Play all audios:
ABSTRACT The p53 tumor suppressor protein inhibits proliferation by inducing either cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in response to cellular stresses. Mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) provide a
primary cell model system in which to examine both functions of p53. MEFs treated with gamma-rays undergo p53-dependent G1 arrest, while oncogene-expressing MEFs treated with a variety of
DNA-damaging agents undergo p53-dependent apoptosis. Although the p53-dependent G1 arrest checkpoint response to gamma-rays in MEFs has been well characterized, the response to other
DNA-damaging agents has not. Here, we examine the effects of commonly utilized chemotherapeutics, including doxorubicin, etoposide, and cisplatin, on cell cycle arrest in MEFs, and we define
the p53 dependence of these effects. In addition, we examine the response of MEFs to ultraviolet light (UVC), as a representative agent acting by inducing pyrimidine dimers. Although p53 is
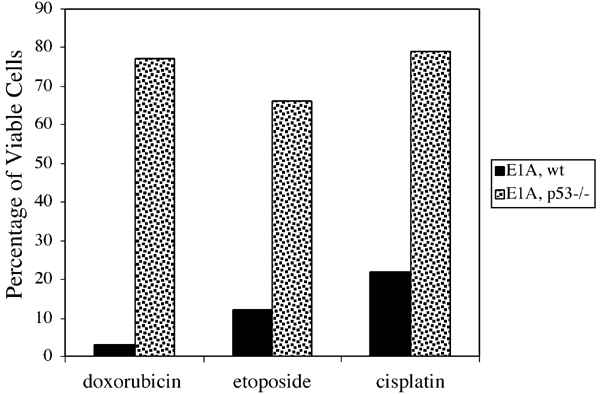
clearly activated by all the agents examined, as measured by p21 induction, there are surprising differences in the activities of these agents. For example, doxorubicin but not cisplatin
can effectively induce a p53-dependent G1 arrest. UVC, in contrast, induces a p53-independent G1 arrest response. Thus, the exact response of cells to DNA damage depends on the specific
agent used. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe
to this journal Receive 50 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $5.18 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF
Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact
customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS THE NUCKS1-SKP2-P21/P27 AXIS CONTROLS S PHASE ENTRY Article Open access 29 November 2021 PPM1D ACTIVITY PROMOTES CELLULAR
TRANSFORMATION BY PREVENTING SENESCENCE AND CELL DEATH Article Open access 05 September 2024 EMBRYONIC GENOME INSTABILITY UPON DNA REPLICATION TIMING PROGRAM EMERGENCE Article Open access 28
August 2024 REFERENCES * Appella E and Anderson CW . (2001). _Eur. J. Biochem._, 268, 2764–2772. * Attardi LD, Reczek EE, Cosmas C, Demicco EG, McCurrach ME, Lowe SW and Jacks T . (2000).
_Genes Dev._, 14, 704–718. * Bargonetti J and Manfredi JJ . (2002). _Curr. Opin. Oncol._, 14, 86–91. * Brugarolas J, Chandrasekaran C, Gordon JI, Beach D, Jacks T and Hannon GJ . (1995).
_Nature_, 377, 552–557. * Chang D, Chen F, Zhang F, McKay BC and Ljungman M . (1999). _Cell Growth Differ._, 10, 155–162. * Deng C, Zhang P, Harper JW, Elledge SJ and Leder P . (1995).
_Cell_, 82, 675–684. * El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1993). _Cell_, 75, 817–825. * Johnstone RW, Ruefli
AA and Lowe SW . (2002). _Cell_, 108, 153–164. * Kapoor M and Lozano G . (1998). _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_, 95, 2834–2837. * Kastan MB, Zhan Q, el-Deiry WS, Carrier F, Jacks T, Walsh WV,
Plunkett BS, Vogelstein B and Fornace Jr AJ . (1992). _Cell_, 71, 587–597. * Lowe SW, Ruley HE, Jacks T and Housman DE . (1993). _Cell_, 74, 957–967. * Lu H, Taya Y, Ikeda M and Levine AJ .
(1998). _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_, 95, 6399–6402. * Nelson WG and Kastan MB . (1994). _Mol. Cell. Biol._, 14, 1815–1823. * O'Dwyer PJ, Johnson SW and Hamilton TC . (1997).
_Principles and Practice of Oncology_. DeVita Jr V, Hellman S and Rosenberg SA (eds). Lippincott-Raven: Philadelphia, pp. 419–432. Google Scholar * Pines J . (1994). _Nature_, 369, 520–521.
* Soengas MS, Alarcon RM, Yoshida H, Giaccia AJ, Hakem R, Mak TW and Lowe SW . (1999). _Science_, 284, 156–159. * Stewart CF and Ratain MJ . (1997). _Principles and Practice of Oncology_.
DeVita Jr V, Hellman S and Rosenberg SA (eds). Lippincott-Raven: Philadelphia, pp. 452–467. Google Scholar * Tang D, Wu D, Hirao A, Lahti JM, Liu L, Mazza B, Kidd VJ, Mak TW and Ingram AJ .
(2002). _J. Biol. Chem._, 277, 12710–12717. * Wahl GM and Carr AM . (2001). _Nat. Cell. Biol._, 3, E277–E286. * Waldman T, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1995). _Cancer Res._, 55,
5187–5190. * Zamble DB, Jacks T and Lippard SJ . (1998). _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_, 95, 6163–6168. * Zhou BB and Elledge SJ . (2000). _Nature_, 408, 433–439. Download references
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank J Sage, J Brugarolas, E Flores, A Giaccia, M Brown, G Chu, G Wahl, S Lowe, K Cimprich, S Artandi, R Ihrie, and T Johnson for critical reading of the manuscript.
This work has been supported by the American Cancer Society, the Bunting Institute at Radcliffe College, Merck, and the Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation to LDA and by the Dutch Cancer
Society to ADV. This work has been supported by the HHMI and NCI funding to TJ. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Radiation Oncology and Department of Genetics,
Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, 94305-5152, CA, USA Laura D Attardi * Laboratory of Toxicology, Pathology and Genetics, National Institute of Public Health, Bilthoven, 3720
BA, The Netherlands Annemieke de Vries * Department of Biology, MIT, Cambridge, 02139, MA, USA Tyler Jacks * Howard Hughes Medical Institute, MIT, Cambridge, 02139, MA, USA Tyler Jacks
Authors * Laura D Attardi View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Annemieke de Vries View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * Tyler Jacks View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Laura D Attardi.
RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Attardi, L., de Vries, A. & Jacks, T. Activation of the p53-dependent G1 checkpoint response in mouse
embryo fibroblasts depends on the specific DNA damage inducer. _Oncogene_ 23, 973–980 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207026 Download citation * Received: 12 May 2003 * Revised: 18
July 2003 * Accepted: 21 July 2003 * Published: 29 January 2004 * Issue Date: 29 January 2004 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207026 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following
link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature
SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * p53 * cell cycle arrest * apoptosis * chemotherapeutics * DNA damage