Play all audios:
ABSTRACT ShcC is a family member of the Shc docking proteins that possess two different phosphotyrosine-binding motifs and conduct signals as Grb2-binding substrates of various receptor
tyrosine kinases. We have recently shown that some neuroblastoma cell lines, such as NB-39-nu cells, express a protein complex of hyperphosphorylated ShcC and anaplastic lymphoma kinase
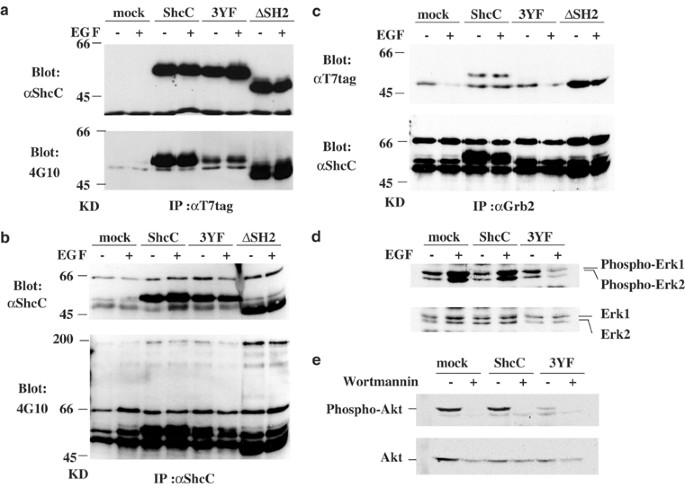
(ALK), which is self-activated by gene amplification. Here, we demonstrate that the expression of a mutant ShcC lacking Grb2-binding sites, 3YF-ShcC, significantly impaired the survival,
differentiation and motility of NB-39-nu cells by blocking the ERK and Akt pathways. On the other hand, cells overexpressing ShcC or 3YF-ShcC, but not a mutant ShcC that lacks SH2, showed
decreased anchorage independency and _in vivo_ tumorigenicity, suggesting a novel ShcC-specific suppressive effect through its SH2 domain on cell transformation. Notably, overexpression of
ShcC suppressed the sustained phosphorylation of Src family kinase after cell detachment, which might be independent of phosphorylation of Grb2-binding site. It was indicated that the
Src/Fyn-Cas pathway is modulated as a target of these suppressive effects by ShcC. Reciprocal change of ShcC expression and phosphorylation observed in malignant neuroblastoma cell lines
might be explained by these phosphotyrosine-dependent and -independent functions of ShcC. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access
via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 50 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $5.18 per issue Learn more Buy
this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: *
Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS EPS8 PHOSPHORYLATION BY SRC MODULATES ITS ONCOGENIC
FUNCTIONS Article Open access 09 July 2020 GRB2 BINDING INDUCES PHOSPHORYLATION-INDEPENDENT ACTIVATION OF SHP2 Article Open access 01 April 2021 PKD PHOSPHORYLATION AND COP9/SIGNALOSOME
MODULATE INTRACELLULAR SPRY2 PROTEIN STABILITY Article Open access 12 April 2023 REFERENCES * Andrechek ER, Hardy WR, Siegel PM, Rudnicki MA, Cardiff RD and Muller WJ . (2000). _Proc. Natl.
Acad. Sci. USA_, 97, 3444–3449. * Collins LR, Ricketts WA, Yeh L and Cheresh D . (1999). _J. Cell Biol._, 147, 1561–1568. * Folkman J and Moscona A . (1978). _Nature_, 273, 345–349. *
Freedman VH and Shin SI . (1974). _Cell_, 3, 355–359. * Frisch SM and Francis H . (1994). _J. Cell Biol._, 124, 619–626. * Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y and Ben-Sasson SA . (1992). _J. Cell Biol._,
119, 493–501. * Giancotti FG . (1997). _Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol._, 9, 691–700. * Gu J, Tamura M, Pankov R, Danen EH, Takino T, Matsumoto K and Yamada KM . (1999). _J. Cell Biol._, 146,
389–403. * Honda H, Nakamoto T, Sakai R and Hirai H . (1999). _Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun._, 262, 25–30. * Honda H, Oda H, Nakamoto T, Honda Z, Sakai R, Suzuki T, Saito T, Nakamura K,
Nakao K, Ishikawa T, Katsuki M, Yazaki Y and Hirai H . (1998). _Nat. Genet._, 19, 361–365. * Iwahara T, Fujimoto J, Wen D, Cupples R, Bucay N, Arakawa T, Mori S, Ratzkin B and Yamamoto T .
(1997). _Oncogene_, 14, 439–449. * Kumar CC . (1998). _Oncogene_, 17, 1365–1373. * McNeil PL, McKenna MP and Taylor DL . (1985). _J. Cell Biol._, 101, 372–379. * Miyake I, Hakomori Y,
Shinohara A, Gamou T, Saito M, Iwamatsu A and Sakai R . (2002). _Oncogene_, 21, 5823–5834. * Morris SW, Naeve C, Mathew P, James PL, Kirstein MN, Cui X and Witte DP . (1997). _Oncogene_, 14,
2175–2188. * Nakamura N, Chin H, Miyasaka N and Miura O . (1996a). _J. Biol. Chem._, 271, 19483–19488. * Nakamura T, Sanokawa R, Sasaki Y, Ayusawa D, Oishi M and Mori N . (1996b).
_Oncogene_, 13, 1111–1121. * O'Bryan JP, Martin CB, Songyang Z, Cantley LC and Der CJ . (1996a). _J. Biol. Chem._, 271, 11787–11791. * O'Bryan JP, Songyang Z, Cantley L, Der CJ and
Pawson T . (1996b). _Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA_, 93, 2729–2734. * Parsons JT and Weber MJ . (1989). _Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol._, 147, 79–127. * Pawson T, Gish GD and Nash P . (2001).
_Trends Cell Biol._, 11, 504–511. * Pelicci G, Dente L, De Giuseppe A, Verducci-Galletti B, Giuli S, Mele S, Vetriani C, Giorgio M, Pandolfi PP, Cesareni G and Pelicci PG . (1996).
_Oncogene_, 13, 633–641. * Pelicci G, Lanfrancone L, Grignani F, McGlade J, Cavallo F, Forni G, Nicoletti I, Pawson T and Pelicci PG . (1992). _Cell_, 70, 93–104. * Pelicci G, Troglio F,
Bodini A, Melillo RM, Pettirossi V, Coda L, De Giuseppe A, Santoro M and Pelicci PG . (2002). _Mol. Cell. Biol._, 22, 7351–7363. * Rozakis-Adcock M, Fernley R, Wade J, Pawson T and Bowtell D
. (1993). _Nature_, 363, 83–85. * Sakai R, Henderson JT, O'Bryan JP, Elia AJ, Saxton TM and Pawson T . (2000). _Neuron_, 28, 819–833. * Sakai R, Iwamatsu A, Hirano N, Ogawa S, Tanaka
T, Mano H, Yazaki Y and Hirai H . (1994). _EMBO J._, 13, 3748–3756. * Sidell N, Altman A, Haussler MR and Seeger RC . (1983). _Exp. Cell Res._, 148, 21–30. * Stevenson LE, Ravichandran KS
and Frackelton Jr AR . (1999). _Cell Growth Differ._, 10, 61–71. * Thomas D and Bradshaw RA . (1997). _J. Biol. Chem._, 272, 22293–22299. * van der Geer P, Wiley S, Gish GD and Pawson T .
(1996). _Curr. Biol._, 6, 1435–1444. * van der Geer P, Wiley S, Lai VK, Olivier JP, Gish GD, Stephens R, Kaplan D, Shoelson S and Pawson T . (1995). _Curr. Biol._, 5, 404–412. * Wang Y and
Sheibani N . (2002). _J. Cell. Biochem._, 87, 424–438. * Wary KK, Mainiero F, Isakoff SJ, Marcantonio EE and Giancotti FG . (1996). _Cell_, 87, 733–743. * Wary KK, Mariotti A, Zurzolo C and
Giancotti FG . (1998). _Cell_, 94, 625–634. * Wei L, Yang Y, Zhang X and Yu Q . (2002). _J. Cell. Biochem._, 87, 439–449. * Weng Z, Thomas SM, Rickles RJ, Taylor JA, Brauer AW, Seidel-Dugan
C, Michael WM, Dreyfuss G and Brugge JS . (1994). _Mol. Cell. Biol._, 14, 4509–4521. * Windham TC, Parikh NU, Siwak DR, Summy JM, McConkey DJ, Kraker AJ and Gallick GE . (2002). _Oncogene_,
21, 7797–7807. Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This study was supported by the Program for Promotion of Fundamental Studies in Health Sciences of Organization for Pharmaceutical Safety
and Research of Japan, and was also supported by a grant from SBS, Inc. Izumi Miyake is the recipient of Research Resident Fellowships from the Japan Health Sciences Foundation. AUTHOR
INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Growth Factor Division, National Cancer Center Research Institute, 5-1-1 Tsukiji, Chuo-ku, Tokyo, 104-0045, Japan Izumi Miyake, Yuko Hakomori &
Ryuichi Sakai * Department of Pediatrics, Kitasato University School of Medicine, 1-15-1 Kitasato, Sagamihara-shi, Kanagawa, 228-8555, Japan Izumi Miyake, Yoko Misu, Hisaya Nakadate &
Nobuo Matsuura * Department of Pathology, Keio University School of Medicine, 35 Shinanomachi, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo, 160-8582, Japan Michiie Sakamoto Authors * Izumi Miyake View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Yuko Hakomori View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Yoko Misu View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Hisaya Nakadate View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Nobuo Matsuura View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Michiie Sakamoto View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * Ryuichi Sakai View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Ryuichi Sakai. ADDITIONAL
INFORMATION Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc) SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE (TIF 174 KB) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS
Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Miyake, I., Hakomori, Y., Misu, Y. _et al._ Domain-specific function of ShcC docking protein in neuroblastoma cells. _Oncogene_
24, 3206–3215 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208523 Download citation * Received: 12 October 2004 * Revised: 30 December 2004 * Accepted: 12 January 2005 * Published: 21 February
2005 * Issue Date: 28 April 2005 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208523 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable
link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * ShcC *
neuroblastoma * dominant-negative form * SH2 domain * Src family kinase