Play all audios:
ABSTRACT This study investigated the relation of diet quality indexes (DQI) with breast cancer incidence among women from the Multiethnic Cohort (MEC). Participants completed a questionnaire
with a validated food frequency questionnaire. Scores for Healthy Eating Index 2015 (HEI-2015), Alternate Healthy Eating Index 2010 (AHEI-2010), alternate Mediterranean diet score (aMED),
and Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) were divided into quintiles (Q1–Q5). Cox regression was applied to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for DQIs
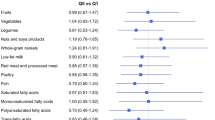
and breast cancer risk adjusted for known risk factors. The respective HRs for Q5 vs. Q1 were: 1.06 (95% CI, 0.98–1.14) for HEI-2015, 0.96 (95% CI, 0.90–1.04) for AHEI-2010, 1.01 (95% CI,
0.94–1.09) for aMED, and 0.95 (95% CI, 0.88–1.02) for DASH (_p_trend > 0.05 for all). However, overweight and obesity were significantly associated with breast cancer incidence. Despite
the null association for DQIs, diet quality may lower breast cancer risk through its positive influence on weight status. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview
of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only
$21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS ASSOCIATION BETWEEN OVERALL
DIET QUALITY AND POSTMENOPAUSAL BREAST CANCER RISK IN FIVE FINNISH COHORT STUDIES Article Open access 18 August 2021 ASSOCIATION BETWEEN HEALTHY EATING INDEX-2020, ALTERNATIVE MEDITERRANEAN
DIET SCORES, AND GASTROINTESTINAL CANCER RISK IN NHANES 2005–2018 Article Open access 01 February 2025 LOW-FAT DIETARY PATTERN AND BREAST CANCER MORTALITY BY METABOLIC SYNDROME COMPONENTS: A
SECONDARY ANALYSIS OF THE WOMEN’S HEALTH INITIATIVE (WHI) RANDOMISED TRIAL Article 18 May 2021 REFERENCES * Picon‐Ruiz M, Morata‐Tarifa C, Valle‐Goffin JJ, Friedman ER, Slingerland JM.
Obesity and adverse breast cancer risk and outcome: mechanistic insights and strategies for intervention. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:378–97. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21405. Article
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Liese AD, Krebs-Smith SM, Subar AF, George SM, Harmon BE, Neuhouser ML, et al. The dietary patterns methods project: synthesis of findings across
cohorts and relevance to dietary guidance. J Nutr. 2015;145:393–402. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.114.205336. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Kant AK. Dietary patterns
and health outcomes. J Am Diet Assoc. 2004;104:615–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2004.01.010. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Norat T, Chan D, Vingeliene S, Aune D, Polemiti E,
Vieira AR, et al. World Cancer Research Fund International systematic literature review: the associations between food, nutrition and physical activity and the risk of breast cancer.
Imperial College London: World Cancer Research Fund International; 2017. https://www.wcrf.org/sites/default/files/breast-cancer-slr.pdf. * Harmon BE, Boushey CJ, Shvetsov YB, Ettienne R,
Reedy J, Wilkens LR, et al. Associations of key diet-quality indexes with mortality in the Multiethnic Cohort: the Dietary Patterns Methods Project. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015;101:587–97.
https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.114.090688. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Park SY, Boushey CJ, Wilkens LR, Haiman CA, Le Marchand L. High-quality diets associate with
reduced risk of colorectal cancer: analyses of Diet Quality Indexes in the multiethnic cohort. Gastroenterology 2017;153:386–394.e2. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.04.004. Article
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Maskarinec G, Jacobs S, Park SY, Haiman CA, Setiawan VW, Wilkens LR, et al. Type 2 diabetes, obesity, and breast cancer risk: the multiethnic
cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2017;26:854–61. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-16-0789. Article Google Scholar * Stram DO, Hankin JH, Wilkens LR, Pike MC, Monroe KR, Park S,
et al. Calibration of the Dietary Questionnaire for a Multiethnic Cohort in Hawaii and Los Angeles. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;151:358–70. Article CAS Google Scholar * Haridass V, Ziogas A,
Neuhausen SL, Anton-Culver H, Odegaard AO. Diet quality scores inversely associated with postmenopausal breast cancer risk are not associated with premenopausal breast cancer risk in the
California teachers study. J Nutr. 2018;148:1830–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxy187. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Turati F, Carioli G, Bravi F, Ferraroni M, Serraino D, Montella M,
et al. Mediterranean diet and breast cancer risk. Nutrients. 2018;10. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030326. * Xiao Y, Xia J, Li L, Ke Y, Cheng J, Xie Y, et al. Associations between dietary
patterns and the risk of breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Breast Cancer Res. 2019;21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-019-1096-1. * Wolongevicz
DM, Zhu L, Pencina MJ, Kimokoti RW, Newby PK, D’Agostino RB, et al. Diet quality and obesity in women: the Framingham Nutrition Studies. Br J Nutr. 2010;103:1223–9.
https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114509992893. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by the following grants from the National Cancer
Institute: U01 CA164973, R03 CA223890, and U54 CA143727 (fellowship for RDC). AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * University of Hawaii Cancer Center, Honolulu, HI, USA Rica Dela
Cruz, Song-Yi Park, Yurii B. Shvetsov, Carol J. Boushey, Loïc Le Marchand & Gertraud Maskarinec * Department of Preventive Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA,
USA Kristine R. Monroe Authors * Rica Dela Cruz View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Song-Yi Park View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Yurii B. Shvetsov View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Carol J. Boushey View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Kristine R. Monroe View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Loïc Le
Marchand View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Gertraud Maskarinec View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Rica Dela Cruz. ETHICS DECLARATIONS CONFLICT OF INTEREST All authors declare no conflict of interest in this research study. ADDITIONAL
INFORMATION PUBLISHER’S NOTE Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and
permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Dela Cruz, R., Park, SY., Shvetsov, Y.B. _et al._ Diet Quality and Breast Cancer Incidence in the Multiethnic Cohort. _Eur J Clin Nutr_ 74,
1743–1747 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-020-0627-2 Download citation * Received: 16 January 2020 * Revised: 25 March 2020 * Accepted: 30 March 2020 * Published: 14 April 2020 *
Issue Date: December 2020 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-020-0627-2 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
