Play all audios:
Mammary carcinogenesis possesses great challenges due to the lack of effectiveness of the multiple therapeutic options available. Gene therapy-based cancer treatment strategy provides more
targeting accuracy, fewer side effects, and higher therapeutic efficiency. Downregulation of the oncogene mTOR by mTOR-siRNA is an encouraging approach to reduce cancer progression. However,
its employment as means of therapeutic strategy has been restricted due to the unavailability of a suitable delivery system.
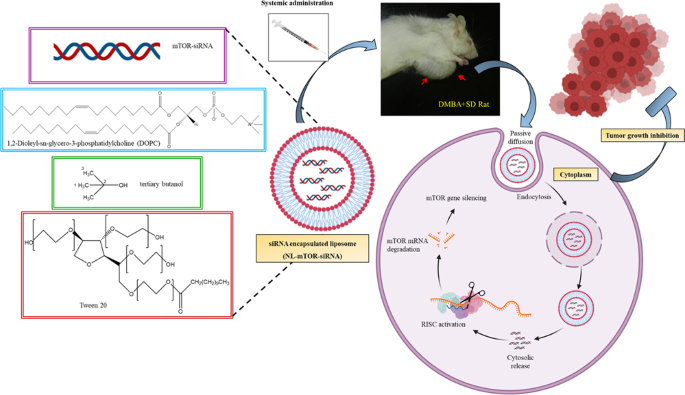
A suitable nanocarrier system made up of 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine (DOPC) has been developed to prevent degradation and for proficient delivery of siRNA. This was
followed by in vitro and in vivo anti-breast cancer efficiency analysis of the mTOR siRNA-loaded neutral liposomal formulation (NL-mTOR-siRNA).
In our experiment, a profound reduction in MCF-7 cell growth, proliferation and invasion was ascertained following extensive downregulation of mTOR expression. NL-mTOR-siRNA suppressed
tumour growth and restored morphological alterations of DMBA-induced breast cancer. In addition, neutral liposome enhanced accumulation of siRNA in mammary cancer tissues facilitating its
deep cytosolic distribution within the tumour, which allows apoptosis thereby facilitating its anti-tumour potential.
Hence, the current study highlighted the augmented ground for therapies aiming toward cancerous cells to diminish mTOR expression by RNAi in managing mammary carcinoma.
We acknowledge the support provided by the Central Instrumentation facility (CIF), Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, Ranchi and HR-TEM facility of Vellore Institute of Technology in the
characterisation of liposomal preparation.
This study was supported by Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Technology, Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, Ranchi, India. This work has been funded by UGC
(201819-NFO-2018-19-OBC-ORI-80495).
These authors contributed equally: Roja Sahu, Shakti Prasad Pattanayak.
Division of Advanced Pharmacology, Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences & Technology, Birla Institute of Technology (BIT), Mesra, Ranchi, Jharkhand, 835 215, India
Division of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences & Technology, Birla Institute of Technology (BIT), Mesra, Ranchi, Jharkhand, 835 215, India
Department of Pharmacy, School of Health Science, Central University of South Bihar (Gaya), Gaya, Bihar, 824 236, India
RS and SPP conducted the experiments and wrote the manuscript with equal contribution. SPP and RS was responsible for confocal microscopy, Western blot, immunohistochemistry and flow
cytometry. RS and SJ took part in the in vivo experiments. SJ analysed the data and revised the manuscript. SPP designed the research plan, analysed the data and revised the manuscript. All
authors have approved the manuscript.
This animal study was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee, Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, Ranchi (approval no. 1972/PH/BIT/113/20/IAEC). All animal experiments were
conducted in accordance with the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee (IAEC) regulation. This study did not include patient participation or analysis of patient data.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author
self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: