Play all audios:
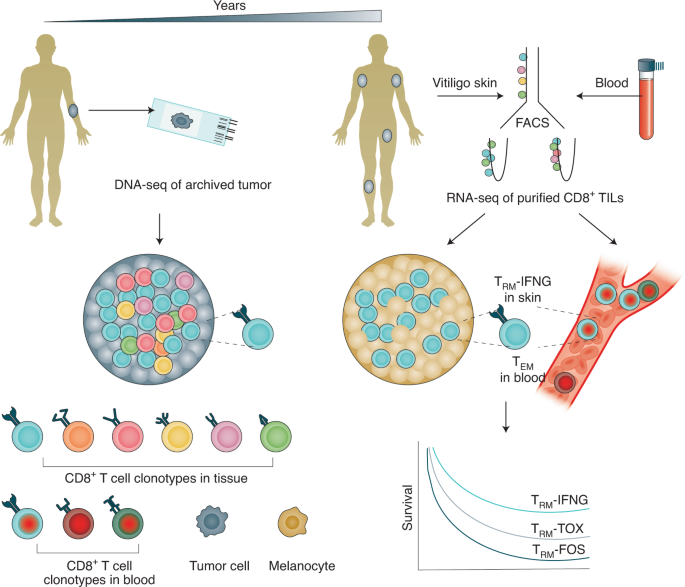
Shedding light on the mechanisms that underlie a durable response to immunotherapy, a recent study evaluating long-term survivors of melanoma treated with immunotherapy finds that
tumor-associated T cell clonotypes are sustained over years and persist as expanded, cytokine IFN-γ–expressing resident memory T cells in the skin, with effector memory counterparts in the
blood. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Access Nature
and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription $29.99 / 30 days cancel any time Learn more Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 digital issues
and online access to articles $119.00 per year only $9.92 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject
to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support REFERENCES *
Wherry, E. J. _Nat. Immunol._ 12, 492–499 (2011). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sharma, P. & Allison, J. P. _Cell_ 161, 205–214 (2015). Article CAS Google Scholar * Topalian, S. L.
et al. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 366, 2443–2454 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar * Chen, P. L. et al. _Cancer Discov._ 6, 827–837 (2016). Article Google Scholar * Huang, A. C. et al.
_Nature_ 545, 60–65 (2017). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sade-Feldman, M. et al. _Cell_ 175, 998–1013.e1020 (2018). Article CAS Google Scholar * Riaz, N. et al. _Cell_ 171,
934–949.e916 (2017). Article CAS Google Scholar * Ganesan, A. P. et al. _Nat. Immunol._ 18, 940–950 (2017). Article CAS Google Scholar * Savas, P. et al. _Nat. Med._ 24, 986–993
(2018). Article CAS Google Scholar * Edwards, J. et al. _Clin. Cancer Res._ 24, 3036–3045 (2018). Article CAS Google Scholar * Han, J. et al. _Nat. Cancer_
https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-021-00180-1 (2021). Article Google Scholar * Malik, B. T. et al. _Sci. Immunol._ 2, eaam6346 (2017). Article Google Scholar * Scott, A. C. et al. _Nature_
571, 270–274 (2019). Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS A.-P.G. is funded by US National Institutes of Health K08 (5K08CA230164-03). AUTHOR INFORMATION
AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * La Jolla Institute for Allergy & Immunology, La Jolla, CA, USA Anusha-Preethi Ganesan & Christian H. H. Ottensmeier * Division of Pediatric Hematology
Oncology, Rady Children’s Hospital, University of California San Diego, San Diego, CA, USA Anusha-Preethi Ganesan * University of Liverpool, Institute of Systems, Molecular and Integrative
Biology, Head and Neck Center, Liverpool, UK Christian H. H. Ottensmeier * The Clatterbridge Cancer Center NHS Foundation Trust, Liverpool, UK Christian H. H. Ottensmeier Authors *
Anusha-Preethi Ganesan View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Christian H. H. Ottensmeier View author publications You can also search for
this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Christian H. H. Ottensmeier. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Ganesan, AP., Ottensmeier, C.H.H. Melanoma-reactive T cells take up residence. _Nat Cancer_ 2, 253–255
(2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-021-00189-6 Download citation * Published: 24 March 2021 * Issue Date: March 2021 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-021-00189-6 SHARE THIS ARTICLE
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided
by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative