Play all audios:
ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Obesity is frequently associated with an increase in the early inflammation marker C-reactive protein (CRP), insulin resistance and changes in lipoprotein metabolism.
Increased CRP is known as an independent cardiovascular risk factor. Since the apolipoproteins (apo) E and CIII components of HDL are associated with reduced cardiovascular risk and since
apoE has _in vitro_ anti-inflammatory effect, we have investigated the relationships between apoE, apoCIII (in apoB and non apoB containing lipoproteins) and CRP in obese adults. METHODS:
The following parameters from 34 healthy obese fasting women (age 22–64 y, body mass index (BMI) 28–68 kg/m2) were measured: (1) ApoE and apoCIII, in total plasma, in apoB- (E LpB, CIII LpB)
and non-apoB-containing lipoproteins (E LpnonB, CIII LpnonB); (2) CRP and cytokine secreted by adipose tissue (TNF-α and its soluble receptor TNFR2); (3) triglyceride, HDL-cholesterol,
systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, waist and hip circumferences, insulin, glucose. HOMA, a marker of insulin sensitivity, and the ratio E/CIII in LpB and LpnonB were
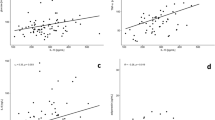
calculated. RESULTS: CRP was positively correlated with BMI (_P_<0.05), waist circumference (WC, _P_<0.05), triglyceride (_P_<0.05) and negatively correlated with apoE (_P_<0.01)
and E LpnonB (_P_<0.05). Two multiple regression models including parameters related to CRP with a _P_<0.25 were run stepwise to assess their independent contribution to CRP
concentration. In the first model (including BMI, WC, HOMA, insulin, triglyceride, apoE, E LpnonB), apoE was the best predictor of CRP (_P_=0.01) together with triglyceride (_P_=0.02) and
BMI (_P_=0.08). The second model took into account E/CIII LpnonB ratio with the parameters included in the first model. In this second model, E/CIII LpnonB was the best predictor of CRP
(_P_=0.007), explaining 39% of CRP variance. CONCLUSION: ApoE is strongly correlated with CRP and could have an anti-inflammatory effect _in vivo_ in obese subjects. This correlation could
be limited to LpnonB lipoproteins, depending on their apoE and CIII relative content. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via
your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this
article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in
* Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS ASSESSMENT OF METABOLIC SYNDROME PREDICTORS IN RELATION TO
INFLAMMATION AND VISCERAL FAT TISSUE IN OLDER ADULTS Article Open access 03 January 2023 PERICARDIAL FAT, THORACIC PERI-AORTIC ADIPOSE TISSUE, AND SYSTEMIC INFLAMMATORY MARKER IN
NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER AND ABDOMINAL OBESITY PHENOTYPE Article Open access 04 February 2022 DIET-RELATED INFLAMMATION IS POSITIVELY ASSOCIATED WITH ATHEROGENIC INDICES Article Open access
08 June 2024 REFERENCES * Ford ES . Body mass index, diabetes, and C-reactive protein among U.S. adults _Diabetes Care_ 1999 12: 1971–1977. Article Google Scholar * Visser M, Bouter LMMGM,
Wener MH, Harris TB . Elevated C-reactive protein levels in overweight and obese adults _JAMA_ 1999 282: 2131–2135. Article CAS Google Scholar * Cook DG, Mendall MA, Whincup PH, Carey
IM, Ballam L, Morris JE, Miller GJ, Strachan DP . C-reactive protein concentration in children: relationship to adiposity and other cardiovascular risk factor _Atherosclerosis_ 2000 149:
139–150. Article CAS Google Scholar * Hak AE, Stehouwer CD, Bots ML, Polderman KH, Schalkwijk CG, Westendorp IC, Hofman A, Witteman JC . Association of C-reactive protein with measures of
obesity, insulin resistance and subclinical atherosclerosis in healthy, middle-aged women _Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol_ 1999 19: 1986–1991. Article CAS Google Scholar * Yudkin JS,
Stehouwer CD, Emeis JJ, Coppack SW . C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: associations with obesity, insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: a potential role for cytokines
originating from adipose tissue? _Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol_ 1999 19: 972–978. Article CAS Google Scholar * Danesh J, Muir J, Wong YK, Ward M, Gallimore JR, Pepys MB . Risk factors
for coronary heart disease and acute-phase proteins. A population-based study _Eur Heart J_ 1999 20: 954–959. Article CAS Google Scholar * Ross R . Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease
_New Engl J Med_ 1999 340: 115–126. Article CAS Google Scholar * Liuzzo G, Biasucci LM, Gallimore JR, Grillo RL, Rebuzzi AG, Pepys MB, Maseri AM . The pronostic value of C-reactive
protein and serum amyloid a protein in severe unstable angina _New Engl J Med_ 1994 331: 417–424. Article CAS Google Scholar * Haverkate F, Thompson SG, Pyke SDM, Gallimore JR, Pepys MB .
Production of C-reactive protein and risk of coronary events in stable and unstable angina _Lancet_ 1997 349: 462–466. Article CAS Google Scholar * Mendall MA, Patel P, Ballam L,
Strachan D, Northfield TC . C-reactive protein and its relation to cardiovascular risk factors: a population based cross sectional study _Br Med J_ 1996 312: 1061–1065. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Kern PA, Saghizageh M, Ong JM, Bosch RJ, Deem R, Simsolo RB . The expression of tumor necrosis factor in human adipose tissue. Regulation by obesity, weight loss and relationship
to lipoprotein lipase _J Clin Invest_ 1995 95: 2111–2119. Article CAS Google Scholar * Torre-Amione G, Vooletich MT, Farmer JA . Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the progression of
heart failure: therapeutic implications _Drugs_ 2000 59: 745–751. Article CAS Google Scholar * Van der PT, van Deventer SJ, Hack CE, Wolbink GJ, Aarden LA, Buller HR, Ten Cate JW .
Effects on leukocytes after injection of tumor necrosis factor into healthy humans _Blood_ 1992 79: 693–698. Google Scholar * Hotamisligil GS, Budavari A, Murray DL, Spiegelman BM . Reduced
tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor in obesity diabetes: central role of tumor necrosis factor α _J Clin Invest_ 1994 94: 1543–1549. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Hotamisligil GS, Armer P, Atkinson RL, Spiegelman BM . Differential regulation of the p80 tumor necrosis factor receptor in human obesity and insulin resistance _Diabetes_ 1997 46: 451–455.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Hardardottir I, Grünfeld C, Feingold KR . Effects of endotoxin and cytokines on lipid metabolism _Curr Opin Lipidol_ 1994 5: 207–215. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Kahn BB, Flier JS . Obesity and insulin resistance _J Clin Invest_ 2000 106: 473–481. Article CAS Google Scholar * Reaven GM . Role of insulin resistance in human disease
_Diabetes_ 1988 37: 1595–1607. Article CAS Google Scholar * Austin MA . Plasma triglycerides and coronary heart disease _Arterioscler Thromb_ 1991 11: 2–14. Article CAS Google Scholar
* Mahley RW . Plasma lipoproteins: apolipoprotein structure and function _J Lipid Res_ 1984 25: 1277–1294. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Havel RJ, Kane JP, Kashyap ML . Interchange of
apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man _J Clin Invest_ 1973 52: 32–38. Article CAS Google Scholar * Berman M, Hall M, Levy RI,
Eisenberg S, Bilheimer DW, Phair RD, Goebel RH . Metabolism of apoB and apoC lipoproteins in man: kinetics studies in normal and hyperlipoproteinemic subjects _J Lipid Res_ 1978 19: 38–56.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Blum CB . Dynamics of apoE metabolism in humans _J Lipid Res_ 1982 23: 1308–1316. CAS Google Scholar * Eisenberg S, Olivecrona T . Very low Density
lipoprotein. Fate of phospholipids, cholesterol and apolipoprotein C during lipolysis _in vitro_ _J Lipid Res_ 1979 20: 614–623. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Nestel PJ, Huff MW, Billington
T, Fidge NH . Changes in the plasma lipoprotein distribution of apolipoprotein CII, CIII1, CIII2 and apoB after heparin-induced lipolysis _Biochim Biophys Acta_ 1982 712: 94–102. Article
CAS Google Scholar * Gibson JC, Brown WV . Effect of lipoprotein lipase and hepatic triglycerides lipase activity on the distribution of apolipoprotein E among the plasma lipoproteins
_Atherosclerosis_ 1988 75: 45–55. Article Google Scholar * Jeppensen J, Hollenbeck CB, Zhou MY, Coulston AM, Jones C, Chen YD, Reaven GM . Relation between insulin resistance,
hyperinsulinemia, postheparin plasma lipoprotein lipase activity and postprandial lipemia _Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol_ 1995 15: 320–324. Article Google Scholar * Che YD, Facchini F,
Landau C, Hollenbeck CB, Reaven GM . Plasma postheparin lipoprotein lipase activity is decreased in normal individuals who are resistant to insulin mediated glucose uptake _Endocrinol Metab_
1994 1: 153–158. Google Scholar * Bard JM, Charles MA, Juhan-Vague I, Vague P, André P, Safar M, Fruchart JC, Eschwège E, on behalf of the BIGPRO study group . Accumulation of
triglycerides-rich lipoproteins in subjects with abdominal obesity. The biguanides and the prevention of the risk of obesity (BIGPRO)1-study _Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol_ 2001 21: 407–414.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Blankenhorn DH, Alaupovic P, Wickham E, Chin HP, Azen SP . Prediction of angiographic change in native human coronary arteries and aortocoronary bypass
grafts _Circulation_ 1990 81: 470–476. Article CAS Google Scholar * Hodis HN, Mack WJ, Azen SP, Alaupovic P, Podoga JM, Labree L, Hemphill LC, Kramsch DM, Blakenhorn DH . Triglyceride-
and cholesterol-rich lipoproteins have a differential effect on mild/moderate and severe lesion progression as assessed by quantitative coronary angiography in a controlled trial of
lovastatin _Circulation_ 1994 90: 42–49. Article CAS Google Scholar * Shimano H, Yamada N, Katsuki M, Yamamoto K, Gotoda T, Harada K, Shimada M, Yazaki Y . Plasma lipoprotein metabolism
in transgenic mice overexpressing apolipoprotein E. Accelerated clearance of lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein B _J Clin Invest_ 1992 90: 2084–2091. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Nikouli IR, Curtiss LK . An apolipoprotein E synthetic peptide targets to lipoproteins in plasma and mediates both cellular lipoprotein interactions in vitro and acute clearance of
cholesterol-rich lipoproteins in vivo _J Clin Invest_ 1998 101: 223–234. Article Google Scholar * Zhu Y, Bellosta S, Langer C, Bernini F, Pitas RE, Mahley RW, Assman G, Eckardstein AV .
Low dose expression of a human apolipoprotein E transgene in macrophages restores cholesterol efflux capacity of apolipoprotein E-deficient mouse plasma _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1998 95:
7585–7590. Article CAS Google Scholar * Boisvert WA, Black AS, Curtiss LK . Apolipoprotein AI reduces free cholesterol accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions of apoE-deficient mice
transplanted with apolipoprotein E-expressing macrophages _Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol_ 1999 19: 525–530. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhang SH, Reddick RL, Piedrarita JA, Maeda N .
Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E _Science_ 1992 258: 468–472. Article CAS Google Scholar * Plump AS, Smith JD, Hayek T, Aalto-Setälä
K, Walsh A, Verstuyft JG, Rubin EM, Breslow JL . Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apoE deficient mice created by homologous recombinaison in ES cell _Cell_ 1992 71:
343–353. Article CAS Google Scholar * Piedrarita JA, Zhang SH, Hagamon JR, Oliver PM, Maeda N . Generation of mice carrying a mutant apolipoprotein E gene inactivated by gene targeting in
embryonic stem cells _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1992 89: 4471–4475. Article Google Scholar * Hasty AH, Linton MF, Swift LL, Fazio S . Determination of the lower threshold of apolipoprotein
E resulting in remnant lipoprotein clearance _J Lipid Res_ 1999 40: 1529–1538. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Arai T, Rinninger F, Varban L, Fairchild-Huntress V, Liang C-P, Chen W, Seo T,
Deckelbaum R, Huszar D, Tall AR . Decreased selective uptake of high density lipoprotein cholesteryl esters in apolipoprotein E knock-out mice _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 1999 96: 12050–12055.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Schaefer EJ, Gregg RE, Ghiselli G, Forte TM, Ordovas JM, Zech LA, Brewer HB . Familial apolipoprotein E deficiency _J Clin Invest_ 1986 78: 1206–1219. Article
CAS Google Scholar * Scheer WD, Boudreau DA, Malcom GT, Middaugh JP . Apolipoprotein E and atherosclerosis in Alaska natives _Atherosclerosis_ 1995 114: 197–202. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Klezovitch O, Formato M, Cherchi GM, Weissgraber KH, Scanu AM . Structural determinants in the C-terminal domain of apolipoprotein E mediating binding to the protein core of human
aortic biglycan _J Biol Chem_ 2000 275: 18913–18918. Article CAS Google Scholar * Paka L, Goldberg IJ, Obunike JC, Choi SY, Saxena U, Goldberg ID, Pillarisetti S . Perlecan mediates the
anti proliferative effect of apolipoprotein E on smooth muscle cells _J Biol Chem_ 1999 274: 36403–36408. Article CAS Google Scholar * Pepe MG, Curtiss LK . ApoE is a biologically active
constituent of the normal immunoregulatory lipoprotin, LDL-in _J Immunol_ 1986 3716: 3723. Google Scholar * Ishigami M, Swertfeger DK, Granholm NA, Hui DY . Apolipoprotein E inhibits
platelet derived growth factor-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation by suppressing signal transduction and preventing cell entry to G1 phase _J Biol Chem_ 1998
273: 20156–20161. Article CAS Google Scholar * Barger SW, Harmon AD . Microglial activation by Alzheimer amyloïd precursor protein and modulation by apolipoprotein E _Nature_ 1997 388:
878–881. Article CAS Google Scholar * La Du MJ, Shah JA, Reardon CA, Getz GS, Bu G, Hu J, Guo L, Eldik LJV . Apolipoprotein E receptor mediates the effects of β-amyloid on astrocyte
cultures _J Biol Chem_ 2000 275: 33974–33980. Article CAS Google Scholar * Desai K, Bruckdorfer R, Hutton RA, Owen JS . Binding of apolipoprotein E-rich high density lipoprotein particles
by saturable sites on human blood platelets inhibits agonist-induced platelet aggregation _J Lipid Res_ 1989 30: 831–840. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zhou MY, Paulsson G, Hansson GK .
Hypercholesterolemia is associated with a T helper (Th)1/Th2 switch of the auto-immune response in atherosclerotic apoE-knockout mice _J Clin Invest_ 1998 101: 1717–1725. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS . Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge
_Clin Chem_ 1972 18: 499–502. CAS Google Scholar * Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC . Homeostatic model assessment: insulin resistance and β cell
function from fasting glucose and insulin concentrations in man _Diabetologia_ 1985 28: 412–419. Article CAS Google Scholar * Alaupovic P, McConathy WJ, Fesmire J, Tavella M, Bard JM .
Profiles of apolipoproteins and apolipoprotein B-containing lipoprotein particles in dyslipoproteinemia _Clin Chem_ 1988 34 (8B): B13–B27. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Menzel H-J, Utermann
G . Apolipoprotein E phenotyping from serum by Western Blotting _Electrophoresis_ 1986 7: 492–495. Article CAS Google Scholar * Kelly ME, Clay MA, Mistry MJ, Hsieh-li HM, Harmony JAK .
Apolipoprotein E inhibition of proliferation of mitrogen-activated T lymphocytes: production of Interleukine 2 with reduced biological activity _Cell Immunol_ 1994 159: 124–139. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Song H, Saito K, Fujigaki S, Noma A, Ishiguro H, Nagatsu T, Seishima M . II-1β and TNFα suppress apolipoprotein (apo) E secretion and apo-AI expression in HepG2 cells
_Cytokine_ 1998 10: 275–280. Article CAS Google Scholar * Panichi V, Migliori M, De Pietro S, Taccola D, Andreini B, Metelli MR, Giovannini L, Palla R . The link of biocompatibility to
cytokine production _Kidney Int_ 2000 58: 96–103. Article Google Scholar * Mahley RW . Apolipoprotein E: from atherosclerosis to Alzheimer's disease and beyond _Curr Opin Lipidol_
1999 10: 207–217. Article CAS Google Scholar * Curtiss LK, Boisvert WA . Apolipoprotein E and atherosclerosis _Curr Opin Lipidol_ 2000 11: 243–251. Article CAS Google Scholar * Mazzone
T . Apolipoprotein E secretion by macrophages: its potential physiological functions _Curr Opin Lipidol_ 1996 7: 303–307. Article CAS Google Scholar * Yudkin JS, Kumari M, Humphries SE,
Mohamed-Ali V . Inflammation, obesity, stress and coronary heart disease: is interleukine-6 the link? _Atherosclerosis_ 2000 148: 209–214. Article CAS Google Scholar Download references
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by la Direction de la Recherche Clinique University Hospital, CHU Hôtel-Dieu, Nantes, France. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS *
Laboratoire de Biochimie fondamentale et appliquée, UFR de Pharmacie, Nantes, France K Bach-Ngohou, H Nazih, F Nazih-Sanderson & JM Bard * INSERM U539, CHU, Hôtel-Dieu, Nantes, France K
Bach-Ngohou, H Nazih, Y Zaïr, M Krempf & JM Bard * Laboratoire de Biochimie Spécialisée, CHU, Hôtel-Dieu, Nantes, France K Bach-Ngohou, D Le Carrer & JM Bard * Clinique
d'Endocrinologie, Maladies Métaboliques et Nutrition, CHU, Hôtel-Dieu, Nantes, France Y Zaïr & M Krempf Authors * K Bach-Ngohou View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * H Nazih View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * F Nazih-Sanderson View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Y Zaïr View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * D Le Carrer View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M Krempf View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * JM Bard View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to JM Bard. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE
Bach-Ngohou, K., Nazih, H., Nazih-Sanderson, F. _et al._ Negative and independent influence of apolipoprotein E on C-reactive protein (CRP) concentration in obese adults. Potential
anti-inflammatory role of apoE _in vivo_. _Int J Obes_ 25, 1752–1758 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801833 Download citation * Received: 06 February 2001 * Revised: 23 May 2001 *
Accepted: 13 June 2001 * Published: 11 December 2001 * Issue Date: 01 December 2001 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801833 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with
will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt
content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * apolipoprotein E * C-reactive protein * inflammation * cardiovascular disease * insulin resistance
