Play all audios:
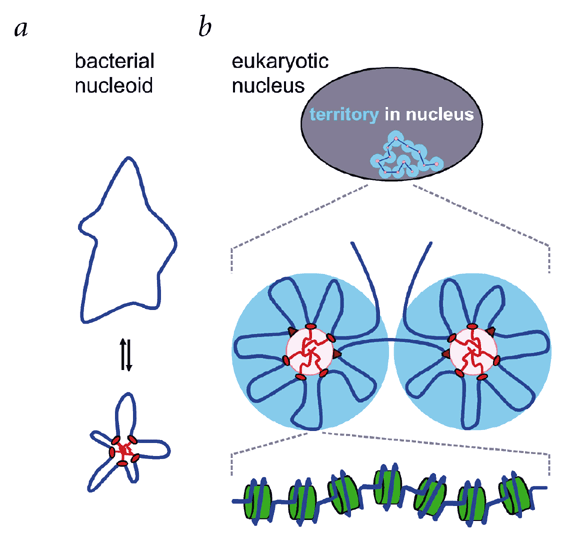
We would like to be able to predict how genomes are folded in the cell from the primary DNA sequence. A model for the three-dimensional structure of all genomes is presented; it is based on
the structure of the bacterial nucleoid, where RNA polymerases cluster and loop the DNA. Loops appear and disappear as polymerases initiate and terminate, but the microscopic structure is
'self-organizing' and, to some extent, predictable. At the macroscopic level, transcriptional activity drives pairing between homologous sequences, inactivity allows genome
compaction, and the segregation machinery orients whole chromosomes. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article *
Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn
about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support REFERENCES * Jackson, D.A., Dickinson, P. & Cook, P.R. The size of chromatin loops in HeLa cells. _EMBO J._
9, 567–571 (1990). Article CAS Google Scholar * Pettijohn, D.E. in _Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: Cellular and Molecular Biology_ (eds Neidhardt, F.C., Curtiss, R.,
Ingraham, J.L., Lin, E.C.C., Low, K.B., Magasanik, B., Reznifoff, W.S., Riley, M., Schaechter, M. & Umbarger, H.E.) 158–166 (ASM Press, Washington, 1996). Google Scholar * Cook, P.R.
_Principles of Nuclear Structure and Function_ (Wiley, New York, 2001). Google Scholar * Sachs, R.K., van den Engh, G., Trask, B., Yokota, H. & Hearst, J.E. A random walk/giant loop
model for interphase chromosomes. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 92, 2710–2714 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sedat, J. & Manuelidis, L. A direct approach to the structure of
eukaryotic chromosomes. _Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol._ 42, 331–350 (1978). Article CAS Google Scholar * Saitoh, Y. & Laemmli, U.K. From the chromosomal loops and the scaffold
to the classic bands of metaphase chromosomes. _Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol._ 58, 755–765 (1978). Article Google Scholar * Cook, P.R. A chromomeric model for nuclear and chromosome
structure. _J. Cell Sci._ 108, 2927–2935 (1995). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Manuelidis, L. A view of interphase chromosomes. _Science_ 250, 1533–1540 (1990). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Li, G., Sudlow, G. & Belmont, A.S. Interphase cell cycle dynamics of a late replicating, heterochromatic homogeneously staining region: precise choreography of
condensation/decondensation and nuclear positioning. _J. Cell Biol._ 140, 975–989 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Jackson, D.A., McCready, S.J. & Cook, P.R. Replication and
transcription depend on attachment of DNA to the nuclear cage. _J. Cell Sci. Suppl._ 1, 59–79 (1984). Article CAS Google Scholar * McManus, J. et al. Unusual chromosome structure of
fission yeast DNA in mouse cells. _J. Cell Sci._ 107, 469–486 (1994). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Misteli, T. The concept of self-organization in cellular architecture. _J. Cell Biol._
155, 181–185 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Nedelec, F., Surrey, T., Maggs, A.C. & Leibler, S. Self-organization of microtubules and motors. _Nature_ 389, 305–308 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Minton, A.P. The influence of macromolecular crowding and macromolecular confinement on biochemical reactions in physiological media. _J. Biol. Chem._ 256,
10577–10580 (2001). Article Google Scholar * Ishihama, A. Subunit of assembly of _Escherichia coli_ RNA polymerase. _Adv. Biophys._ 14, 1–35 (1981). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Minsky,
A., Shimoni, E. & Frenkiel Krispin, D. Stress, order and survival. _Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol._ 3, 50–60 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Mascarenhas, J., Weber, M.H. &
Graumann, P.L. Specific polar localization of ribosomes in _Bacillus subtilis_ depends on active transcription. _EMBO Rep._ 2, 685–689 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Haaf, T. &
Ward, D.C. Inhibition of RNA polymerase II transcription causes chromatin decondensation, loss of nucleolar structure, and dispersion of chromosomal domains. _Exp. Cell. Res._ 224, 163–173
(1996). Article CAS Google Scholar * Chubb, J.R., Boyle, S., Perry, P. & Bickmore, W.A. Chromatin motion is constrained by association with nuclear compartments in human cells. _Curr.
Biol._ 12, 439–445 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Cook, P.R. The organization of replication and transcription. _Science_ 284, 1790–1795 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Gelles, J. & Landick, R. RNA polymerase as a molecular motor. _Cell_ 93, 13–16 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Maniatis, T. & Reed, R. An extensive network of coupling among
gene expression machines. _Nature_ 416, 499–506 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lewis, P.J., Thaker, S.D. & Errington, J. Compartmentalization of transcription and translation in
_Bacillus subtilis_. _EMBO J._ 19, 710–718 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Bremer, H. & Dennis, P.P. in _Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: Cellular and Molecular
Biology_ (eds Neidhardt, F.C., Curtiss, R., Ingraham, J.L., Lin, E.C.C., Low, K.B., Magasanik, B., Reznifoff, W.S., Riley, M., Schaechter, M. & Umbarger, H.E.) 1553–1569 (ASM Press,
Washington, 1996). Google Scholar * Shaw, P.J. & Jordan, E.G. The nucleolus. _Ann. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol._ 11, 93–121 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Jackson, D.A., Iborra, F.J.,
Manders, E.M.M. & Cook, P.R. Numbers and organization of RNA polymerases, nascent transcripts and transcription units in HeLa nuclei. _Mol. Biol. Cell_ 9, 1523–1536 (1998). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Lemon, K.P. & Grossman, A.D. The extrusion capture model for chromosome partitioning in bacteria. _Genes Dev._ 15, 2031–2041 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Pombo, A. et al. Regional and temporal specialization in the nucleus: a transcriptionally-active nuclear domain rich in PTF, Oct1 and PIKA antigens associates with specific chromosomes early
in the cell cycle. _EMBO J._ 17, 1768–1778 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Frey, M.R., Bailey, A.D., Weiner, A.M. & Matera, A.G. Association of snRNA genes with coiled bodies is
mediated by nascent snRNA transcripts. _Curr. Biol._ 9, 126–135 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Cook, P.R. The transcriptional basis of chromosome pairing. _J. Cell Sci._ 110,
1033–1040 (1997). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * McKee, B.D., Habera, L. & Vrana, J.A. Evidence that intergenic spacer repeats of _Drosophila melanogaster_ rRNA genes function as X–Y
pairing sites in male meiosis, and a general model for achiasmatic pairing. _Genetics_ 132, 529–544 (1992). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hiraoka, Y. et al. The onset of
homologous chromosome pairing during _Drosophila melanogaster_ embryogenesis. _J. Cell Biol._ 120, 591–600 (1993). Article CAS Google Scholar * Henikoff, S. Heterochromatin function in
complex genomes. _Biochim. Biophys. Acta._ 1470, 1–8 (2000). Google Scholar * Kurz, A. et al. Active and inactive genes localize preferentially in the periphery of chromosome territories.
_J. Cell Biol._ 135, 1195–1205 (1996). Article CAS Google Scholar * Abranches, R., Beven, A.F., Aragon-Alcaide, L. & Shaw, P.J. Transcription sites are not correlated with chromosome
territories in wheat nuclei. _J. Cell Biol._ 143, 5–12 (1998). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sudbrak, R. et al. X chromosome specific cDNA arrays: identification of genes that escape from
X inactivation and other applications. _Hum. Mol. Genet._ 10, 77–83 (2001). Article CAS Google Scholar * Jenuwein, T. & Allis, C.D. Translating the histone code. _Science_ 201,
1074–1080 (2001). Article Google Scholar * Pederson, T. Half a century of 'the nuclear matrix'. _Mol. Biol. Cell_ 11, 799–805 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Jackson,
D.A., Bartlett, J. & Cook, P.R. Sequences attaching loops of nuclear and mitochondrial DNA to underlying structures in human cells: the role of transcription units. _Nucleic Acids Res._
24, 1212–1219 (1996). Article CAS Google Scholar * Christensen, M.O. et al. Dynamics of human DNA topoisomerases IIα and IIβ in living cells. _J. Cell Biol._ 157, 31–44 (2002). Article
CAS Google Scholar * Gribnau, J., Diderich, K., Pruzina, S., Calzolari, R. & Fraser, P. Intergenic transcription and developmental remodeling of chromatin subdomains in the human
β-_globin_ locus. _Mol. Cell_ 5, 377–386 (2000). Article CAS Google Scholar * Glover, D.M., Leibowitz, M.H., McLean, D.A. & Parry, H. Mutations in _aurora_ prevent centrosome
separation leading to the formation of monopolar spindles. _Cell_ 81, 95–105 (1995). Article CAS Google Scholar * Nickerson, J.A. Experimental observations of a nuclear matrix. _J. Cell
Sci._ 114, 463–474 (2001). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Manders, E.M.M., Kimura, H. & Cook, P.R. Direct imaging of DNA in living cells reveals the dynamics of chromosome formation. _J.
Cell Biol._ 144, 813–822 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sugaya, K., Vigneron, M. & Cook, P.R. Mammalian cell lines expressing functional RNA polymerase II tagged with the green
fluorescent protein. _J. Cell Sci._ 113, 2679–2683 (2000). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gustafsson, M.G. Extended resolution fluorescence microscopy. _Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol._ 9,
627–634 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Dekker, J., Rippe, K., Dekker, M. & Kleckner, N. Capturing chromosome conformation. _Science_ 295, 1306–1311 (2002). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Levsky, J.M., Shenoy, S.M., Pezo, R.C. & Singer, R.H. Single-cell gene expression profiling. _Science_ 297, 836–840 (2002). Article CAS Google Scholar * Pombo, A. et al.
Regional specialization in human nuclei: visualization of discrete sites of transcription by RNA polymerase III. _EMBO J._ 18, 2241–2253 (1999). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lercher,
M.J., Urrutia, A.O. & Hurst, L.D. Clustering of housekeeping genes provides a unified model of gene order in the human genome. _Nat. Genet._ 31, 180–183 (2002). Article CAS Google
Scholar * Marshall, W.F. et al. Interphase chromosomes undergo constrained diffusional motion in living cells. _Curr. Biol._ 7, 930–939 (1997). Article CAS Google Scholar * Liu, L.F.
& Wang, J.C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. _Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA_ 84, 7024–7027 (1987). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I
thank the Wellcome Trust for support and A. Pombo and M. Lloyd for providing figures and software. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Sir William Dunn School of Pathology,
University of Oxford, South Parks Road, Oxford, OX1 3RE, UK Peter R. Cook Authors * Peter R. Cook View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar RIGHTS
AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Cook, P. Predicting three-dimensional genome structure from transcriptional activity. _Nat Genet_ 32, 347–352
(2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1102-347 Download citation * Received: 05 April 2002 * Accepted: 10 September 2002 * Issue Date: 01 November 2002 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1102-347
SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to
clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative