sequential base and acid treatments). A representative
infrared absorbance spectrum of GO collected in the transmission mode is shown in Fig. 3e (black) and can be used for comparison with the spectra of b-GO, ba-GO* (b-GO followed by
neutralization with the acid at RT) and ba-GO (b-GO treated with the acid at 120 °C) (Fig. 3e). As previously reported,39 infrared spectra of as-synthesized GO indicate contributions from
various oxygen functional groups. These groups include contributions from hydroxyls (C-OH for phenols or lactols at ~3,000–3,600 and ~1,050–1,150 cm−1), carbonyls (C=O, generalized for
ketonic edge groups such as anhydrides, lactones and pyrones at ~1,500–1,850 cm−1), carboxyls (COOH at ~1650–1750, ~3,000–3,600 and ~1,050–1,200 cm−1), epoxides (C–O–C at ~850 and
~1,280–1,330 cm−1), ethers (C–O at ~800–1,200 cm−1) and sp2-hybridized C=C (sp2-C, in-plane vibrations at ~1,580 cm−1) (Fig. 3e, black). In contrast to GO, the intensity of the hydroxyl band
at ~3,000–3,600 cm−1 in b-GO (Fig. 3e, red) is low. The carboxyl band at ~1,650–1,750 cm−1 is also considerably weaker, whereas the sp2-C mode at ~1,580 cm−1 is stronger. This spectral
information suggests an increase of sp2-conjugated domain density in the carbon backbone following the base treatment, which overlaps with the possible contributions from carboxylates
(COO−). The bands at ~1,750–1,800 cm−1 originate from ketones or quinones as these are stable in basic conditions39. To find out whether the functional groups that are affected by the base
treatment can be regenerated, b-GO was immersed in a HCl solution (0.1M) at RT for 1 h to produce ba-GO*. Following such a treatment, intensity of the carboxyl peak (~1,650–1,750 and
~1,050–1,200 cm−1) increases, due to the reprotonation of COO– groups. This observation also confirms the presence of such carboxyl groups after the base treatment. However, hydroxyls
(~3,000–3,600 and ~1,050–1,150 cm−1) and epoxides (~850 and ~1,280–1,330 cm−1) could not be recovered (Fig. 3e, blue). Spectral analysis of both ba-GO* and thermally treated GO
(Supplementary Fig. S4) further revealed the fact that the base treatment produced similar effect as thermal treatment in chemically reducing the hydroxyl and epoxy species. In both of these
processes, the intensity of sp2-conjugated C=C stretch ~1,580 cm−1 recovered as shown in Supplementary Fig. S5. The differences in the intensity of the hydroxyl bands between ba-GO* (b-GO
treated with the acid at RT) and ba-GO (b-GO treated with the acid at a high temperatures) suggest that hydroxyl groups (~3,000–3,600 and ~1,050–1,150 cm−1) could be further removed during
the acid-refluxing process (Fig. 3e, blue and Fig. 3f, green). After sequential base and acid treatments, _in-situ_ FTIR analysis reveals that the residual oxygen functional groups in ba-GO
are mainly ketones, epoxides (significantly reduced) and carboxylic acids. The hydroxyl groups have been largely removed. To test how the catalysis is affected by the further reduction of
residual oxygen functional groups, ba-GO were treated with NaBH4 (Fig. 3f, purple), a well-known reducing agent for GO12. Indeed, the yield was reduced dramatically to 11% in the oxidative
coupling of benzylamine (Supplementary Table S2, entry 18). However, reduction in the catalytic efficiency can either originate from the reduction of the oxygen-functionalities such as
quinones, epoxides or from the deprotonation of the carboxylic acid groups. To investigate whether the base effect of NaBH4 has affected the catalytic reaction, a neutralization step with
acid (Fig. 3f, magenta) was carried out at RT. This resulted in a regeneration of the carboxyl peak at ~1,650–1,750 cm−1 along with a remarkable recovery of the catalytic activity with a 78%
yield (Supplementary Table S2, entry 19). This finding therefore provides strong evidence that the carboxylic acid groups have a vital role in the catalysis reactions as it is unlikely that
the neutralization treatment can recover the reduced oxygen functionalities or introduce additional oxygen functionalities. This explanation agrees well with our observation that the
catalytic properties of base-treated GO (b-GO) is much poorer than those of the ba-GO and the catalytic activity is enhanced only after the acid neutralization (Supplementary Table S2,
entries 8 and 20). All these findings point strongly to the significant contribution of the carboxylic acids in the catalytic conversion here. To confirm the role of carboxylic acids in this
synthetic transformation, 1-pyrene carboxylic acid was used as a molecular analogue to mimic the graphene-based catalytic system. To our delight, 1-pyrenecarboxylic acid exhibits a 95%
yield in the oxidative coupling of benzylamine (Supplementary Table S4, entry 2), which is comparable with the activity of ba-GO. We also observed that pyrene itself has no activity in the
aerobic oxidation of amines. We have further tested a large range of carboxylic acids without large π-conjugation system, and these did not exhibit any reactivity (Supplementary Table S4).
According to the widely accepted Lerf–Klinowski model,40 epoxy and hydroxyl groups reside on the GO basal plane, whereas the periphery of the GO sheets is decorated mainly by carboxyl,
anhydride, lactone, phenol, lactol or pyrone groups. As the carboxylic acids are mainly residing at the periphery of the sheet, its coverage will be expected to be relatively low compared
with the other oxygenated groups and it is difficult to explain the observed catalytic activity. Scanning tunnelling microscope (STM) imaging (Fig. 4) reveals that GO sheets become highly
porous after the base treatment with an average pore area of around 5 nm2. These holes could be created during the harsh oxidation process, which were enlarged by the etching process during
the base treatment. Infrared spectroscopy studies also confirmed the hole defect formation by indicating a CO2 production during thermal annealing of base-treated GO (Supplementary Fig. S6).
This fact could be further confirmed by atomic force microscopy studies (Supplementary Fig. S7). These findings suggested that the active catalysis sites in ba-GO are likely to be hole
defects in the conjugated domain, and the edges of the hole defect are terminated by the carboxylic acids. Our studies showed that the base reduction of GO generates nanovoids that are
surrounded by conjugated domains. Localized spins originating from the non-bonding π electron states are likely to be created at the edges, analogous to non-kekulè molecules having open
shell unpaired electrons. To confirm this fact, we performed electron spin resonance (ESR) measurements for GO subjected to different treatments. The ESR spectra shown in Fig. 4g–i can be
fitted by two kinds of Lorentzian curves; one having a narrower linewidth and the other with a broader one. Sharper peaks appear in all samples, with linewidth close to that for sigma
dangling bond spins observed in nanoporous carbon materials (~0.1 mT)41. On the other hand, the broader peak, which is only observed in ba-GO, has a linewidth similar to that of localized
spins originating from the edge of nanographene (~1 mT)42,43. The π-electron radical at the edges of graphene is delocalized along the edges to some extent, and exhibits fast spin-lattice
relaxation through interaction with the adjacent π-electron system, giving rise to a broad linewidth in ESR. Only ba-GO exhibits the broader ESR signal, with an intensity ratio of the broad
peak to narrow peak of about 5:1. Therefore, it can be inferred that the observed catalytic ability is related to the localized spins created at the edge of π-electron system. One way to
study whether the spin states are important in catalysis is to quench them. It is well known that the coupling of diazonium to graphene occurs via a radical pathway, and therefore regions on
graphene with unpaired electrons should be highly reactive towards such coupling reactions. In this case, we functionalized ba-GO with phenyl carboxylic acid using diazonium coupling
reactions. Introduction of the phenyl carboxylic groups ensures that the density of the carboxylic functionalities is preserved after the coupling reactions, although the density of unpaired
spins in ba-GO will be reduced. Indeed, the ESR response of the broad peak is now significantly reduced after the diazonium coupling, and this is associated with the decrease in the
catalytic activity of ba-GO-PhCOOH from 89 to 30% in the oxidative coupling of benzylamine (Supplementary Table S2, entries 8 and 21). This suggests that radical states at the edge sites are
important in the catalysis besides carboxylic groups. To shed light on the mechanism, we employed a spin-trapping electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) technique using
5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline _N_-oxide (DMPO) as the spin trap to detect the intermediates formed during reaction. DMPO is a particularly useful probe for trapping oxygen-derived radicals (for
example, ·O2− radicals) because of the relative stability and the diverse spectral characteristics of the spin adducts. As shown below, the EPR signal shows the characteristic fingerprint of
spin adducts due to superoxide radical (·O2−) (DMPO·OO(H)). Control studies show that in the absence of ba-GO catalyst or O2, spin signals due to oxygen radical show very low intensity
(Fig. 5b). The formation of H2O2, which is one of the postulated intermediates in the aerobic oxidation reactions is also detected by using the catalysed oxidation of _N_, _N_-diethyl-1,
4-phenylenediammonium sulphate (DPD) by Horseradish peroxidase (POD), where two absorption peaks centred at ca. 510 and 551 nm (Fig. 5c) can be seen. These result show that the aerobic
oxidation in our catalytic system proceeds via superoxide radical (·O2−) and H2O2 is the intermediate product. We suggest that these edge sites with unpaired electrons constitute the active
catalytic sites and afford enhanced kinetics for the trapping and activation of molecular oxygen by a sequence of electron transport and reduction to superoxide radical. One plausible
mechanism involving both the unpaired electron and the carboxylic groups is proposed as following: Benzylamine 1A binds to the acidic carboxyl groups _via_ hydrogen bond, and forms an
electron-donor complex B. The unpaired electrons of porous GO reduce molecular oxygen to form ·O2−, which stays surface-bound to the GO to stabilize the positive charge of the hole. At the
same time, the anchored amine is oxidized by positive charge of the hole to form the cation radical complex. The superoxide radical (·O2−) can abstract hydrogen atom from the amine radial
cation to produce imine intermediates and H2O2. Meanwhile, the active site is released for another catalytic cycle, giving rise to a turnover mechanism. The imine intermediates can react
with the free amines to furnish the coupling products (Fig. 5a, pathway a) or with water to produce benzaldehydes, which are then transferred to coupling products via condensation reactions
shown with 1A (Fig. 5a, pathway b). DISCUSSION The role of base and acid treatment in enhancing the catalytic performance of GO can now be understood. Refluxing in base helps to increase the
density of the nanovoids in GO, which gives rise to a high density of edges that can have localized spins. Another important effect of the base reduction is the removal of the hydroxyl
groups. This has the effect of changing the dynamics of water solvation layer around GO, which allows greater access to the catalytic sites by the reactant. A subsequent acid neutralization
step is needed to recover the active carboxylic groups, which serves as hydrogen bonding sites to the amines and also facilitates the proton transfer reactions due to its acidic properties.
More excitingly, we discovered that ba-GO catalyst can be used under solvent-free, open-air condition and is recyclable, this has tremendous implication for green catalysis and the full
potential of this material remains to be discovered. In conclusion, we have identified a chemical treatment that is needed to impart high catalytic activities on GO in the aerobic oxidation
of various amines and investigated the catalytic origins. As GO is an amphiphilic material with pH-sensitive functional groups, appropriate base and acid treatments are needed to activate
the catalytic sites in GO. The carboxylic groups at the edges of defects, along with the localized unpaired electrons, work synergistically to trap molecular oxygen and the amine molecules,
thus facilitating intermolecular arrangements. In view of the fact that the production of GO is now being scaled up industrially, these chemical processing steps can be adopted as the
standard protocol to render GO catalytically active, thus opening the possibility for the large-scale industrial applications of GO in industrial catalysis. METHODS BASE–ACID TREATMENT OF
GRAPHENE OXIDE (BA-GO) The as-produced GO was dispersed in 750 ml DI water at a concentration of 0.6 mg ml−1. Three grams of NaOH plate was added into GO solution (0.1 mol l−1). The mixture
was refluxed in a round-bottom flask under constant magnetic stirring for 1 h. Subsequently, the base-treated GO were separated by centrifuging at 13,000 r.p.m. and dispersing in 750 ml DI
water. Then, 7.5 ml HCl (37%) was added into the solution slowly. The mixture was refluxed for another 1 h. The final ba-GO obtained were filtered and washed by DI water and acetone. The
synthesized ba-GO was kept in vacuum desiccators. Debris (Supplementary Fig. S7a and Supplementary Fig. S8) present in the GO solution was isolated by using ammonia as the base according to
the reported reference26. SYNTHESIS OF COMPOUND 2A IN CH3CN The obtained ba-GO (200 mg) was dispersed in acetonitrile (50 ml) in round-bottom flask and ultrasonicated for 1 h. Benzylamine
(1.0 g) was added into the solution. The mixture was stirred with continual oxygen bubbling and slightly refluxed for 10 h. After that, the solution was cooled to RT and 1.0 g of anisole was
added. The reaction mixture samples were taken out by syringe and checked by GC–MS: 98% GC Yield. ba-GO catalyst can be recovered by simple filtration and rising in CH3CN (Supplementary
Fig. S9). SOLVENT-FREE AND AEROBIC SYNTHESIS OF COMPOUND 2A The obtained ba-GO (50 mg) was dispersed in 1.0 g of benzylamine and ultrasonicated for 30 min. The mixture was stirred at 90 °C
for 12 h under open air. After that, the solution was cooled to RT and 1.0 g of anisole was added. After filtration and washing by CH3CN, aliquots of the mixture were extracted using a
syringe and checked by GC–MS (98% GC-yield). Evaporation under vacuum (2 mbar, 65 °C) afforded 2A in 95% yield (867 mg). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 25 °C, TMS): _δ_=8.45 (s, 1H), 7.80−8.00 (m,
2H), 7.20−7.60 (m, 8H), 4.89 ppm (s, 2H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3, 25 °C, TMS): _δ_=65.0, 126.9, 127.9, 128.2, 128.4, 128.5, 130.7, 136.1, 139.2, 161.9 ppm; MS (70 eV, EI) _m/z_: 195 (M+).
ba-GO catalyst can be reused for multi-runs by simple filtration and rising in CH3CN. SYNTHESIS OF COMPOUND 5A The as-made ba-GO (40 mg) was dispersed in acetonitrile (10 ml) in a
round-bottom flask and ultrasonicated for 1 h. _N_-phenyl tetrahydroisoquinoline 3A (52.3 mg) and nitromethane (0.2 ml) was added into the solution. The mixture was stirred with continual
oxygen bubbling and slightly refluxed for 24 h. Filtration, evaporation and column chromatography on silica gel afforded 5A in 78% yield (52.0 mg). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 25 °C, TMS):
_δ_=7.16−7.40 (m, 6H), 7.03 (d, _J_=7.9 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (t, _J_=7.3 Hz, 1H), 5.60 (t, _J_=7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.92 (dd, _J1_=7.7 Hz, _J2_=11.8 Hz, 1H), 4.92 (dd, _J1_=6.6 Hz, _J2_=11.9 Hz, 1H),
3.60−3.80 (m, 2H), 3.06−3.20 (m, 1H), 2.76−2.90 ppm (m, 1H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3, 25 °C, TMS): _δ_=26.4, 42.0, 58.1, 78.7, 115.1, 119.4, 126.6, 126.9, 128.1, 129.1, 129.4, 132.9, 135.2,
148.4 ppm. ESR MEASUREMENTS FOR GO SAMPLES ESR measurements were performed with an ESR X-band spectrometer (JEOL JES-TE200) at RT for typically 4.5 mg samples sealed in a quartz sample tube.
The samples were evacuated to <10−6 Torr at RT for 20 h to avoid influence of adsorbed oxygen, which often bury the intrinsic ESR signals of porous material in advance. The incident
microwave power of 250 μW, where saturation does not occur, is applied for excitation. DETECTING H2O2 Sample preparation: DPD reagent was prepared by dissolving 0.1 g of DPD in 10 ml 0.05
mol l−1 H2SO4 and stored in dark at 5 °C. POD reagent was prepared by dissolving l0 mg peroxidase product from horseradish in 10 ml of tridistilled water. The standard solution was stored at
5 °C. Both DPD and POD were prepared freshly on demand. Typical procedure for the detection of H2O2: The obtained ba-GO (25 mg) was dispersed in CH3CN (10 ml) and ultrasonicated for 1 h.
Benzylamine (53.5 mg, 0.5 mmol) was added into the solution. The mixture was stirred at 80 °C for 5 h. After that, the solution was cooled to RT and filtered to remove ba-GO. Twenty
milliliter DI water was added to the solution, and the mixture was further extracted by EtOAc (20 ml × 3) to remove the organic compounds. The aqueous solution was diluted to 400 ml by DI
water. 9 ml aqueous solution and 1 ml PBS buffer (pH 7.4) was added into the beaker with stirring, and used as the test sample. The ultraviolet-visible spectra of test sample were recorded
after adding 20 μl DPD and 20 μl POD. The mixture that contains all reagents except POD was used to record the baseline absorption (Supplementary Fig. S10). DETECTING SUPEROXIDE RADICAL
ANION Typical spectrometer parameters: Microwave power: 20 mW. Microwave Freq.: 9.4 GHz. Scan time: 1 min. Modulation amplitude: 0.02 mT. Modulation Freq.:100 kHz. Receiver gain: 10 × 2.
Time constant: 0.01. Typical EPR spectra of reaction system: ba-GO (25 mg), Benzylamine 1A (53.5 mg, 0.5 mmol), MeOH (2 ml). The reaction mixture was vigorously stirred at 60 °C bubbling
with oxygen for 0.5 h. This reaction solution was taken out into a small tube followed by the addition of DMPO. Then, the mixture was analysed by EPR (Supplementary Fig. S11).
CHARACTERIZATION SEM images were recorded using the JEOL 6701 FESEM (field emission scanning electron microscopy) at 30 kV. STM images were recorded in the constant current mode at RT after
annealing the samples at specified temperature. Atomic force microscopy images were collected using the X100c, and the specimens studied were coated freshly on highly ordered pyrolytic
graphite (HOPG) substrates by spin coating. TGA and differential thermal analysis were recorded using a Rigaku TG8101D and TAS 300 data-processing system with an aluminium pan under N2 with
a heating rate of 10 °C min−1. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy was performed with the Phobios 100 electron analyzer equipped with 5 channeltrons, using an unmonochromated Al Kα X-ray source
(1,486.6 eV). ESR measurements were performed with an ESR X-band spectrometer (JEOL JES-TE200) at RT for typically 4.5 mg samples sealed in a quartz sample tube. FTIR measurements were
performed at RT in a continuous vacuum environment with data collected typically 500 scans per loop in the transmission mode. A deuterated triglycine sulphate detector having a mirror
optical velocity of 0.6329, cm s−1 was used at a 4 cm−1 resolution. The samples were placed in an annealing chamber and positioned at an infrared incident angle close to the Brewster’s angle
(70°). For annealing studies, data collection per loop was performed at 60 °C. The annealing time was 5 mins at each temperature for a stepwise reduction and the total annealing time for
the overall experiment per sample was ~8 h. See more details in Supplementary Methods section. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Su, C. _et al_. Probing the catalytic activity
of porous graphene oxide and the origin of this behaviour. _Nat. Commun_. 3:1298 doi: 10.1038/ncomms2315 (2012). REFERENCES * Clark J. H. Solid acids for green chemistry. _Acc. Chem. Res._
35, 791–797 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Anastas P. T., Kirchhoff M. M. Origins, current status, and future challenges of green chemistry. _Acc. Chem. Res._ 35, 686–694 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Leitner W. Green chemistry - Frontiers in benign chemical syntheses and processes. _Science_ 284, 1780–1781 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Su D. S.
et al. Metal-free heterogeneous catalysis for sustainable chemistry. _Chemsuschem_ 3, 169–180 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Bitter J. H. Nanostructured carbons in catalysis a Janus
material-industrial applicability and fundamental insights. _J. Mater. Chem_ 20, 7312–7321 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Dreyer D. R., Bielawski C. W. Carbocatalysis:
heterogeneous carbons finding utility in synthetic chemistry. _Chem. Sci._ 2, 1233–1240 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wang Y., Wang X. C., Antonietti M. Polymeric graphitic carbon
nitride as a heterogeneous organocatalyst: from photochemistry to multipurpose catalysis to sustainable chemistry. _Angew. Chem. Int. Ed._ 51, 68–89 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Hayashi M. Oxidation using activated carbon and molecular oxygen system. _Chem. Rec._ 8, 252–267 (2008). Article CAS Google Scholar * Geim A. K., Novoselov K. S. The rise of graphene.
_Nat. Mater._ 6, 183–191 (2007). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Park S., Ruoff R. S. Chemical methods for the production of graphenes. _Nat. Nanotech._ 4, 217–224 (2009). Article ADS
CAS Google Scholar * Loh K. P., Bao Q. L., Eda G., Chhowalla M. Graphene oxide as a chemically tunable platform for optical applications. _Nat. Chem._ 2, 1015–1024 (2010). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Dreyer D. R., Park S., Bielawski C. W., Ruoff R. S. The chemistry of graphene oxide. _Chem. Soc. Rev._ 39, 228–240 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Loh K. P., Bao Q.
L., Ang P. K., Yang J. X. The chemistry of graphene. _J. Mater. Chem._ 20, 2277–2289 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Bai H., Li C., Shi G. Q. Functional composite materials based on
chemically converted graphene. _Adv. Mater._ 23, 1089–1115 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Machado B. F., Serp P. Graphene-based materials for catalysis. _Catal. Sci. Technol._ 2,
54–75 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar * Dreyer D. R., Jia H. P., Todd A. D., Geng J. X., Bielawski C. W. Graphite oxide: a selective and highly efficient oxidant of thiols and
sulfides. _Org. Biomol. Chem._ 9, 7292–7295 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Jia H. P., Dreyer D. R., Bielawski C. W. C-H oxidation using graphite oxide. _Tetrahedron_ 67, 4431–4434
(2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Dreyer D. R., Jia H. P., Bielawski C. W. Graphene oxide: a convenient carbocatalyst for facilitating oxidation and hydration reactions. _Angew. Chem.
Int. Ed._ 49, 6813–6816 (2010). CAS Google Scholar * Kumar A. V., Rao K. R. Recyclable graphite oxide catalyzed Friedel-Crafts addition of indoles to alpha,beta-unsaturated ketones.
_Tetrahedron Lett._ 52, 5188–5191 (2011). Article Google Scholar * Verma S. et al. Graphene oxide: an efficient and reusable carbocatalyst for aza-Michael addition of amines to activated
alkenes. _Chem. Commun._ 47, 12673–12675 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Chauhan S. M. S., Mishra S. Use of graphite oxide and graphene oxide as catalysts in the synthesis of
dipyrromethane and calix[4]pyrrole. _Molecules_ 16, 7256–7266 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Dreyer D. R., Jarvis K. A., Ferreira P. J., Bielawski C. W. Graphite oxide as a
carbocatalyst for the preparation of fullerene-reinforced polyester and polyamide nanocomposites. _Polym. Chem._ 3, 757–766 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar * Pyun J. Graphene oxide as
catalyst: application of carbon materials beyond nanotechnology. _Angew. Chem. Int. Ed._ 50, 46–48 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Gao W., Alemany L. B., Ci L. J., Ajayan P. M. New
insights into the structure and reduction of graphite oxide. _Nat. Chem._ 1, 403–408 (2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Bagri A. et al. Structural evolution during the reduction of
chemically derived graphene oxide. _Nat. Chem._ 2, 581–587 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * He W. H. L., Lu L. H. Revisiting the structure of graphene oxide for preparing new-style
graphene-based ultraviolet absorbers. _Adv. Funct. Mater._ 22, 1–8 (2012). Article Google Scholar * Rourke J. P. et al. The real graphene oxide revealed: Stripping the oxidative debris
from the graphene-like sheets. _Angew. Chem. Int. Ed._ 50, 3173–3177 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Leadbeater N. E. Cross coupling: when is free really free? _Nat. Chem._ 2,
1007–1009 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Prades A., Peris E., Albrecht M. Oxidations and oxidative couplings catalyzed by triazolylidene ruthenium complexes. _Organometallics_ 30,
1162–1167 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhu B. L., Lazar M., Trewyn B. G., Angelici R. J. Aerobic oxidation of amines to imines catalyzed by bulk gold powder and by
alumina-supported gold. _J. Catal._ 260, 1–16 (2008). Article CAS Google Scholar * Grirrane A., Corma A., Garcia H. Highly active and selective gold catalysts for the aerobic oxidative
condensation of benzylamines to imines and one-pot, two-step synthesis of secondary benzylamines. _J. Catal._ 264, 138–144 (2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Chu G. B., Li C. B.
Convenient and clean synthesis of imines from primary benzylamines. _Org. Biomol. Chem._ 8, 4716–4719 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Li C. J. Cross-dehydrogenative coupling (CDC):
Exploring C-C bond formations beyond functional group transformations. _Acc. Chem. Res._ 42, 335–344 (2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sun C. L., Li B. J., Shi Z. J. Direct C-H
transformation via iron catalysis. _Chem. Rev._ 111, 1293–1314 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Li Z. P., Bohle D. S., Li C. J. Cu-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenative coupling: A
versatile strateav for C-C bond formations via the oxidative activation of sp(3) C-H bonds. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 103, 8928–8933 (2006). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Li C. J.,
Trost B. M. Green chemistry for chemical synthesis. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 105, 13197–13202 (2008). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Segal M. Selling graphene by the ton. _Nat.
Nanotech._ 4, 611–613 (2009). ADS Google Scholar * Liao K. H. et al. Aqueous only route toward graphene from graphite oxide. _ACS Nano_ 5, 1253–1258 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Acik M. et al. The role of oxygen during thermal reduction of graphene oxide studied by infrared absorption spectroscopy. _J. Phys. Chem. C_ 115, 19761–19781 (2011). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Lerf A., He H. Y., Forster M., Klinowski J. Structure of graphite oxide revisited. _J. Phys. Chem. B_ 102, 4477–4482 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Takai K., Suzuki T.,
Enoki T., Nishihara H., Kyotani T. Structure and magnetic properties of curved graphene networks and the effects of bromine and potassium adsorption. _Phys. Rev. B_ 81, 205420 (2010).
Article ADS Google Scholar * Enoki T., Takai K. The edge state of nanographene and the magnetism of the edge-state spins. _Solid State Commun._ 149, 1144–1150 (2009). Article ADS CAS
Google Scholar * Joly V. L. J. et al. Effect of electron localization on the edge-state spins in a disordered network of nanographene sheets. _Phys. Rev. B_ 81, 115408 (2010). Article ADS
Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS K.P.L. thank the support of National Research Foundation for the CRP project ‘Graphene and Related Materials’ R-143-000-380-281, as
well as Singapore Millenium Foundation/NUS Research Horizon Fund R-143-000-417-646. C.L.S. acknowledges support of Economic Development Board (SPORE, COY-15-EWI-RCFSA/N197-1). Q.L.B.
acknowledges financial support from the Lee Kuan Yew Postdoctoral Fellowship. Y.J.C. and M.A. acknowledge the full financial support of the US Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy
Sciences, Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering under Award DE-SC001951. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Chemistry, Graphene Research Centre, National
University of Singapore, 3 Science Drive 3, Singapore, 117543, Singapore Chenliang Su, Jiong Lu, Yi Zheng, Pingping Wu, Qiaoliang Bao & Kian Ping Loh * Department of Materials Science
and Engineering, University of Texas at Dallas, 800 W. Campbell Road, RL10, Richardson, 75080, Texas, USA Muge Acik & Yves J. Chabal * Department of Chemistry, Tokyo Institute of
Technology, 2-12-1, Ookayama, Meguro, 152-8550, Tokyo, Japan Kazuyuki Takai, Si-jia Hao & Toshiaki Enoki Authors * Chenliang Su View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * Muge Acik View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Kazuyuki Takai View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Jiong Lu View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Si-jia Hao View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Yi Zheng View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Pingping Wu View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Qiaoliang Bao View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Toshiaki Enoki View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Yves J. Chabal View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Kian Ping Loh
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS K.P.L. supervised the overall project. C.L.S. and K.P.L. conceived and designed the
experiments. C.L.S., J.L., Y.Z. and P.P.W. performed the experiments. C.L.S. and Q.L.B. drew the schematics. M.A. and Y.J.C. contributed to the FTIR experiments including annealing studies
and data interpretation. K.T., T.E. and S.J.H. contributed ESR data. K.P.L. and C.L.S. discussed the results and analysed the data and wrote the manuscript. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR
Correspondence to Kian Ping Loh. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
Supplementary Figures S1-S11, Supplementary Tables S1-S4 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 2923 kb) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Su, C.,
Acik, M., Takai, K. _et al._ Probing the catalytic activity of porous graphene oxide and the origin of this behaviour. _Nat Commun_ 3, 1298 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2315
Download citation * Received: 02 July 2012 * Accepted: 22 November 2012 * Published: 18 December 2012 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2315 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the
following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer
Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative