Play all audios:
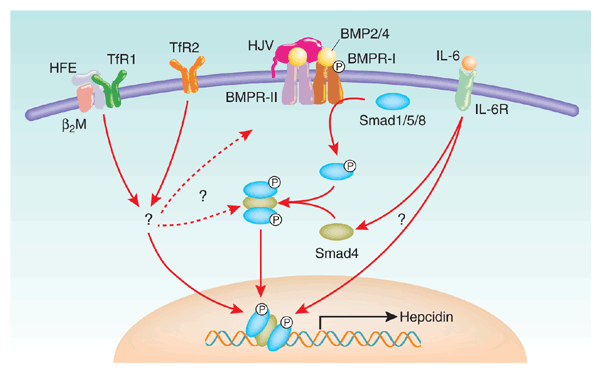
Mutations in hemojuvelin disrupt its ability to stimulate expression of the iron regulatory peptide hepcidin and result in the severe iron loading disorder juvenile hemochromatosis. A new
study shows that hemojuvelin acts through the multifunctional bone morphogenetic protein pathway to modulate hepcidin levels, providing new insights into communication within a key
physiological pathway. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution
Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full
article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs *
Contact customer support REFERENCES * Camaschella, C. _Blood_ 106, 3710–3717 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ganz, T. & Nemeth, E. _Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol._
290, G199–G203 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Bridle, K.R. et al. _Lancet_ 361, 669–673 (2003). Article CAS Google Scholar * Nemeth, E. et al. _Blood_ 105, 1803–1806 (2005).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Papanikolaou, G. et al. _Nat. Genet._ 36, 77–82 (2004). Article CAS Google Scholar * Babitt, J.L. et al. _Nat. Genet._ 38, 531–539 (2006). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Chen, D., Zhao, M. & Mundy, G.R. _Growth Factors_ 22, 233–241 (2004). Article CAS Google Scholar * Samad, T.A. et al. _J. Biol. Chem._ 280, 14122–14129 (2005).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Babitt, J.L. et al. _J. Biol. Chem._ 280, 29820–29827 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wang, R. et al. _Cell Metab._ 2, 399–409 (2005). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Frazer, D.M. & Anderson, G.J. _Blood Cells Mol. Dis._ 30, 288–297 (2003). Article CAS Google Scholar * Pietrangelo, A. et al. _Gastroenterology_ 128, 470–479 (2005).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Lin, L., Goldberg, P. & Ganz, T. _Blood_ 106, 2884–2889 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Nicolas, G. et al. _J. Clin. Invest._ 110, 1037–1044
(2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lee, P. et al. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 102, 1906–1910 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND
AFFILIATIONS * Iron Metabolism Laboratory, Queensland Institute of Medical Research, PO Royal Brisbane Hospital, Brisbane, 4029, Queensland, Australia Gregory J Anderson & David M Frazer
Authors * Gregory J Anderson View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * David M Frazer View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Anderson, G., Frazer, D. Iron metabolism meets signal transduction. _Nat
Genet_ 38, 503–504 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0506-503 Download citation * Issue Date: 01 May 2006 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0506-503 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the
following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer
Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative