Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Progressive kidney failure is a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of disorders. Podocyte foot processes and the interposed glomerular slit diaphragm are essential
components of the permeability barrier in the kidney. Mutations in genes encoding structural proteins of the podocyte lead to the development of proteinuria, resulting in progressive kidney
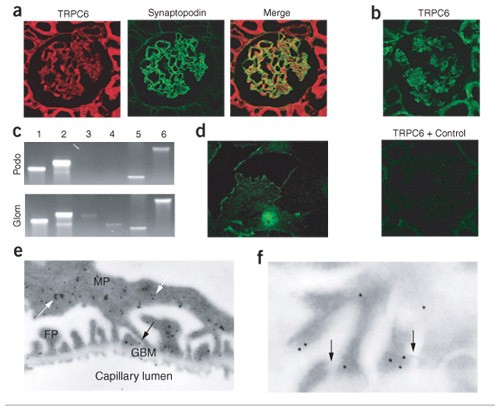
failure and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Here, we show that the canonical transient receptor potential 6 (TRPC6) ion channel is expressed in podocytes and is a component of the
glomerular slit diaphragm. We identified five families with autosomal dominant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in which disease segregated with mutations in the gene TRPC6 on chromosome
11q. Two of the TRPC6 mutants had increased current amplitudes. These data show that TRPC6 channel activity at the slit diaphragm is essential for proper regulation of podocyte structure and
function. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to
this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy
now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact
customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS KIF21A DEFICIENCY LEADS TO IMPAIRED GLOMERULAR FILTRATION BARRIER FUNCTION Article Open access 06 November 2023 DISTINCT FUNCTIONAL
REQUIREMENTS FOR PODOCALYXIN IN IMMATURE AND MATURE PODOCYTES REVEAL MECHANISMS OF HUMAN KIDNEY DISEASE Article Open access 10 June 2020 PODOCYTE-SPECIFIC CRB2 KNOCKOUT MICE DEVELOP FOCAL
SEGMENTAL GLOMERULOSCLEROSIS Article Open access 15 October 2021 REFERENCES * Zandi-Nejad, K., Eddy, A.A., Glassock, R.J. & Brenner, B.M. Why is proteinuria an ominous biomarker of
progressive kidney disease? _Kidney Int. Suppl._, S76–S89 (2004). * Somlo, S. & Mundel, P. Getting a foothold in nephrotic syndrome. _Nat. Genet._ 24, 333–335 (2000). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Pavenstadt, H., Kriz, W. & Kretzler, M. Cell biology of the glomerular podocyte. _Physiol. Rev._ 83, 253–307 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Pollak, M.R. Inherited podocytopathies: FSGS and nephrotic syndrome from a genetic viewpoint. _J. Am. Soc. Nephrol._ 13, 3016–3023 (2002). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Winn, M.P. et
al. A mutation in the TRPC6 cation channel causes familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. _Science_, published online 5 May 2005 (10.1126/science.1106215). * Montell, C. The TRP
superfamily of cation channels. _Sci. STKE_ 2005, re3 (2005). PubMed Google Scholar * Clapham, D.E. TRP channels as cellular sensors. _Nature_ 426, 517–524 (2003). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Facemire, C.S., Mohler, P.J. & Arendshorst, W.J. Expression and relative abundance of short transient receptor potential channels in the rat renal microcirculation.
_Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol._ 286, F546–F551 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mundel, P. et al. Synaptopodin: an actin-associated protein in telencephalic dendrites and
renal podocytes. _J. Cell Biol._ 139, 193–204 (1997). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Mundel, P. et al. Rearrangements of the cytoskeleton and cell contacts induce
process formation during differentiation of conditionally immortalized mouse podocyte cell lines. _Exp. Cell Res._ 236, 248–258 (1997). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Schnabel, E.,
Dekan, G., Miettinen, A. & Farquhar, M.G. Biogenesis of podocalyxin–the major glomerular sialoglycoprotein–in the newborn rat kidney. _Eur. J. Cell Biol._ 48, 313–326 (1989). CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Boute, N. et al. NPHS2, encoding the glomerular protein podocin, is mutated in autosomal recessive steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. _Nat. Genet._ 24, 349–354 (2000).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kestila, M. et al. Positionally cloned gene for a novel glomerular protein–nephrin–is mutated in congenital nephrotic syndrome. _Mol. Cell_ 1,
575–582 (1998). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kim, J.M. et al. CD2-associated protein haploinsufficiency is linked to glomerular disease susceptibility. _Science_ 300, 1298–1300
(2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Reiser, J. et al. Induction of B7–1 in podocytes is associated with nephrotic syndrome. _J. Clin. Invest._ 113, 1390–1397 (2004). Article CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Putaala, H., Soininen, R., Kilpelainen, P., Wartiovaara, J. & Tryggvason, K. The murine nephrin gene is specifically expressed in kidney,
brain and pancreas: inactivation of the gene leads to massive proteinuria and neonatal death. _Hum. Mol. Genet._ 10, 1–8 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hamano, Y. et al.
Determinants of vascular permeability in the kidney glomerulus. _J. Biol. Chem._ 277, 31154–31162 (2002). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kaplan, J.M. et al. Mutations in ACTN4,
encoding alpha-actinin-4, cause familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. _Nat. Genet._ 24, 251–256 (2000). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pavenstadt, H. & Bek, M. Podocyte
electrophysiology, _in vivo_ and _in vitro_. _Microsc. Res. Tech._ 57, 224–227 (2002). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Drenckhahn, D. & Franke, R.P. Ultrastructural organization
of contractile and cytoskeletal proteins in glomerular podocytes of chicken, rat, and man. _Lab. Invest._ 59, 673–682 (1988). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Huber, T.B. et al. Nephrin and
CD2AP associate with phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and stimulate AKT-dependent signaling. _Mol. Cell. Biol._ 23, 4917–4928 (2003). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Verma, R. et al. Fyn binds to and phosphorylates the kidney slit diaphragm component Nephrin. _J. Biol. Chem._ 278, 20716–20723 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hisatsune, C.
et al. Regulation of TRPC6 channel activity by tyrosine phosphorylation. _J. Biol. Chem._ 279, 18887–18894 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bandyopadhyay, B.C. et al. Apical
localization of a functional TRPC3/TRPC6-Ca2+-signaling complex in polarized epithelial cells. Role in apical Ca2+ influx. _J. Biol. Chem._ 280, 12908–12916 (2005). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Reiser, J., Kriz, W., Kretzler, M. & Mundel, P. The glomerular slit diaphragm is a modified adherens junction. _J. Am. Soc. Nephrol._ 11, 1–8 (2000). CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Notredame, C., Higgins, D.G. & Heringa, J. T-Coffee: A novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment. _J. Mol. Biol._ 302, 205–217 (2000). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank the family members for their participation in these studies and M.A. Arnaout for discussions about the manuscript.
This work was supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health (M.R.P., P.M. and R.K.) as well as the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (P.L.S. and D.E.C.). J.R. was supported by
the KMD Foundation and the KUFA-ASN Research Grant. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Medicine, Renal Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical
School, Boston, 02129, Massachusetts, USA Jochen Reiser, Clemens C Möller, Mehmet M Altintas & Changli Wei * Renal Division, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital and
Harvard Medical School, Boston, 02115, Massachusetts, USA Krishna R Polu, Peter Kenlan, Stephanie Herbert & Martin R Pollak * Department of Medicine, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New
York, 10029, New York, USA Christian Faul & Peter Mundel * Renal Unit, Instituto del Riñon-Fresenius Medical Care, Colombia Ivan Villegas * Department of Pathology, Instituto Nacional
de Cardiologia Ignacio Chavez, Mexico, 14080, D.F., Mexico Carmen Avila-Casado * Program in Membrane Biology and Renal Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School,
Boston, 02129, Massachusetts, USA Mary McGee & Dennis Brown * Department of Medicine, Center for Matrix Biology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston,
02115, Massachusetts, USA Hikaru Sugimoto & Raghu Kalluri * Department of Cardiology, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Children's Hospital, Boston, 02115, Massachusetts, USA Paula L
Smith & David E Clapham Authors * Jochen Reiser View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Krishna R Polu View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Clemens C Möller View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Peter Kenlan View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Mehmet M Altintas View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Changli
Wei View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Christian Faul View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
* Stephanie Herbert View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ivan Villegas View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Carmen Avila-Casado View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Mary McGee View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Hikaru Sugimoto View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Dennis Brown View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Raghu Kalluri View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Peter Mundel View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Paula L Smith View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * David E
Clapham View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Martin R Pollak View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to Jochen Reiser or Martin R Pollak. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests. SUPPLEMENTARY
INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. 1 Summary of TRPC6 mutations. (PDF 99 kb) SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE 1 Primer sequences. (PDF 43 kb) SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE Clinical information. (PDF 40 kb) RIGHTS AND
PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Reiser, J., Polu, K., Möller, C. _et al._ TRPC6 is a glomerular slit diaphragm-associated channel required for
normal renal function. _Nat Genet_ 37, 739–744 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1592 Download citation * Received: 12 April 2005 * Accepted: 23 May 2005 * Published: 27 May 2005 * Issue
Date: 01 July 2005 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1592 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable
link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative