Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Transcription factors (TFs) coordinate the on-and-off states of gene expression typically in a combinatorial fashion. Studies from embryonic stem cells and other cell types have
revealed that a clique of self-regulated core TFs control cell identity and cell state. These core TFs form interconnected feed-forward transcriptional loops to establish and reinforce the
cell-type-specific gene-expression program; the ensemble of core TFs and their regulatory loops constitutes core transcriptional regulatory circuitry (CRC). Here, we summarize recent
progress in computational reconstitution and biologic exploration of CRCs across various human malignancies, and consolidate the strategy and methodology for CRC discovery. We also discuss
the genetic basis and therapeutic vulnerability of CRC, and highlight new frontiers and future efforts for the study of CRC in cancer. Knowledge of CRC in cancer is fundamental to
understanding cancer-specific transcriptional addiction, and should provide important insight to both pathobiology and therapeutics. SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS TARGETING
TRANSCRIPTION CYCLES IN CANCER Article 21 October 2021 TRANSCRIPTIONAL CO-ACTIVATORS: EMERGING ROLES IN SIGNALING PATHWAYS AND POTENTIAL THERAPEUTIC TARGETS FOR DISEASES Article Open access
13 November 2023 INFERENCE OF PHENOTYPE-RELEVANT TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATORY NETWORKS ELUCIDATES CANCER TYPE-SPECIFIC REGULATORY MECHANISMS IN A PAN-CANCER STUDY Article Open access 08
February 2021 INTRODUCTION Transcriptional regulation is one of the fundamental molecular processes occurring in a cell. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins, also known as transcription
factors (TFs), orchestrate gene-expression patterns in various cell types and growth conditions [1]. Although thousands of TFs have been identified, only a limited cohort of master TFs
controls the core transcriptional programs governing cell identity [2,3,4]. Master TFs are highly expressed in a given cell type. Master TFs bind to the majority of cell-type-specific
enhancers and dictate expression of cell-type-specific genes. Till now, one critical goal in biology remains to understand the composition and hierarchy of transcriptional regulatory network
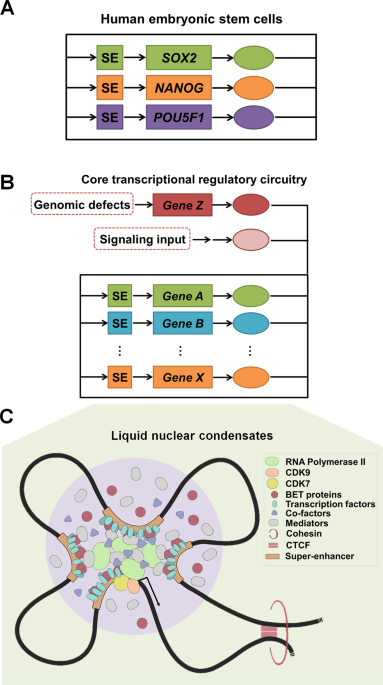
in each specified cell type/lineage. One of the best-studied models is embryonic stem cells (ESCs). In ESCs, three master TFs (pluripotency factors) NANOG, POU5F1/OCT4 and SOX2 form
interconnected feed-forward transcriptional loops to maintain gene-expression program associated with ESC identity (Fig. 1a) [5, 6]. Such a pluripotent transcriptional regulatory network
nurtured the model/concept of core transcriptional regulatory circuitry (CRC) in ESCs [7]. Apart from core TFs, additional layers of core regulators have been discovered and integrated into
the pluripotent transcription circuitry including external signaling pathways [8], chromatin/histone modifiers (Polycomb group proteins [9], histone acetyltransferase MOF [10], and WDR5
[11]), basal transcription machinery TF IID complex [12], histone modifications (H3K56ac [13]), noncoding RNAs (microRNAs [14] and lncRNAs [15]), and transposable elements [16]. Insights
from ESC-associated CRC have guided subsequent exploration of similar core feed-forward transcriptional networks during lineage specification, development, and tumorigenesis
[17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. These studies suggest widespread existence and critical function of CRCs in both physiological and pathological conditions. This review mainly focuses on the progress
of CRC studies in human cancers, diseases of uncontrolled cell growth. We have learned from genomic sequencing projects that cancer is driven by genetic alterations [24]. Oncogenic genetic
abnormalities invariably reprogram transcriptome in order to establish and maintain cancerous identity/state [25]. As featured by defective terminal differentiation, cancer cells are often
locked into a growth state resembling either stem/progenitor cells or cells in a certain developmental stage. A growing body of evidence shows that dysregulated transcriptional programs in
cancers are dominated by a clique of interconnected master TFs [21, 26,27,28,29,30]. These master regulators form feed-forward autoregulatory loops, and function in a combinatorial way to
enhance expression of cancer-promoting genes. Aberrations in cancer genome, signaling transduction, and epigenetic regulation (e.g., super enhancer (SE)) activate cancer-specific expression
of master TFs, which frequently hijack lineage-specific TFs, pioneer factors, epigenetic readers, mediators, and chromatin-regulating machineries to reshape epigenome [4, 21, 29,
31,32,33,34,35]. Cancer-specific activation of core TFs and subsequent rewiring of lineage-associated CRC components establish the genetic basis of oncogenic CRCs (Fig. 1b). Phase-separated
condensation of core TFs, BRD4, mediators, and RNA polymerase II emerges as a biophysical mechanism to ensure high local availability of chromatin regulators, and transcription machineries
for productive oncogenic transcription (Fig. 1c) [36,37,38]. Elucidating the core transcriptional regulatory programs will provide better understanding of molecular carcinogenesis.
Lineage-specific components in CRC can inform on both cell-of-origin in cancer and selective oncogenic dependencies. Moreover, disruption of CRC in cancer cells by either genetic approach or
pharmacological inhibition greatly impairs their malignant characteristics and tumorigenicity. Thus, CRC represents a mechanism of oncogenic addiction and a potential target for novel
therapeutic interventions in cancer. Here, we summarize recent efforts to identify, characterize, and target CRCs across various human cancers, and highlight key insights that have emerged
from these seminal studies. STRATEGY AND METHODOLOGY FOR CRC IDENTIFICATION Inspired from ESC studies, self-regulation and interconnection are two important mechanisms to stabilize TF
network. Key features of CRC include (1) self-regulated expression of each core TF, (2) direct regulation among core factors, and (3) feed-forward transcriptional control. Hence,
identification of CRC is highly dependent on mapping of TF binding sites and biological verification of cross regulation. Genomic occupancy analysis of candidate core TFs enables systematic
annotation of their direct targets. Indeed, initial modeling of CRCs in ESCs [5], hepatocytes [18], and T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) [21] was based on genome-wide discovery of
TF-DNA interactions via chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) followed by either microarray hybridization or high-throughput sequencing (ChIP-seq). Typically, core TFs occupy their own
promoters/enhancers. Meanwhile, core TFs often bind in close proximity to cis-regulatory elements of their target genes, producing a “co-occupancy” pattern of genomic binding. Potential
biochemical mechanism of this “co-occupancy” pattern is associated with either direct protein–protein interactions (e.g., SOX2-OCT4 heterodimer) or co-existence of core TFs within
multi-subunit protein complexes. The mutual co-occupancy of core TFs within their own cis-regulatory elements constitutes an interconnected autoregulatory loop, while co-loading of TFs
across the vast majority of downstream target genes implicates their substantial co-operation in gene regulation. To ensure feed-forward regulation within CRC, core TFs commonly bind to
cis-regulatory elements and open chromatin regions, including promoters, enhancers, DNase I hypersensitive sites, and SEs [4]. Since TF motifs are overrepresented in genomic regions occupied
by respective TFs, systematic identification of TF motifs across the cis-regulatory elements of a given sample will provide raw materials to reconstruct a regulatory network. SEs have been
characterized as constituent enhancers, which are bound densely by multiple TFs [4, 31]. Since SEs are frequently engaged in expression of lineage-specific and/or disease-promoting genes
including core TFs, SE-driven TFs serve as promising candidates for core TFs in CRC. Based on the principles of “self-regulation” and “interconnection,” several computational programs have
been developed to wire potential regulatory nodes and to model CRC. Saint-André et al. [23] developed a “CRC Mapper” program to reconstruct human CRC models of SE-associated TFs (Fig. 2a).
This approach utilized FIMO software [39] package from the MEME suite [40] to scan TF motifs inside SE regions (with 500-bp extension of each SE boundary), and then retrieved both
auto-regulated TFs and all possible fully interconnected regulatory circuitries. Top-scoring circuitry of which TFs exhibited the highest frequency of occurrence across all predicted
circuitries was designated as CRC in a given sample. “CRC Mapper” has demonstrated excellent performance to recapitulate experimentally verified CRCs in ESCs and T-ALL. So far, this program
has been implemented to build CRC models in a large variety of samples [19, 41, 42]. Remarkably, dbCoRC (http://dbcorc.cam-su.org), a comprehensive online database of “CRC Mapper”-inferred
circuitries in over 230 human/murine samples has been developed and is freely accessible, representing a valuable resource to explore transcriptional regulatory networks [41]. Using similar
principles of motif-based TF connectivity for network construction, Lin et al. [26] developed a “Coltron” python package (https://pypi.org/project/coltron), which quantified degree of inward
(IN) and outward (OUT) regulation of SE-regulated TFs (NODEs) across putative nucleosome-free regions (NFRs) of their constituent enhancers. Based on motif analysis, IN-degree for a given
SE-regulated TF (NODE) was defined as the number of SE-regulated TFs bound to its proximal/assigned SE; OUT-degree was calculated as the number of TF-associated SEs bound by a given
SE-regulated TF. Total degree (IN + OUT) of each NODE can be applied to rank the connectivity of TFs. CRC was defined as the top-ranked autoregulatory TF network (CLIQUE), which showed
highest average enrichment of core TFs among all CLIQUEs [27]. The capability of “Coltron” to predict motif-based TF binding is enhanced, as it scans TF motifs inside NFRs instead of whole
SE domain (Fig. 2b) [43]. Further, either incorporation of experimentally derived TF footprints data (DNase I hypersensitive sites) or accessible regions from ATAC-seq (Assay for
Transposase-Accessible Chromatin using sequencing) can improve the prediction of TF binding sites [2, 27, 44,45,46]. In addition to genomic occupancy and TF connectivity, regulatory readout
of core TFs and their functional impact on cell behaviors are other fundamental aspects for CRC. Since core TFs with feed-forward transcriptional regulation often show positively correlated
expression, co-expression analysis of TFs among cancer type/subtype of interest can be employed to shortlist candidate core TFs. Furthermore, genetic manipulation assays represent the “gold
standard” to validate both regulatory circuitry among core TFs and functional importance of TFs in maintaining cell identity. Depletion of individual core TFs will reduce expression of other
members within CRC, and subsequently impair cellular phenotypes (e.g., proliferation and differentiation). Systematic analysis of putative downstream targets will also help to identify
important mediators/executors in regulating cell identity. EXPERIMENTALLY VERIFIED CRCS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS IN CANCER PATHOBIOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS To gain insight into the roles of CRCs
in human cancers, we next summarize current knowledge of biologically verified CRCs in human cancers. T-CELL ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA (T-ALL) T-ALL is a disease with cancerous
proliferation of immature thymocytes. Genetic lesions affecting an oncogenic TF TAL1/SCL are frequently observed in human T-ALL cells [47]. Either chromosomal translocation involving T-cell
receptor loci or intrachromosomal deletion of an 80-kb DNA fragment in 1p33 involving STIL (SIL-TAL1 deletion or TAL1d) has been shown to contribute to the overexpression of TAL1 [47]. TAL1
activation blocks T-cell differentiation, reactivates stem cell genes, and leads to malignant transformation [48]. In TAL1-positive T-ALL (e.g., Jurkat and CCRF-CEM cells), Sanda et al.
identified a positive feed-forward regulatory circuitry among TAL1, RUNX1, and GATA3 based on ChIP-seq and expressional analyses [21]. TAL1 transcriptional complex included HEB, E2A, LMO1/2,
and MYB; MYB was further established as an additional core TF to extend the aforementioned core regulatory loop in T-ALL [49] (Fig. 3a). Remarkably, Mansour et al. reported a mechanism of
monoallelic TAL1 activation involving somatic mutation of an enhancer element at 7.5-kb upstream of the transcription start site of TAL1 [49]. These mutations introduced de novo MYB binding
site to the TAL1 SE, facilitating the subsequent recruitment of MYB, histone acetyltransferase CBP, and additional components of TAL1 complex. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of TAL1 enhancer
mutation profoundly impaired both MYB binding and H3K27ac signals in this SE. Of note, TAL1, RUNX1, GATA3, and MYB bound to the respective enhancers or SE regions of each other, as well as
those of their own. They also co-occupied the regulatory elements of many downstream targets, such as the leukemogenic TRIB2, ARID5B, CDK6, and lncRNAs [50,51,52]. Among these targets,
ARID5B was further characterized as a collaborating oncogenic factor to maintain expression of core TFs and participate in the transcriptional program of T-ALL [51]. Functional studies
demonstrated that depletion of either TAL1 or other components of the circuitry not only disrupted the expression of all core TFs, but also attenuated survival of TAL1-positive T-ALL cells.
In addition, RUNX1 has been reported to be required for the growth of both TAL1-induced murine T-ALL cells and human T-ALL cells [53]. Given the prevalent alterations of TAL1 expression in
T-ALL, activation of TAL1 and subsequent establishment of T-ALL-associated CRC are likely the primary events during malignant transformation of TAL1-positive cases. Either selective
degradation of bromodomain and extra terminal (BET) proteins or targeted inhibition of kinases of RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain (e.g., CDK7 and CDK9) effectively collapsed the
core regulatory circuitries in T-ALL cells, hence exhibiting potent antineoplastic activities [54,55,56]. MEDULLOBLASTOMA Medulloblastoma is the most common type of pediatric brain tumor,
which can be classified into four molecular subtypes: WNT, SHH, Group 3, and Group 4 [57]. Lin et al. charted the active enhancer landscape of 28 primary medulloblastoma specimens based on
simultaneous profiling of DNA methylome, transcriptome, and chromatin loading of BRD4 and H3K27ac [26]. In this study, “Coltron” was developed for computational reconstruction of
subtype-specific TF regulatory networks. This analysis of SE-regulated TFs identified cliques of TFs with a high likelihood of motif co-occurrence, interconnectivity, and protein–protein
interaction. A CRC blueprint was generated for each subgroup, providing valuable insights to heterogeneous identities of medulloblastomas. WNT-subtype medulloblastomas may be driven by core
TFs including LEF1, MAF, RUNX2, and EMX2. SHH subtype potentially enrolled OTX1, BARHL2, MAFF, and GLI2 as core TFs. Group 3 tumors were initially predicted to enrich CRX, HLX, LHX2, and
OTX2, yet the top-ranked CRC model was revised to include OTX2, NRL, and CRX (Fig. 3b) after re-analysis of TF-enhancer interaction networks using an updated TF motif database (allocation of
MAF motifs to NRL motifs) [58]. In support of this, OTX2 is frequently amplified and overexpressed in this group [59, 60]. OTX2 has been shown as a pathogenic TF that shapes the chromatin
landscape of Group 3 medulloblastomas [61]. Further, OTX2 was recruited to SE regions of NRL and CRX. OTX2 expression also showed a strong positive correlation with both NRL and CRX
expression in this subtype. Meanwhile, NRL and CRX were inferred to occupy ~2/3 of all SE-associated genes in Group 3 [58]. Functionally, these two core TFs cooperated to regulate a
photoreceptor transcriptional program and expression of several oncogenes (e.g., CCND2 and BCL2L1), suggesting identity of photoreceptor lineage for Group 3 medulloblastomas. Group 4
medulloblastomas relied on the feed-forward co-expression of LMX1A, LHX2, and EOMES (Fig. 3c) [26]. Group 4-specific regulatory circuitry was partially verified by ChIP-seq analysis of LMX1A
and LHX2. Notably, Group 4 CRC also resembled an expressional pattern of progenitors in cerebellar upper rhombic lip, suggesting a potential cell-of-origin for these tumors. Collectively,
these medulloblastoma studies exemplify insightful applications of CRC reconstruction in understanding of tumor cell-of-origin and pathobiology. NEUROBLASTOMA As a cancer derived from
multipotent neural crest cells (NCCs) of the peripheral sympathetic nervous system, neuroblastoma represents one of the most common pediatric malignancies. Boeva and colleagues applied
“Coltron” to infer CRC models from SE landscapes of human neuroblastoma cell lines, patient-derived xenografts (PDXs), and primary NCC lines [28]. They reported three types of identity among
these samples. Group 1 samples comprised the majority of neuroblastoma cell lines and PDXs, and engaged SE-associated master TFs (e.g., PHOX2B, HAND2 and GATA3) to control sympathetic
adrenergic cell identity. This module of core TFs showed strong co-expression and constituted a conserved CRC in both group 1 neuroblastoma cell lines and PDXs. In addition to the physical
interaction between PHOX2B and GATA3, all three TFs co-localized in the regulatory sequences of their own loci, as well as many other prominent driver genes including MYCN and ALK. Group 2
samples resembled the SE pattern of NCCs, which were driven by a CRC module containing AP-1 TFs, e.g., FOSL1 and FOSL2. The third group of neuroblastomas was characterized by a mixture of
both Groups 1 and 2 modules; indeed, most primary neuroblastoma specimens exhibited mixed expression of TFs of both modules. In line with the observation that most MYCN-amplified
neuroblastoma cells enriched the adrenergic TF module, functional genomics studies with CRISPR-Cas9 screen identified MYCN, PHOX2B, HAND2, GATA3, and additional SE-regulated TFs including
ISL1 and TBX2 as key dependency genes showing selective requirement for proliferation and survival of MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma cells [32]. Compound depletion of MYCN and TBX2 exerted a
greater deleterious impact on both cell growth and downstream FOXM1/E2F network [62]. Notably, MYCN, PHOX2B, HAND2, GATA3, ISL1, and TBX2 demonstrated clustered binding across open chromatin
regions (as “epicenters”) of their own genes and interdependent expression. ASCL1 and an auxiliary adapter protein (LMO1) further expanded this adrenergic transcriptional regulatory
circuitry by co-binding to target regions (Fig. 3d) [63]. Both ASCL1 and LMO1 maintained proliferative potential of neuroblastoma cells. ASCL1 overexpression also suppressed pathways
involved in the development of sympathetic nervous system and noradrenergic lineage commitment. Remarkably, MYCN and TBX2 are frequently targeted by somatic genomic alterations in high-risk
neuroblastoma samples. Genomic amplification of MYCN rendered its function as an exceptional CRC member whose overexpression surpassed the regulatory impact from many other core TFs [32]. In
contrast, in case of cells with single copy of MYCN (e.g., CLB-GA), MYCN expression was dependent on TBX2 [62]. Segmental gains and rare focal amplification of chromosome 17q coincided with
elevated expression of TBX2 [62]. Germline single nucleotide polymorphism (rs2168101 G>T) within intron 1 of LMO1 has also been associated with predisposition to neuroblastoma [64]. This
risk allele increased LMO1 expression by creating a GATA3 binding site within its SE element. Hence, both somatic and germline genomic changes contribute to neuroblastoma development via
aberrant activation of adrenergic transcriptional regulatory module. Several attempts to disrupt the adrenergic transcriptional regulatory circuitry in neuroblastoma have been made,
including combined treatment of CDK7 inhibitor (THZ1) with either BET protein inhibitor (JQ1) or HDAC inhibitor (Panobinostat) [32, 62]. Combination of THZ1 and JQ1 demonstrated synergistic
repressive effects on both cell viability and CRC gene expression. Since plasticity of CRCs in neuroblastomas has been observed during chemotherapeutic treatment [28], incorporation of
CRC-disrupting agents into current therapeutic scheme may provide additional benefit to neuroblastoma patients. RHABDOMYOSARCOMA (RMS) RMS is an aggressive soft-tissue cancer that arises
from skeletal muscle precursors. Fusion-positive rhabdomyosarcoma (FP-RMS) is defined by translocations involving chimeric TFs either PAX3-FOXO1 (P3F) or PAX7-FOXO1 [65]. Amplification of
MYCN is also frequently detected in FP-RMS [66]. Four core TF modules have been identified in RMS samples: (1) a normal- and tissue-specific module including NR4A1 and MEF2D; (2) a
RMS-general module including MYOD1 and MYOG; (3) a fusion-negative (FN)-RMS module including PAX7 and AP-1 members; and (4) a FP-RMS-specific module including MYCN and the oncofusion TFs
[34]. In FN-RMS with RAS mutations, aberrant MAPK activity enhanced cell proliferation, whereas blocked myogenic differentiation [35]. Targeted inhibition of RAS pathway with MEK inhibitor
(trametinib) rewired substantially the core TF connectivity (modeled by “Coltron”) via MYOG-dependent chromatin remodeling and SE formation at genes required for late myogenic
differentiation [35]. Although more biological verification is required to support the subtype-specific CRC in FN-RMS, this study implicates a mechanism that signaling driver mutations
integrate with core TF circuitry to promote cancer development. By far, FP-RMS represents an insightful example of CRC driven by oncogenic fusion TF. Gryder et al. found that P3F reprogramed
the cis-regulatory landscape of RMS and established a myogenic SE circuitry together with additional master TFs (MYOG, MYOD, and MYCN) [29]. HiChIP analysis of H3K27ac verified the
interactions between core TF genes and their SEs [34]. These core TFs were overexpressed in FP-RMS compared to normal tissues, and collaborated on a myogenic transcriptional program.
Ablation of MYOG, MYOD, or MYCN attenuated the expression of all core TFs, while silencing of P3F reduced MYOD and MYCN, but not MYOG. In addition, P3F, MYOG, and MYOD enhanced expression of
SOX8, which was a marker for muscle satellite cells and a repressor of transcriptional program associated with differentiation from myoblasts to myotubes [34]. SOX8 also co-localized with
other core TFs across the majority of SEs, coordinating the transcriptional chromatin topologies in FP-RMS [67]. The SEs controlling P3F (at FOXO1 locus), MYOD, MYCN, and SOX8 were
co-occupied by all core TFs (Fig. 3e). However, MYOG SE was bound by all core TFs except P3F, which was thought to be consistent with the sequential activation of TFs during normal
myogenesis. Disruption of SOX8 paradoxically elevated expression of P3F, MYOD1, and MYOG, indicative of a potential negative feedback to block terminal differentiation in FP-RMS. Hence, SOX8
is more likely a co-regulatory TF, which acts as a downstream target of CRC and provides either positive or negative feedback to distinct subsets of core TFs. Importantly, functional
screening of SE-associated TFs using a DNA-binding domain-focused CRISPR knockout library affirmed the oncogenic dependency of FP-RMS on SOX8 and the rest of core TFs [34]. Together, P3F and
MYCN calibrate the balance between myogenic and anti-myogenic core oncogenic TF circuitries to maintain dedifferentiated state of FP-RMS cells. Biochemical studies revealed that P3F
functioned as a pioneering factor to open chromatin, and subsequently recruited mediator proteins/co-activators (e.g., MED1, p300, BRD4) to enable enhancer looping and transcriptional
activation [29]. Functional interplay between P3F and BRD4 yielded a significant susceptibility of FP-RMS cells to BRD inhibition by JQ1. JQ1 destabilized P3F protein and demonstrated a
remarkable, selective suppression of P3F targets including core TFs and SE-driven kinases (e.g., ALK). Interestingly, both p300 and HDAC showed extensive co-occupancy with P3F, core TFs and
BRD4 across the “epicenters” within SE regions [34, 67]. A JQ1-like SE selectivity was recapitulated by small molecules targeting histone-acetylation writers (p300/CBP) and erasers
(HDAC1/2/3), but not general transcriptional modulators (e.g., triptolide, α-Amanitin, and flavopiridol). Triple inhibition of HDAC1/2/3 with either Entinostat or combination of a HDAC1/2
inhibitor Merck60 and a HDAC3 inhibitor LW3 disrupted profoundly the expression of core TFs in FP-RMS cells. Such a SE selectivity of HDAC inhibitors was achieved through excessive increase
in the chromatin accessibility of genomic loci, which were co-loaded with both HDAC and core TFs. In contrast, HDAC binding sites without co-binding of core TFs showed a weaker change. As a
result of HDAC inhibition, local concentration of acetylated histones was increased around “epicenters.” Aberrant increase in histone acetylation enhanced H3K27ac spreading toward distal
boundaries of H3K27ac domains, especially for shorter TF genes (e.g., SOX8, MYOG, MYOD1, and MYCN). Meanwhile, hyper-acetylation of histones also triggered new chromatin contacts at the
expense of endogenous, transcription-supportive SE loops within CTCF-defined domains. For instance, Entinostat induced enhancer spreading and aberrant new interactions across 40-kb gap
between two MYOD1 SEs, while it diminished their initial interaction. Furthermore, quantitative ChIP-seq analysis (by ChIP-Rx assay) upon HDAC inhibition revealed a general reduction in
occupancy of RNA polymerase II, P3F, SOX8, and MYOD1 at regulatory elements of core TFs. In the meantime, genomic binding of MYOG, p300, HDAC2, and HDAC3 remained stable, whereas loading of
YY1, RAD21, and BRD4 was significantly increased. The unloading of RNA polymerase II from chromatin may act through two mechanisms: (1) inhibition of pause release at the global scale and
(2) alteration of phase separation at core TFs. Notably, HDAC inhibition rapidly dissolved RNA polymerase II condensates, which have been reported to dynamically touch SEs [36,37,38], while
phase-separated BRD4 resisted chromatin hyper-acetylation. Therefore, P3F-driven CRC in FP-RMS is vulnerable to agents targeting the histone-acetylation axis. DEDIFFERENTIATED LIPOSARCOMA
(DDLPS) DDLPS represents a high-grade subtype of adipocytic mesenchymal tumors. Enhancer profiling of both established cell lines and primary DDLPS tumors enabled discovery of SE-driven
FOSL2, MYC, and RUNX1 as top co-operative core TFs (Fig. 3f) [68]. Genomic occupancy analysis revealed a substantial binding and co-loading of BRD2, BRD3, BRD4, FOSL2, and RUNX proteins
across active enhancers, especially SE regions of core TFs. Moreover, FOSL2, MYC, and RUNX1 demonstrated inter-dependent expression in DDLPS cells, which was further supported by their
robust co-expression in primary tumor specimens. The prominent function of FOSL2 suggests high activity of AP-1 complex in DDLPS. As genomic studies have identified frequent amplification of
another AP-1 member JUN in this disease [69], JUN amplification likely contributes to the DDLPS-specific regulatory circuitry. In search of key downstream targets of CRC, SNAI2 was
identified as a leading hit whose expression was elevated in DDLPS tumors and was associated with adverse prognosis. Of note, all of the above-mentioned BET bromodomain proteins, core TFs
and SNAI2 were essential for both proliferation and tumorigenicity of DDLPS cells. BET protein degraders (e.g., ARV-825 and dBET6) inhibited preferentially SE-associated genes including core
TFs and SNAI2, and exerted stronger anti-DDLPS activities than conventional BET bromodomain inhibitors. Therefore, BET protein degraders are promising modalities to subvert oncogenic
dependence on disease-driving CRC. ESOPHAGEAL CANCER Esophageal cancer ranks globally among the top ten most common cancers. This disease can be sub-grouped into esophageal adenocarcinoma
(EAC) and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), two entities showing many contrasting features at epidemiological, clinical, and molecular levels [70]. In line with the significant
disparities in transcriptome, cancer genome, DNA methylatome, and chromatin profiles, EAC and ESCC display subtype-specific enhancer topography and master TF connectivity [71, 72]. By
analyzing EAC-specific SE engagement and co-expression, Chen et al. identified a clique of four master TFs (i.e., ELF3, KLF5, GATA6, and EHF) forming an interconnected circuitry to dictate
EAC transcriptome [71]. Overexpression of these four TFs in EAC cells was mutually dependent on the expression of each other. ChIP-seq analysis of ELF3, KLF5, and GATA6 revealed co-occupancy
of these TFs at the SE regions of their own and EHF, except for a weak signal of ELF3 binding at GATA6 enhancers (Fig. 3g). Based on integrative analysis of H3K27ac ChIP-seq and circular
chromosome conformation capture sequencing (4C-seq), five constituent enhancers (E1–E5) of ELF3 were identified within SE. Among these ELF3 enhancers, E1 demonstrated a strong EAC-specific
enhancer activity and was concurrently bound by ELF3, KLF5, and GATA6. Blocking chromatin accessibility of E1 by CRISPR/dCas9-KRAB was able to decrease expression of ELF3, as well as the
rest core TFs. Furthermore, ELF3, KLF5, and GATA6 localized in close proximity to each other across the EAC genome. Genes with their enhancers bound by one or more core TFs showed higher
expression than those with no binding. Consistent with substantial involvement of these core TFs in EAC transcriptome, they played positive roles to maintain survival and proliferation of
EAC cells. SE-driven LIF, LIFR and HNF4A represented leading candidates for CRC downstream targets which exhibited both disease-specificity and therapeutic venerability [71, 73]. In ESCC
cells, TP63, SOX2, and KLF5 established a disease-driving CRC to maintain chromatin accessibility and oncogenic transcription (Fig. 3h) [72]. TP63, SOX2, and KLF5 were reported to interact
directly with each other and have overlapping occupancy at the SE elements including those of their own. Knockdown of individual core TF abolished expression of all three TFs and downstream
targets (e.g., ALDH3A1 and BRD4), which was accompanied by a marked decrease in chromatin accessibility at target enhancers. Moreover, TP63, SOX2, and KLF5 maintained transcription of
enhancer RNAs from various TP63 enhancers (e.g., E2, E7, and E8). Strikingly, genomic deletion of these TP63 enhancer elements was sufficient to abolish the expression of all three core TFs
and inhibit colony forming ability of ESCC cells. Interestingly, BRD4 was one of the downstream targets of ESCC-specific CRC, as knockdown of any core TF disrupted both transcription and
protein expression of BRD4. BET protein degraders (e.g., ARV-771, MZ1, and ARV-825) and HDAC inhibitors (Romidepsin, Panobinostat and JNJ-26481585) were identified as potent anti-ESCC
agents. Single agent treatment of Romidepsin degraded TP63 and abolished the expression of all core TFs in a proteasome-dependent manner. Further, combination of Romidepsin and ARV-771
induced substantial chromatin remodeling in ESCC cells, yielding a strong synergistic anti-ESCC effect both in vitro and in vivo. Interestingly, KLF5 appears as a common core TFs in both EAC
and ESCC, albeit the co-operative master TFs are very different. In addition, KLF5 engaged a mutual crosstalk with collaborating factors GATA4 and GATA6 to maintain oncogenic
transcriptional regulatory network in gastric cancer [74]. These studies suggest that rewiring connectivity of master TFs is fundamental to disease/subtype identity. Of note, amplification
of SOX2 and TP63 is common in ESCC [75], representing a genomic driver for ESCC-specific CRC. Genomic amplification and somatic SE duplication of KLF5 have also been reported in squamous
cell carcinoma, EAC, and gastric cancer [74, 76, 77]. In addition, CCAT1, a SE-driven long noncoding RNA was reported to mediate the binding affinity of SOX2-TP63 complex on target SE (i.e.,
enhancer of EGFR) [78]. Engagement of noncoding components in CRC may further extend the connectivity and function of TFs. IMPLEMENTATION OF CIRCUITRY ANALYSIS IN CANCER RESEARCH Based on
findings from biologically verified CRCs, core TFs are vital for cell identity and transcriptional homeostasis under both physiological and pathological conditions. Many other studies have
also implemented CRC analysis in uncovering critical transcriptional programs in various cancer types (Table 1) [27, 30, 79,80,81,82,83,84]. For instance, by analyzing publically available
ChIP-seq data from the ENCODE project [85], Fournier et al. modeled core TF connectivity including ESR1, FOXA1, FOSL2, and JUND in MCF7 breast cancer cells; HNF4A, FOXA1, FOXA2, and CEBPB in
HEPG2 liver cancer cells; as well as FOXA1, FOXA2, FOSL2, JUND, and ATF3 in A549 lung carcinoma cells [83]. Depletion of FOXA effectively inhibited the viability and clonogenicity of all
three cell lines. With information of active chromatin architecture, computational reconstruction of enhancer/NFR-centric CRCs represents an insightful approach to discover TFs with
principal functions in a disease/development/subtype-specific transcriptional regulatory network. TF circuitry analysis implicated SOX9, RFX2, SOX2, and ZBTB16 as generally essential factors
for ependymoma cells [30]. Top-scored CRC of chronic lymphocytic leukemia predicted PAX5, ETV6, and IRF2 as centralized regulators [27]. Other examples of enhancer/NFR-centric CRC network
construction include gastrointestinal stromal tumors [82, 86], multiple myeloma [44], and keratinocyte stem cells [46]. In addition, dbCoRC serves as a valuable database to explore
H3K27ac/enhancer-centric core circuitries in over 230 samples including cervical adenocarcinoma, chronic myelogenous leukemia, colorectal cancer, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, gastric
cancer, small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and prostate cancer. CONCLUSIONS The above examples demonstrate the successful application of CRC models to address scientific questions
related to cell identity, cancer biology, and therapeutic responses, highlighting the prevalence and importance of CRC in human cancers. Current paradigm of CRC in human cancers involves
four principles: (1) enrolment of master TFs showing high expression and substantial chromatin loading, (2) existence of autoregulation and mutual regulation of core TFs based on either ChIP
analysis or motif detection among their regulatory elements, (3) evidence of co-expression of core TFs and transcriptional co-dependencies on each other, and (4) essential function of core
TFs and downstream targets in maintaining malignant characteristics of cancer cells. Computational reconstruction, ChIP-seq, and biologic verification represent the main technical route for
CRC studies. Computational algorithms are highly dependent on TF motif analysis. As TFs function in concert with additional co-factors and partners, deviation of actual TF occupancy from
motif-based binding sites could compromise the power of computational modeling. Update and refinement of TF motif database warrant more accurate and comprehensive prediction of TF
connectivity and network of TFs. Additional efforts can include incorporation of either publically available TF ChIP-seq data or TF ChIP-seq signals from cells of similar identity [87]. In
supplement to the enhancer/NFR-centric CRC prediction, integrative analysis of genomic profiling, DNA methylome, chromatin compartmentalization, and enhancer-promoter interactions will
extend and clarify regulatory loops. Further improvements in detection and assignment of open chromatin regions to target genes (e.g., 4C-seq) will benefit CRC construction. Since cancer
cells are vulnerable to genetic inactivation of core TFs, functional genomics data from genome-wide CRISPR or shRNA loss-of-function viability screening will be useful to interrogate
functional importance of candidate core TFs. To this end, the Cancer Dependency Map project (https://depmap.org/portal/), which hosts functional genomics data of over 700 cell lines, serves
as a valuable resource to identify TF dependency and cancer vulnerabilities. Remarkably, both germline polymorphisms and genomic abnormalities can lead to either overexpression or de novo
fusion of TFs. These genetically activated TFs are further integrated into the aberrant oncogenic transcriptional programs via CRC formation in collaboration with additional core factors.
Driver mutations in signaling pathways can also fuel tumor-promoting CRC via activating their downstream executive TFs. Therefore, CRC operates as a nexus of genomic, signaling, and
epigenetic dysregulations in oncogenesis (Fig. 1b). In addition, cancer-associated CRCs often hijack a stem/progenitor cell TF network, which prevents transformed cells from terminal
differentiation and in turn conveys information of cell-of-origin. Systematic survey of TF aberrations across human cancer genomes will provide valuable insights for cancer-associated CRC;
cancers driven by fusion TFs are fertile grounds of CRC study. Knowledge of the biologic basis of CRC is growing. CRC frequently enrolls master TFs with pioneer factor activity and/or
cancer-specific genomic lesion. Core TFs recruit chromatin/histone modifiers, mediators, and cohesin proteins to reshape epigenetic landscape and establish an oncogenic state [83]. Broad
chromatin domain and clustered binding of core TFs at “epicenters” concentrate further co-factors and co-regulators with intrinsically disordered regions (e.g., MED1 and BRD4) to form
phase-separated condensates. After compartmentalization, mediator droplets are able to enrich transcription apparatus. Therefore, these condensates in turn provide high local concentrations
of trans-activating TFs, chromatin regulators, and transcription machineries for robust expression of target genes (Fig. 1c). Liquid–liquid phase separation emerges as a biophysical
mechanism to form dynamic, multivalent condensates of TFs, mediators, and RNA polymerase II to activate SE-associated transcription, especially the expression of core TFs [34, 36,37,38].
However, regulation and structural basis of the functional dynamics and cooperativity among interacting components within condensates await further exploration. Besides, negative feedback
mechanisms that calibrate the strength of feed-forward regulation remain poorly explored. Therapeutic targeting of histone-acetylation axis and transcriptional apparatus represents an
auspicious strategy to disrupt cancer-associated CRC (Table 2). Since BET proteins, CDK7, CDK9, and HDACs, serve as actionable targets in many cancers addicted to CRC, combination of
CRC-disrupting agents with either current treatment modalities or novel antitumor compounds may improve therapeutic response. Of interest to note, condensates of RNA polymerase II are
sensitive to transcriptional stress, while those of BRD4 and mediators are more resilient [34, 36]. Selective blockage of phase separation or co-inhibition of multiple components in
phase-separated condensates may have synergistic effects to break transcriptional circuitry in tumor cells. Although many aspects remain unexplored, plasticity and heterogeneity of CRC have
been implicated in human cancers [28, 35]. CRC-guided tumor stratification and therapeutic development are promising fields for future investigation. REFERENCES * Lambert SA, Jolma A,
Campitelli LF, Das PK, Yin Y, Albu M, et al. The human transcription factors. Cell. 2018;172:650–65. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Neph S, Stergachis AB, Reynolds A, Sandstrom R, Borenstein
E, Stamatoyannopoulos JA. Circuitry and dynamics of human transcription factor regulatory networks. Cell. 2012;150:1274–86. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhang S, Tian D,
Tran NH, Choi KP, Zhang L. Profiling the transcription factor regulatory networks of human cell types. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:12380–7. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Whyte WA, Orlando DA, Hnisz D, Abraham BJ, Lin CY, Kagey MH, et al. Master transcription factors and mediator establish super-enhancers at key cell identity genes. Cell. 2013;153:307–19. CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Boyer LA, Lee TI, Cole MF, Johnstone SE, Levine SS, Zucker JP, et al. Core transcriptional regulatory circuitry in human embryonic stem cells.
Cell. 2005;122:947–56. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Jaenisch R, Young R. Stem cells, the molecular circuitry of pluripotency and nuclear reprogramming. Cell.
2008;132:567–82. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Cole MF, Young RA. Mapping key features of transcriptional regulatory circuitry in embryonic stem cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp
Quant Biol. 2008;73:183–93. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chen X, Xu H, Yuan P, Fang F, Huss M, Vega VB, et al. Integration of external signaling pathways with the core
transcriptional network in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2008;133:1106–17. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Endoh M, Endo TA, Endoh T, Fujimura Y, Ohara O, Toyoda T, et al. Polycomb group
proteins Ring1A/B are functionally linked to the core transcriptional regulatory circuitry to maintain ES cell identity. Development. 2008;135:1513–24. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Li X,
Li L, Pandey R, Byun JS, Gardner K, Qin Z, et al. The histone acetyltransferase MOF is a key regulator of the embryonic stem cell core transcriptional network. Cell Stem Cell.
2012;11:163–78. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ang YS, Tsai SY, Lee DF, Monk J, Su J, Ratnakumar K, et al. Wdr5 mediates self-renewal and reprogramming via the embryonic stem cell
core transcriptional network. Cell. 2011;145:183–97. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Pijnappel WW, Esch D, Baltissen MP, Wu G, Mischerikow N, Bergsma AJ, et al. A central
role for TFIID in the pluripotent transcription circuitry. Nature. 2013;495:516–9. PubMed Google Scholar * Xie W, Song C, Young NL, Sperling AS, Xu F, Sridharan R, et al. Histone h3 lysine
56 acetylation is linked to the core transcriptional network in human embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell. 2009;33:417–27. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Marson A, Levine SS,
Cole MF, Frampton GM, Brambrink T, Johnstone S, et al. Connecting microRNA genes to the core transcriptional regulatory circuitry of embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2008;134:521–33. CAS PubMed
PubMed Central Google Scholar * Guttman M, Donaghey J, Carey BW, Garber M, Grenier JK, Munson G, et al. lincRNAs act in the circuitry controlling pluripotency and differentiation.
Nature. 2011;477:295–300. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Kunarso G, Chia NY, Jeyakani J, Hwang C, Lu X, Chan YS, et al. Transposable elements have rewired the core regulatory
network of human embryonic stem cells. Nat Genet. 2010;42:631–4. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wontakal SN, Guo X, Smith C, MacCarthy T, Bresnick EH, Bergman A, et al. A core erythroid
transcriptional network is repressed by a master regulator of myelo-lymphoid differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:3832–7. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Odom DT,
Dowell RD, Jacobsen ES, Nekludova L, Rolfe PA, Danford TW, et al. Core transcriptional regulatory circuitry in human hepatocytes. Mol Syst Biol. 2006;2:2006.0017. PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Aldiri I, Xu B, Wang L, Chen X, Hiler D, Griffiths L, et al. The dynamic epigenetic landscape of the retina during development, reprogramming, and tumorigenesis. Neuron.
2017;94:550–68.e10. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Lim CY, Tam WL, Zhang J, Ang HS, Jia H, Lipovich L, et al. Sall4 regulates distinct transcription circuitries in different
blastocyst-derived stem cell lineages. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3:543–54. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Sanda T, Lawton LN, Barrasa MI, Fan ZP, Kohlhammer H, Gutierrez A, et al. Core
transcriptional regulatory circuit controlled by the TAL1 complex in human T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:209–21. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Joo MS, Koo JH, Kim TH, Kim YS, Kim SG. LRH1-driven transcription factor circuitry for hepatocyte identity: super-enhancer cistromic analysis. EBioMedicine. 2019;40:488–503. PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Saint-Andre V, Federation AJ, Lin CY, Abraham BJ, Reddy J, Lee TI, et al. Models of human core transcriptional regulatory circuitries. Genome Res. 2016;26:385–96.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Garraway LA, Lander ES. Lessons from the cancer genome. Cell. 2013;153:17–37. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bradner JE, Hnisz D, Young RA.
Transcriptional addiction in Cancer. Cell. 2017;168:629–43. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Lin CY, Erkek S, Tong Y, Yin L, Federation AJ, Zapatka M, et al. Active
medulloblastoma enhancers reveal subgroup-specific cellular origins. Nature. 2016;530:57–62. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ott CJ, Federation AJ, Schwartz LS, Kasar S,
Klitgaard JL, Lenci R, et al. Enhancer architecture and essential core regulatory circuitry of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2018;34:982–95.e7. CAS PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Boeva V, Louis-Brennetot C, Peltier A, Durand S, Pierre-Eugene C, Raynal V, et al. Heterogeneity of neuroblastoma cell identity defined by transcriptional circuitries. Nat
Genet. 2017;49:1408–13. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gryder BE, Yohe ME, Chou HC, Zhang X, Marques J, Wachtel M, et al. PAX3-FOXO1 establishes myogenic super enhancers and confers BET
bromodomain vulnerability. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:884–99. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Mack SC, Pajtler KW, Chavez L, Okonechnikov K, Bertrand KC, Wang X, et al. Therapeutic
targeting of ependymoma as informed by oncogenic enhancer profiling. Nature. 2018;553:101–5. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pott S, Lieb JD. What are super-enhancers? Nat Genet.
2015;47:8–12. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Durbin AD, Zimmerman MW, Dharia NV, Abraham BJ, Iniguez AB, Weichert-Leahey N, et al. Selective gene dependencies in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma
include the core transcriptional regulatory circuitry. Nat Genet. 2018;50:1240–6. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Boulay G, Sandoval GJ, Riggi N, Iyer S, Buisson R, Naigles
B, et al. Cancer-specific retargeting of BAF complexes by a prion-like domain. Cell. 2017;171:163–78.e19. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Gryder BE, Pomella S, Sayers C, Wu
XS, Song Y, Chiarella AM, et al. Histone hyperacetylation disrupts core gene regulatory architecture in rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat Genet. 2019;51:1714–22. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Yohe ME, Gryder BE, Shern JF, Song YK, Chou HC, Sindiri S, et al. MEK inhibition induces MYOG and remodels super-enhancers in RAS-driven rhabdomyosarcoma. Sci Transl Med.
2018;10:eaan4470. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Cho WK, Spille JH, Hecht M, Lee C, Li C, Grube V, et al. Mediator and RNA polymerase II clusters associate in
transcription-dependent condensates. Science. 2018;361:412–5. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Sabari BR, Dall’Agnese A, Boija A, Klein IA, Coffey EL, Shrinivas K, et al.
Coactivator condensation at super-enhancers links phase separation and gene control. Science. 2018;361:eaar3958. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chong S, Dugast-Darzacq C, Liu Z,
Dong P, Dailey GM, Cattoglio C, et al. Imaging dynamic and selective low-complexity domain interactions that control gene transcription. Science. 2018;361:eaar2555. PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Grant CE, Bailey TL, Noble WS. FIMO: scanning for occurrences of a given motif. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:1017–8. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bailey TL,
Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, et al. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:W202–208. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
* Huang M, Chen Y, Yang M, Guo A, Xu Y, Xu L, et al. dbCoRC: a database of core transcriptional regulatory circuitries modeled by H3K27ac ChIP-seq signals. Nucleic Acids Res.
2018;46:D71–7. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wang L, Hiler D, Xu B, AlDiri I, Chen X, Zhou X, et al. Retinal cell type DNA methylation and histone modifications predict reprogramming
efficiency and retinogenesis in 3D organoid cultures. Cell Rep. 2018;22:2601–14. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ramsey SA, Knijnenburg TA, Kennedy KA, Zak DE, Gilchrist M,
Gold ES, et al. Genome-wide histone acetylation data improve prediction of mammalian transcription factor binding sites. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:2071–5. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Jin Y, Chen K, De Paepe A, Hellqvist E, Krstic AD, Metang L, et al. Active enhancer and chromatin accessibility landscapes chart the regulatory network of primary multiple
myeloma. Blood. 2018;131:2138–50. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Assi SA, Imperato MR, Coleman DJL, Pickin A, Potluri S, Ptasinska A, et al. Subtype-specific regulatory
network rewiring in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet. 2019;51:151–62. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mercado N, Schutzius G, Kolter C, Estoppey D, Bergling S, Roma G, et al. IRF2 is a
master regulator of human keratinocyte stem cell fate. Nat Commun. 2019;10:4676. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Girardi T, Vicente C, Cools J, De Keersmaecker K. The genetics and
molecular biology of T-ALL. Blood. 2017;129:1113–23. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Sanda T, Leong WZ. TAL1 as a master oncogenic transcription factor in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Exp Hematol. 2017;53:7–15. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Mansour MR, Abraham BJ, Anders L, Berezovskaya A, Gutierrez A, Durbin AD, et al. Oncogene regulation. An oncogenic super-enhancer
formed through somatic mutation of a noncoding intergenic element. Science. 2014;346:1373–7. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Tan SH, Yam AW, Lawton LN, Wong RW, Young RA, Look
AT, et al. TRIB2 reinforces the oncogenic transcriptional program controlled by the TAL1 complex in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2016;30:959–62. CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Leong WZ, Tan SH, Ngoc PCT, Amanda S, Yam AWY, Liau WS, et al. ARID5B as a critical downstream target of the TAL1 complex that activates the oncogenic transcriptional program and
promotes T-cell leukemogenesis. Genes Dev. 2017;31:2343–60. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ngoc PCT, Tan SH, Tan TK, Chan MM, Li Z, Yeoh AEJ, et al. Identification of novel
lncRNAs regulated by the TAL1 complex in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2018;32:2138–51. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Choi A, Illendula A, Pulikkan JA, Roderick
JE, Tesell J, Yu J, et al. RUNX1 is required for oncogenic Myb and Myc enhancer activity in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2017;130:1722–33. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Kwiatkowski N, Zhang T, Rahl PB, Abraham BJ, Reddy J, Ficarro SB, et al. Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor. Nature. 2014;511:616–20. CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Olson CM, Jiang B, Erb MA, Liang Y, Doctor ZM, Zhang Z, et al. Pharmacological perturbation of CDK9 using selective CDK9 inhibition or
degradation. Nat Chem Biol. 2018;14:163–70. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Winter GE, Mayer A, Buckley DL, Erb MA, Roderick JE, Vittori S, et al. BET bromodomain proteins function as master
transcription elongation factors independent of CDK9 recruitment. Mol Cell. 2017;67:5–18.e19. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Witt H, Hielscher T,
Eberhart CG, Mack S, et al. Medulloblastoma comprises four distinct molecular variants. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1408–14. PubMed Google Scholar * Garancher A, Lin CY, Morabito M, Richer W,
Rocques N, Larcher M, et al. NRL and CRX define photoreceptor identity and reveal subgroup-specific dependencies in medulloblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2018;33:435–49.e6. CAS PubMed PubMed
Central Google Scholar * Boon K, Eberhart CG, Riggins GJ. Genomic amplification of orthodenticle homologue 2 in medulloblastomas. Cancer Res. 2005;65:703–7. CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Adamson DC, Shi Q, Wortham M, Northcott PA, Di C, Duncan CG, et al. OTX2 is critical for the maintenance and progression of Shh-independent medulloblastomas. Cancer Res. 2010;70:181–91. CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Boulay G, Awad ME, Riggi N, Archer TC, Iyer S, Boonseng WE, et al. OTX2 activity at distal regulatory elements shapes the chromatin landscape of group 3
medulloblastoma. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:288–301. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Decaesteker B, Denecker G, Van Neste C, Dolman EM, Van Loocke W, Gartlgruber M, et al. TBX2 is
a neuroblastoma core regulatory circuitry component enhancing MYCN/FOXM1 reactivation of DREAM targets. Nat Commun. 2018;9:4866. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Wang L, Tan TK,
Durbin AD, Zimmerman MW, Abraham BJ, Tan SH, et al. ASCL1 is a MYCN- and LMO1-dependent member of the adrenergic neuroblastoma core regulatory circuitry. Nat Commun. 2019;10:5622. CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Oldridge DA, Wood AC, Weichert-Leahey N, Crimmins I, Sussman R, Winter C, et al. Genetic predisposition to neuroblastoma mediated by a LMO1
super-enhancer polymorphism. Nature. 2015;528:418–21. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Skapek SX, Ferrari A, Gupta AA, Lupo PJ, Butler E, Shipley J, et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma.
Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2019;5:1. PubMed Google Scholar * Driman D, Thorner PS, Greenberg ML, Chilton-MacNeill S, Squire J. MYCN gene amplification in rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer. 1994;73:2231–7.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Gryder BE, Wu L, Woldemichael GM, Pomella S, Quinn TR, Park PMC, et al. Chemical genomics reveals histone deacetylases are required for core regulatory
transcription. Nat Commun. 2019;10:3004. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chen Y, Xu L, Mayakonda A, Huang ML, Kanojia D, Tan TZ, et al. Bromodomain and extraterminal proteins
foster the core transcriptional regulatory programs and confer vulnerability in liposarcoma. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1353. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Cancer Genome Atlas
Research Network.Comprehensive and integrated genomic characterization of adult soft tissue sarcomas. Cell. 2017;171:950–65.e28. Google Scholar * Lin DC, Dinh HQ, Xie JJ, Mayakonda A, Silva
TC, Jiang YY, et al. Identification of distinct mutational patterns and new driver genes in oesophageal squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas. Gut. 2018;67:1769–79. CAS PubMed
Google Scholar * Chen L, Huang M, Plummer J, Pan J, Jiang YY, Yang Q, et al. Master transcription factors form interconnected circuitry and orchestrate transcriptional networks in
oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Gut. 2020;69:630–40. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Jiang YY, Jiang Y, Li CQ, Zhang Y, Dakle P, Kaur H, et al. TP63, SOX2, and KLF5 establish a core regulatory
circuitry that controls epigenetic and transcription patterns in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Gastroenterology. 2020. In press.
https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.050. * Pan J, Silva TC, Gull N, Yang Q, Plummer JT, Chen S, et al. Lineage-specific epigenomic and genomic activation of oncogene HNF4A promotes
gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 2020;80:2722–36. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Chia NY, Deng N, Das K, Huang D, Hu L, Zhu Y, et al. Regulatory crosstalk between
lineage-survival oncogenes KLF5, GATA4 and GATA6 cooperatively promotes gastric cancer development. Gut. 2015;64:707–19. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lin DC, Hao JJ, Nagata Y, Xu L, Shang
L, Meng X, et al. Genomic and molecular characterization of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2014;46:467–73. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhang X, Choi PS,
Francis JM, Imielinski M, Watanabe H, Cherniack AD, et al. Identification of focally amplified lineage-specific super-enhancers in human epithelial cancers. Nat Genet. 2016;48:176–82. CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Zhang X, Choi PS, Francis JM, Gao GF, Campbell JD, Ramachandran A, et al. Somatic superenhancer duplications and hotspot mutations lead to oncogenic activation of
the KLF5 transcription factor. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:108–25. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Jiang Y, Jiang YY, Xie JJ, Mayakonda A, Hazawa M, Chen L, et al. Co-activation of
super-enhancer-driven CCAT1 by TP63 and SOX2 promotes squamous cancer progression. Nat Commun. 2018;9:3619. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bleu M, Gaulis S, Lopes R, Sprouffske K,
Apfel V, Holwerda S, et al. PAX8 activates metabolic genes via enhancer elements in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2019;10:3739. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * van Groningen
T, Akogul N, Westerhout EM, Chan A, Hasselt NE, Zwijnenburg DA, et al. A NOTCH feed-forward loop drives reprogramming from adrenergic to mesenchymal state in neuroblastoma. Nat Commun.
2019;10:1530. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Riddick G, Kotliarova S, Rodriguez V, Kim HS, Linkous A, Storaska AJ, et al. A core regulatory circuit in glioblastoma stem cells
links MAPK activation to a transcriptional program of neural stem cell identity. Sci Rep. 2017;7:43605. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ran L, Chen Y, Sher J, Wong EWP, Murphy D,
Zhang JQ, et al. FOXF1 defines the core-regulatory circuitry in gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:234–51. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fournier M, Bourriquen G, Lamaze
FC, Cote MC, Fournier E, Joly-Beauparlant C, et al. FOXA and master transcription factors recruit Mediator and Cohesin to the core transcriptional regulatory circuitry of cancer cells. Sci
Rep. 2016;6:34962. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Tsuzuki S, Yasuda T, Kojima S, Kawazu M, Akahane K, Inukai T, et al. Targeting MEF2D-fusion oncogenic transcriptional
circuitries in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Cancer Discov. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-19-0080. * Consortium EP. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA
elements in the human genome. Nature. 2012;489:57–74. Google Scholar * Hemming ML, Lawlor MA, Zeid R, Lesluyes T, Fletcher JA, Raut CP, et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor enhancers
support a transcription factor network predictive of clinical outcome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E5746–55. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Gheorghe M, Sandve GK, Khan
A, Cheneby J, Ballester B, Mathelier A. A map of direct TF-DNA interactions in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:e21. PubMed Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Dr Tuan Zea Tan for kind help with computational analysis and Dr Takaomi Sanda for kind discussion. FUNDING This work is funded by the National Institute of Health (R01-CA200992-03
to HPK; R35CA197628, R01CA137060, R01CA157644, R01CA172558, and R01CA213138 to MM), the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI-55108547 to MM), National Research Foundation Singapore under
its Singapore Translational Research (STaR) Investigator Award (NMRC/STaR/0021/2014 to HPK), the Singapore Ministry of Education Academic Research Fund Tier 2 (MOE2017-T2-1-033 to HPK), the
Singapore Ministry of Health’s National Medical Research Council (NMRC) Centre Grant awarded to National University Cancer Institute of Singapore (NCIS), the National Research Foundation
Singapore and the Singapore Ministry of Education under its Research Centres of Excellence initiatives, and is additionally supported by NMRC Open Fund Young Individual Research Grant
(MOH-OFYIRG18May-0001 to LX), a Seed Funding Program within the NCIS Centre Grant, a NCIS Yong Siew Yoon Research grant through donations from the Yong Loo Lin Trust, and the Wendy Walk
Foundation. MM is also supported by a Wellcome Trust Senior Investigator Award (WT-101880), a Leukemia and Lymphoma Scholar award, the Norman and Sadie Lee Foundation (for Pediatric Cancer),
the Falk Trust through a Falk Medical Research Trust Catalyst Award, the Pediatric Cancer Research Foundation, the Cancer Research Institute through a Clinic and Laboratory Integration
Program grant, and the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine through DISC2-10061. MM is a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) Faculty Scholar. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND
AFFILIATIONS * Cancer Science Institute of Singapore, National University of Singapore, Singapore, 117599, Singapore Ye Chen, Liang Xu, Ruby Yu-Tong Lin & H. Phillip Koeffler *
Department of Systems Biology, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center, Monrovia, CA, 91016, USA Liang Xu & Markus Müschen * College of Life Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou,
310058, China Liang Xu * Department of Medicine, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, 90048, USA H. Phillip Koeffler * National University Cancer Institute, National University
Hospital, Singapore, 119074, Singapore H. Phillip Koeffler Authors * Ye Chen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Liang Xu View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ruby Yu-Tong Lin View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Markus
Müschen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * H. Phillip Koeffler View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS Conceptualization, YC, LX, and HPK; visualization, YC, LX, and RY-TL; writing—original draft, YC and LX; writing—review and editing, YC, LX, MM, and HPK; funding
acquisition, LX, MM, and HPK; supervision, MM and HPK. CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to Ye Chen or Liang Xu. ETHICS DECLARATIONS CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare that they
have no conflict of interest. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PUBLISHER’S NOTE Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS OPEN ACCESS This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and
reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes
were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If
material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain
permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS
ARTICLE Chen, Y., Xu, L., Lin, R.YT. _et al._ Core transcriptional regulatory circuitries in cancer. _Oncogene_ 39, 6633–6646 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01459-w Download
citation * Received: 14 June 2020 * Revised: 30 August 2020 * Accepted: 04 September 2020 * Published: 17 September 2020 * Issue Date: 22 October 2020 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01459-w SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative