Play all audios:
Molecular detection using near-infrared light between 0.9 and 1.3 eV has important biomedical applications because of greater tissue penetration and reduced auto-fluorescent background in
thick tissue or whole-blood media. Carbon nanotubes have a tunable near-infrared emission that responds to changes in the local dielectric function but remains stable to permanent
photobleaching. In this work, we report the synthesis and successful testing of solution-phase, near-infrared sensors, with β-D-glucose sensing as a model system, using single-walled carbon
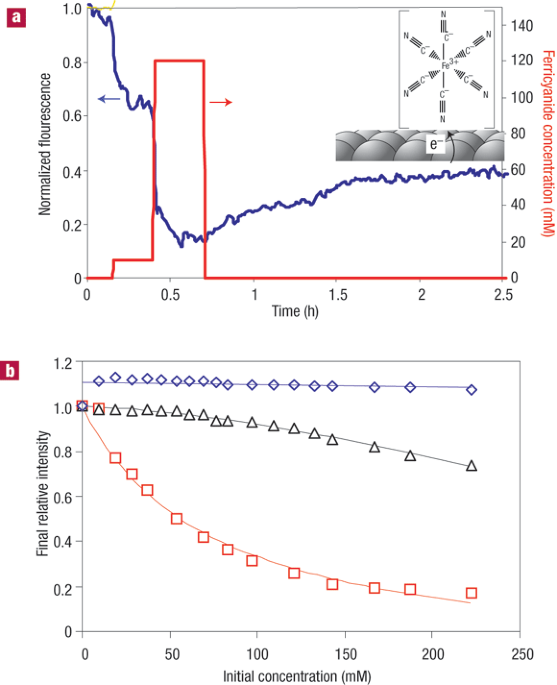
nanotubes that modulate their emission in response to the adsorption of specific biomolecules. New types of non-covalent functionalization using electron-withdrawing molecules are shown to
provide sites for transferring electrons in and out of the nanotube. We also show two distinct mechanisms of signal transduction—fluorescence quenching and charge transfer. The results
demonstrate new opportunities for nanoparticle optical sensors that operate in strongly absorbing media of relevance to medicine or biology.
The authors are grateful for funding from the National Science Foundation (grant no. CTS-0330350), the School of Chemical Sciences at UIUC, and a grant from the Molecular Electronics group,
Dupont Co. The authors thank J. Bahr for providing the blood specimen.
Paul W. Barone and Seunghyun Baik: These authors contributed equally
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Illinois-Urbana/Champaign, 600 S. Mathews Avenue, Urbana, 61801, Illinois, USA
Department of Chemistry, University of Illinois-Urbana/Champaign, 505 S. Mathews Avenue, Urbana, 61801, Illinois, USA
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: