Play all audios:
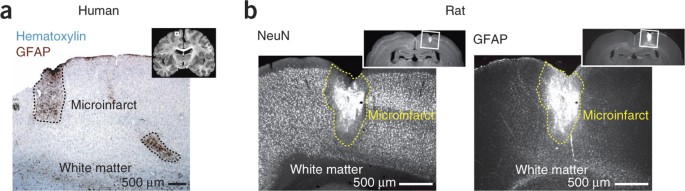
ABSTRACT Microinfarctions are present in the aged and injured human brain. Their clinical relevance is controversial, with postulated sequelae ranging from cognitive sparing to vascular
dementia. To address the consequences of microinfarcts, we used controlled optical methods to create occlusions of individual penetrating arterioles or venules in rat cortex. Single
microinfarcts, targeted to encompass all or part of a cortical column, impaired performance in a macrovibrissa-based behavioral task. Furthermore, the targeting of multiple vessels resulted
in tissue damage that coalesced across cortex, even though the intervening penetrating vessels were acutely patent. Post-occlusion administration of memantine, a glutamate receptor
antagonist that reduces cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease, ameliorated tissue damage and perceptual deficits. Collectively, these data imply that microinfarcts likely contribute
to cognitive decline. Strategies that have received limited success in the treatment of ischemic injury, which include therapeutics against excitotoxicity, may be successful against the
progressive nature of vascular dementia. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through
your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant
access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions *
Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS NEUROVASCULAR COUPLING AND OXYGENATION ARE DECREASED IN HIPPOCAMPUS COMPARED TO NEOCORTEX BECAUSE OF
MICROVASCULAR DIFFERENCES Article Open access 27 May 2021 WHITE MATTER DAMAGE AS A CONSEQUENCE OF VASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN A SPONTANEOUS MOUSE MODEL OF CHRONIC MILD CHRONIC HYPOPERFUSION WITH
ENOS DEFICIENCY Article Open access 10 August 2022 LONGITUDINAL HIPPOCAMPAL VOLUMETRIC CHANGES IN MICE FOLLOWING BRAIN INFARCTION Article Open access 13 May 2021 REFERENCES * Gorelick, P.B.
et al. Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. _Stroke_ 42,
2672–2713 (2011). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Brundel, M., de Bresser, J., van Dillen, J.J., Kappelle, L.J. & Biessels, G.J. Cerebral microinfarcts: a systematic
review of neuropathological studies. _J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab._ 32, 425–436 (2012). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Smith, E.E., Schneider, J.A., Wardlaw, J.M. &
Greenberg, S.M. Cerebral microinfarcts: the invisible lesions. _Lancet Neurol._ 11, 272–282 (2012). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Vinters, H.V. et al. Neuropathologic
substrates of ischemic vascular dementia. _J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol._ 59, 931–945 (2000). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kövari, E. et al. Cortical microinfarcts and
demyelination affect cognition in cases at high risk for dementia. _Neurology_ 68, 927–931 (2007). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Arvanitakis, Z., Leurgans, S.E., Barnes, L.L., Bennett,
D.A. & Schneider, J.A. Microinfarct pathology, dementia and cognitive systems. _Stroke_ 42, 722–727 (2011). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Jouvent, E. et al.
Intracortical infarcts in small vessel disease: a combined 7-T postmortem MRI and neuropathological case study in cerebral autosomal-dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and
leukoencephalopthy. _Stroke_ 42, 27–30 (2011). Article Google Scholar * Blinder, P., Shih, A.Y., Rafie, C.A. & Kleinfeld, D. Topological basis for the robust distribution of blood to
rodent neocortex. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 107, 12670–12675 (2010). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Lauwers, F., Cassot, F., Lauwers-Cances, V., Puwanarajah, P.
& Duvernoy, H. Morphometry of the human cerebral cortex microcirculation: general characteristics and space-related profiles. _Neuroimage_ 39, 936–948 (2008). Article PubMed Google
Scholar * Bär, T. The vascular system of the cerebral cortex. _Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol._ 59, 1–62 (1980). Article Google Scholar * Nishimura, N., Schaffer, C.B., Friedman, B.,
Lyden, P.D. & Kleinfeld, D. Penetrating arterioles are a bottleneck in the perfusion of neocortex. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 104, 365–370 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
* Nguyen, J., Nishimura, N., Fetcho, R.N., Iadecola, C. & Schaffer, C.B. Occlusion of cortical ascending venules causes blood flow decreases, reversals in flow direction, and vessel
dilation in upstream capillaries. _J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab._ 31, 2243–2254 (2011). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Drew, P.J. et al. Chronic optical access through a
polished and reinforced thinned skull. _Nat. Methods_ 7, 981–984 (2010). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Sofroniew, M.V. & Vinters, H.V. Astrocytes: biology and
pathology. _Acta Neuropathol._ 119, 7–35 (2010). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Tsai, P.S. et al. Correlations of neuronal and microvascular densities in murine cortex revealed by direct
counting and colocalization of cell nuclei and microvessels. _J. Neurosci._ 29, 14553–14570 (2009). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Weber, B., Keller, A.L.,
Reichold, J. & Logothetis, N.K. The microvascular system of the striate and extrastriate visual cortex of the macaque. _Cereb. Cortex_ 18, 2318–2330 (2008). Article PubMed Google
Scholar * Svoboda, K., Denk, W., Kleinfeld, D. & Tank, D.W. _In vivo_ dendritic calcium dynamics in neocortical pyramidal neurons. _Nature_ 385, 161–165 (1997). Article CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Kleinfeld, D., Mitra, P.P., Helmchen, F. & Denk, W. Fluctuations and stimulus-induced changes in blood flow observed in individual capillaries in layers 2 through 4 of
rat neocortex. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 95, 15741–15746 (1998). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Shih, A.Y. et al. Active dilation of penetrating arterioles
restores red blood cell flux to penumbral neocortex after focal stroke. _J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab._ 29, 738–751 (2009). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Shih, A.Y. et al. Two-photon
microscopy as a tool to study blood flow and neurovascular coupling in the rodent brain. _J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab._ 32, 1277–1309 (2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Schaffer, C.B. et al. Two-photon imaging of cortical surface microvessels reveals a robust redistribution in blood flow after vascular occlusion. _PLoS Biol._ 4, e22 (2006).
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar * Nishimura, N. et al. Targeted insult to individual subsurface cortical blood vessels using ultrashort laser pulses: three models of
stroke. _Nat. Methods_ 3, 99–108 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Stosiek, C., Garaschuk, O., Holthoff, K. & Konnerth, A. _In vivo_ two-photon calcium imaging of neuronal
networks. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 100, 7319–7324 (2003). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chen, B. et al. Severe blood brain barrier disruption and surrounding
tissue injury. _Stroke_ 40, 666–674 (2009). CAS Google Scholar * Calabrese, V., Mancuso, C., Calvani, M., Rizzarelli, E. & Butterfield, D.A. Nitric oxide in the central nervous system:
neuroprotection versus neurotoxicity. _Nat. Rev. Neurosci._ 8, 766–775 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Friedman, B. et al. Acute vascular disruption and Aquaporin 4 loss
after stroke. _Stroke_ 40, 2182–2190 (2009). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Unal Cevik, I. & Dalkara, T. Intravenously administered propidium iodide labels necrotic
cells in the intact mouse brain after injury. _Cell Death Differ._ 10, 928–929 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Soontornniyomkij, V. et al. Cerebral microinfarcts associated
with severe cerebral beta-amyloid angiopathy. _Brain Pathol._ 20, 459–467 (2010). Article PubMed Google Scholar * Siesjô, B.K. & Bengtsson, F. Calcium fluxes, calcium antagonists and
calcium-related pathology in brain ischemia, hypoglycemia, and spreading depression: a unifying hypothesis. _J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab._ 9, 127–140 (1989). Article PubMed Google Scholar
* Murphy, T.H., Li, P., Betts, K. & Liu, R. Two-photon imaging of stroke onset _in vivo_ reveals that NMDA receptor–independent ischemic depolarization is the major cause of rapid
reversible damage to dendrites and spines. _J. Neurosci._ 28, 1756–1772 (2008). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Orgogozo, J.M., Rigaud, A.S., Stoffler, A., Mobius,
H.J. & Forette, F. Efficacy and safety of Memantine in patients with mild to moderate vascular dementia. _Stroke_ 33, 1834–1839 (2002). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Olivares,
D. et al. N-Methyl D-Aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists and memantine treatment for Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia and Parkinson's disease. _Curr. Alzheimer Res._ 9,
746–758 (2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Woolsey, T.A. & Van Der Loos, H. The structural organization of layer IV in the somatosensory region (SI) of mouse
cerebral cortex. _Brain Res._ 17, 205–242 (1970). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kleinfeld, D. & Deschênes, M. Neuronal basis for object location in the vibrissa scanning
sensorimotor system. _Neuron_ 72, 455–468 (2011). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hutson, K.A. & Masterton, R.B. The sensory contribution of a single
vibrissa's cortical barrel. _J. Neurophysiol._ 56, 1196–1223 (1986). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Masino, S.A., Kwon, M.C., Dory, Y. & Frostig., R.D. Characterization of
functional organization within rat barrel cortex using intrinsic signal optical imaging through a thinned skull. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 90, 9998–10002 (1993). Article CAS PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Armstrong-James, M., Fox, K. & Das-Gupta, A. Flow of excitability within barrel cortex on striking a single vibrissa. _J. Neurophysiol._ 68, 1345–1358
(1992). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lashley, K.S. Mass action in cerebral function. _Science_ 73, 245–254 (1931). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Reisberg, B. et al.
Memantine in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 348, 1333–1341 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wilcock, G.K. Memantine for the treatment of
dementia. _Lancet Neurol._ 2, 503–505 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Woolsey, T.A. et al. Neuronal units linked to microvascular modules in cerebral cortex: response
elements for imaging the brain. _Cereb. Cortex_ 6, 647–660 (1996). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cassot, F. et al. Branching patterns for arterioles and venules of the human
cerebral cortex. _Brain Res._ 1313, 62–78 (2010). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Villringer, A., Mehraein, S. & Einhäupl, K.M. Pathophysiological aspects of cerebral sinus
venous thrombosis (SVT). _J. Neuroradiol._ 21, 72–80 (1994). CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Brown, W.R. & Thore, C.R. Cerebral microvascular pathology in aging and neurodegeneration.
_Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol._ 37, 56–74 (2011). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhang, S. & Murphy, T.H. Imaging the impact of cortical microcirculation on
synaptic structure and sensory-evoked hemodynamic responses _in vivo_. _PLoS Biol._ 5, e119 (2007). Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar * Troncoso, E. et al. Recovery of
evoked potentials, metabolic activity and behavior in a mouse model of somatosensory cortex lesion: role of the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM). _Cereb. Cortex_ 14, 332–341 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Carmichael, S.T. Plasticity of cortical projections after stroke. _Neuroscienist_ 9, 64–75 (2003). Article Google Scholar * Mohajerani, M.H.,
Aminoltejari, K. & Murphy, T.H. Targeted mini-strokes produce changes in interhemispheric sensory signal processing that are indicative of disinhibition within minutes. _Proc. Natl.
Acad. Sci. USA_ 108, E183–E191 (2011). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Rosidi, N.L. et al. Cortical microhemorrhages cause local inflammation but do not trigger widespread
dendrite degeneration. _PLoS ONE_ 6, e26612 (2011). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Nishimura, N., Rosidi, N.L., Iadecola, C. & Schaffer, C.B. Limitations of
collateral flow after occlusion of a single cortical penetrating arteriole. _J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab._ 30, 1914–1927 (2010). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Frostig,
R.D., Lieke, E.E., Ts'o, D.Y. & Grinvald, A. Cortical functional architecture and local coupling between neuronal activity and the microcirculation revealed by _in vivo_
high-resolution optical imaging of intrinsic signals. _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_ 87, 6082–6086 (1990). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Kleinfeld, D. & Delaney,
K.R. Distributed representation of vibrissa movement in the upper layers of somatosensory cortex revealed with voltage sensitive dyes. _J. Comp. Neurol._ 375, 89–108 (1996). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Tsai, P.S. & Kleinfeld, D. _In vivo_ two-photon laser scanning microscopy with concurrent plasma-mediated ablation: principles and hardware realization. in
_Methods for In Vivo Optical Imaging 2nd edn._ (ed. Frostig, R.D.) 59–115 (CRC Press, 2009). * Valmianski, I. et al. Automatic identification of fluorescently labeled brain cells for rapid
functional imaging. _J. Neurophysiol._ 104, 1803–1811 (2010). Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Driscoll, J.D., Shih, A.Y., Drew, P.J., Cauwenberghs, G. & Kleinfeld, D.
Two-photon imaging of blood flow in cortex. in _Imaging in Neuroscience: A Laboratory Manual_ (eds. Helmchen, F., Konnerth, A. & Yuste, R.) 927–938 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press,
New York, 2011). * Shih, A.Y. et al. Optically induced occlusion of single blood vessels in neocortex. in _Imaging in Neuroscience: A Laboratory Manual_ (eds. Helmchen, F., Konnerth, A.
& Yuste, R.) 939–948 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 2011). * Nguyen, Q.-T., Dolnick, E.M., Driscoll, J. & Kleinfeld, D. MPScope 2.0: A computer system for two-photon
laser scanning microscopy with concurrent plasma-mediated ablation and electrophysiology. in _Methods for In Vivo Optical Imaging 2nd edn._ (ed. Frostig, R.D.) 117–142 (CRC Press, 2009). *
Nimmerjahn, A., Kirchhoff, F., Kerr, J.N. & Helmchen, F. Sulforhodamine 101 as a specific marker of astroglia in the neocortex _in vivo_. _Nat. Methods_ 1, 31–37 (2004). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Mehta, S.B., Whitmer, D., Figueroa, R., Williams, B.A. & Kleinfeld, D. Active spatial perception in the vibrissa scanning sensorimotor system. _PLoS Biol._ 5,
309–322 (2007). Article CAS Google Scholar * Paxinos, G. & Watson, C. _The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates_ (Academic Press, San Diego, 1986). Download references
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank A. Schweitzer for constructing the behavioral apparatus, S.E. Black, M. Deschênes, M.E. Diamond, F.F. Ebner, E.E. Smith and R. Swanson for discussions, and C. Mateo
for comments on an early version of the manuscript. This work was supported by the American Heart Association (Post-doctoral fellowship to A.Y.S.) and the US National Institutes of Health
(MH085499, EB003832 and OD006831 to D.K.), which further supported the University of California, San Diego Neuroscience Shared Microscopy Core (NS047101), which was used to image
histological tissue. AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * Andy Y Shih & Pablo Blinder Present address: Present addresses: Department of Neurosciences, Medical University of South Carolina,
Charleston, South Carolina, USA (A.Y.S.), Department of Neuroscience, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel (P.B.)., AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Physics, University of
California at San Diego, La Jolla, California, USA Andy Y Shih, Pablo Blinder, Philbert S Tsai, Geoffrey Stanley & David Kleinfeld * Department of Pharmacology, University of California
at San Diego, La Jolla, California, USA Beth Friedman * Department of Neurology, Cedars-Sinai Hospital, Los Angeles, California, USA Patrick D Lyden * Section of Neurobiology, University of
California at San Diego, La Jolla, California, USA David Kleinfeld Authors * Andy Y Shih View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Pablo Blinder
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Philbert S Tsai View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Beth Friedman View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Geoffrey Stanley View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * Patrick D Lyden View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * David Kleinfeld View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS A.Y.S., B.F., P.D.L. and D.K. designed the study. A.Y.S. and G.S. carried out the experiments. A.Y.S., P.B. and P.S.T. analyzed the data. A.Y.S.,
B.F. and D.K. wrote the manuscript. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to David Kleinfeld. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT AND FIGURES Supplementary Figures 1–8 and Tables 1–3 (PDF 22592 kb) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS
ARTICLE Shih, A., Blinder, P., Tsai, P. _et al._ The smallest stroke: occlusion of one penetrating vessel leads to infarction and a cognitive deficit. _Nat Neurosci_ 16, 55–63 (2013).
https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3278 Download citation * Received: 01 October 2012 * Accepted: 15 November 2012 * Published: 16 December 2012 * Issue Date: January 2013 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3278 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently
available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative