Play all audios:
ABSTRACT The Fc receptor common γ-chain (FcRγ) is a widely expressed adaptor bearing an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) that transduces activation signals from various
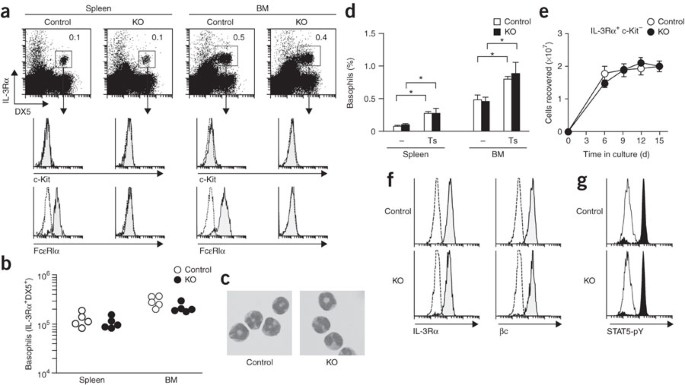
immunoreceptors. We show here that basophils lacking FcRγ developed normally and proliferated efficiently in response to interleukin 3 (IL-3) but were very impaired in IL-3-induced
production of IL-4 and in supporting T helper type 2 differentiation. Through its transmembrane portion, FcRγ associated constitutively with the common β-chain of the IL-3 receptor and
signaled by recruiting the kinase Syk. Retrovirus-mediated complementation demonstrated the essential function of the ITAM of FcRγ in IL-3 signal transduction. Our results identify a
previously unknown mechanism whereby FcRγ functions to 'route' selective cytokine-triggered signals into the ITAM-mediated IL-4 production pathway. Access through your institution
Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and
online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes
which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY
OTHERS CLASS I PI3K REGULATORY SUBUNITS CONTROL DIFFERENTIATION OF DENDRITIC CELL SUBSETS AND REGULATE FLT3L MEDIATED SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION Article Open access 19 July 2022 MOLECULAR MECHANISM
OF IGE-MEDIATED FCΕRI ACTIVATION Article 23 October 2024 KRÜPPEL-LIKE FACTOR 2 CONTROLS IGA PLASMA CELL COMPARTMENTALIZATION AND IGA RESPONSES Article Open access 28 March 2022 REFERENCES *
Nicola, N.A. Cytokine pleiotropy and redundancy: a view from the receptor. _Stem Cells_ 12 Suppl 1, 3–12 (1994). PubMed Google Scholar * Sugamura, K. et al. The interleukin-2 receptor γ
chain: its role in the multiple cytokine receptor complexes and T cell development in XSCID. _Annu. Rev. Immunol._ 14, 179–205 (1996). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Taniguchi, T.
Cytokine signaling through nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinases. _Science_ 268, 251–255 (1995). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Taga, T. & Kishimoto, T. Gp130 and the
interleukin-6 family of cytokines. _Annu. Rev. Immunol._ 15, 797–819 (1997). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Geijsen, N., Koenderman, L. & Coffer, P.J. Specificity in cytokine
signal transduction: lessons learned from the IL-3/IL-5/GM-CSF receptor family. _Cytokine Growth Factor Rev._ 12, 19–25 (2001). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Miyajima, A.,
Kitamura, T., Harada, N., Yokota, T. & Arai, K. Cytokine receptors and signal transduction. _Annu. Rev. Immunol._ 10, 295–331 (1992). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Takatsu, K.
Interleukin 5 and B cell differentiation. _Cytokine Growth Factor Rev._ 9, 25–35 (1998). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bezbradica, J.S. et al. Granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor regulates effector differentiation of invariant natural killer T cells during thymic ontogeny. _Immunity_ 25, 487–497 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Falcone, F.H., Haas, H. & Gibbs, B.F. The human basophil: a new appreciation of its role in immune responses. _Blood_ 96, 4028–4038 (2000). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lopez, A.F.
et al. Stimulation of proliferation, differentiation, and function of human cells by primate interleukin 3. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 84, 2761–2765 (1987). Article CAS PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Reddy, E.P., Korapati, A., Chaturvedi, P. & Rane, S. IL-3 signaling and the role of Src kinases, JAKs and STATs: a covert liaison unveiled. _Oncogene_ 19,
2532–2547 (2000). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Yousefi, S., Hoessli, D.C., Blaser, K., Mills, G.B. & Simon, H.U. Requirement of Lyn and Syk tyrosine kinases for the prevention
of apoptosis by cytokines in human eosinophils. _J. Exp. Med._ 183, 1407–1414 (1996). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pazdrak, K., Schreiber, D., Forsythe, P., Justement, L. &
Alam, R. The intracellular signal transduction mechanism of interleukin 5 in eosinophils: the involvement of lyn tyrosine kinase and the Ras-Raf-1- MEK-microtubule-associated protein kinase
pathway. _J. Exp. Med._ 181, 1827–1834 (1995). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lach-Trifilieff, E., Menear, K., Schweighoffer, E., Tybulewicz, V.L.J. & Walker, C. Syk-deficient
eosinophils show normal interleukin-5-mediated differentiation, maturation, and survival but no longer respond to FcγR activation. _Blood_ 96, 2506–2510 (2000). CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Chan, A.C. & Shaw, A.S. Regulation of antigen receptor signal transduction by protein tyrosine kinases. _Curr. Opin. Immunol._ 8, 394–401 (1996). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Fodor, S., Jakus, Z. & Mocsai, A. ITAM-based signaling beyond the adaptive immune response. _Immunol. Lett._ 104, 29–37 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tsubokawa, M. et
al. Interleukin-3 activates Syk in a human myeloblastic leukemia cell line, AML193. _Eur. J. Biochem._ 249, 792–796 (1997). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Falcone, F.H., Zillikens,
D. & Gibbs, B.F. The 21st century renaissance of the basophil? Current insights into its role in allergic responses and innate immunity. _Exp. Dermatol._ 15, 855–864 (2006). Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Oh, K., Shen, T., Le Gros, G. & Min, B. Induction of Th2 type immunity in a mouse system reveals a novel immunoregulatory role of basophils. _Blood_ 109,
2921–2927 (2007). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hida, S., Tadachi, M., Saito, T. & Taki, S. Negative control of basophil expansion by IRF-2 critical for the regulation of Th1/Th2
balance. _Blood_ 106, 2011–2017 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Sokol, C.L., Barton, G.M., Farr, A.G. & Medzhitov, R. A mechanism for the initiation of allergen-induced T
helper type 2 responses. _Nat. Immunol._ 9, 310–318 (2008). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Schramm, G. et al. Cutting edge: IPSE/alpha-1, a glycoprotein from
Schistosoma mansoni eggs, induces IgE-dependent, antigen-independent IL-4 production by murine basophils _in vivo_. _J. Immunol._ 178, 6023–6027 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Mohrs, K., Wakil, A.E., Killeen, N., Locksley, R.M. & Mohrs, M. A two-step process for cytokine production revealed by IL-4 dual-reporter mice. _Immunity_ 23, 419–429 (2005). Article
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Park, S.Y. et al. Resistance of Fc receptor-deficient mice to fatal glomerulonephritis. _J. Clin. Invest._ 102, 1229–1238 (1998). Article
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Min, B. et al. Basophils produce IL-4 and accumulate in tissues after infection with a Th2-inducing parasite. _J. Exp. Med._ 200, 507–517
(2004). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Mukai, K. et al. Basophils play a critical role in the development of IgE-mediated chronic allergic inflammation independently
of T cells and mast cells. _Immunity_ 23, 191–202 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Takeda, K. et al. Essential role of Stat6 in IL-4 signalling. _Nature_ 380, 627–630 (1996).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Yoshimoto, T. et al. IL-18, although antiallergic when administered with IL-12, stimulates IL-4 and histamine release by basophils. _Proc. Natl.
Acad. Sci. USA_ 96, 13962–13966 (1999). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Denzel, A. et al. Basophils enhance immunological memory responses. _Nat. Immunol._ 9, 733–742
(2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kojima, T. et al. Mast cells and basophils are selectively activated _in vitro_ and _in vivo_ through CD200R3 in an IgE-independent manner.
_J. Immunol._ 179, 7093–7100 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mita, S. et al. Molecular characterization of the β chain of the murine interleukin 5 receptor. _Int. Immunol._
3, 665–672 (1991). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Sakurai, D. et al. FcεRIγ-ITAM Is differentially required for mast cell function in vivo. _J. Immunol._ 172, 2374–2381 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wines, B.D., Trist, H.M., Ramsland, P.A. & Hogarth, P.M. A common site of the Fc receptor γ subunit interacts with the unrelated immunoreceptors
FcαRI and FcεRI. _J. Biol. Chem._ 281, 17108–17113 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Padigel, U.M. & Farrell, J.P. Control of infection with _Leishmania major_ in
susceptible BALB/c mice lacking the common γ-chain for FcR is associated with reduced production of IL-10 and TGF-β by parasitized cells. _J. Immunol._ 174, 6340–6345 (2005). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Kitamura, K. et al. Critical role of the Fc receptor γ-chain on APCs in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation. _J.
Immunol._ 178, 480–488 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Finkelman, F.D. et al. Interleukin-4- and interleukin-13-mediated host protection against intestinal nematode
parasites. _Immunol. Rev._ 201, 139–155 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Schmitz, J. et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related
protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. _Immunity_ 23, 479–490 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tassiulas, I. et al. Amplification of IFN-α-induced STAT1
activation and inflammatory function by Syk and ITAM-containing adaptors. _Nat. Immunol._ 5, 1181–1189 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mocsai, A. et al. Integrin signaling
in neutrophils and macrophages uses adaptors containing immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs. _Nat. Immunol._ 7, 1326–1333 (2006). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Feng, J., Garrity, D., Call, M.E., Moffett, H. & Wucherpfennig, K.W. Convergence on a distinctive assembly mechanism by unrelated families of activating immune receptors.
_Immunity_ 22, 427–438 (2005). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Launay, P. et al. Alternative endocytic pathway for immunoglobulin A Fc receptors (CD89) depends on the
lack of FcRγ association and protects against degradation of bound ligand. _J. Biol. Chem._ 274, 7216–7225 (1999). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Honorio-Franca, A.C., Launay, P.,
Carneiro-Sampaio, M.M.S. & Monteiro, R.C. Colostral neutrophils express Fcα receptors (CD89) lacking γ chain association and mediate noninflammatory properties of secretory IgA. _J.
Leukoc. Biol._ 69, 289–296 (2001). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Nicola, N.A. et al. Functional inactivation in mice of the gene for the interleukin-3 (IL- 3)-specific receptor β-chain:
implications for IL-3 function and the mechanism of receptor transmodulation in hematopoietic cells. _Blood_ 87, 2665–2674 (1996). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Min, B. & Paul, W.E.
Basophils and type 2 immunity. _Curr. Opin. Hematol._ 15, 59–63 (2008). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bieneman, A.P., Chichester, K.L., Chen, Y.H. & Schroeder,
J.T. Toll-like receptor 2 ligands activate human basophils for both IgE-dependent and IgE-independent secretion. _J. Allergy Clin. Immunol._ 115, 295–301 (2005). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Phillips, C., Coward, W.R., Pritchard, D.I. & Hewitt, C.R.A. Basophils express a type 2 cytokine profile on exposure to proteases from helminths and house dust mites. _J.
Leukoc. Biol._ 73, 165–171 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Koga, T. et al. Costimulatory signals mediated by the ITAM motif cooperate with RANKL for bone homeostasis.
_Nature_ 428, 758–763 (2004). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Shi, Y. et al. Protein-tyrosine kinase Syk is required for pathogen engulfment in complement-mediated phagocytosis.
_Blood_ 107, 4554–4562 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tian, X., Takamoto, M. & Sugane, K. Bisphenol A promotes IL-4 production by Th2 cells. _Int. Arch. Allergy
Immunol._ 132, 240–247 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank S. Akira (Osaka University) for _Stat6__−/−_ mice; W.R. Heath (Walter and
Eliza Hall Institute) for OT-II TCR-Tg mice; T. Kitamura (University of Tokyo) for the original pMX-IRES-GFP retroviral vector; and K. Takatsu (University of Toyama) for the Y16 cell line;
and acknowledge the late N. Azuta for technical assistance. Supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan and the Japan Society for the Promotion
of Science (Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research 17047016, 18060016 to S.T. and 19591162 to S.H.). AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Immunology and Infectious
Diseases, Shinshu University Graduate School of Medicine, Matsumoto, 390-8621, Japan Shigeaki Hida, Yuzuru Sakamoto, Masaya Takamoto, Kazuo Sugane & Shinsuke Taki * Laboratory for Cell
Signaling, RIKEN Research Center for Allergy and Immunology, Yokohama, 230-0045, Japan Sho Yamasaki & Takashi Saito * Department of Immune Regulation, Tokyo Medical and Dental University
Graduate School, Tokyo, 113-8519, Japan Kazushige Obata & Hajime Karasuyama * Department of Experimental Immunology, Institute of Development, Aging and Cancer, Tohoku University,
Sendai, 980-8575, Japan Toshiyuki Takai Authors * Shigeaki Hida View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sho Yamasaki View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Yuzuru Sakamoto View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Masaya Takamoto View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Kazushige Obata View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Toshiyuki Takai View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Hajime Karasuyama View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * Kazuo Sugane View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Takashi Saito View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * Shinsuke Taki View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS S.H. designed and did experiments and wrote
the manuscript; S.Y. helped with vector construction and provided critical reagents; Y.S. did experiments; K.O., H.K., T.T. and T.S. provided critical reagents; M.T. and K.S. did the _T.
spiralis_ infection experiments; and S.T. designed and supervised research and wrote the manuscript. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Shinsuke Taki. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT AND FIGURES Supplementary Figures 1–12 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 2001 kb) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Hida,
S., Yamasaki, S., Sakamoto, Y. _et al._ Fc receptor γ-chain, a constitutive component of the IL-3 receptor, is required for IL-3-induced IL-4 production in basophils. _Nat Immunol_ 10,
214–222 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1686 Download citation * Received: 17 June 2008 * Accepted: 31 October 2008 * Published: 21 December 2008 * Issue Date: February 2009 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1686 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently
available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative