Play all audios:
ABSTRACT BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES Mechanisms of obesity-associated insulin resistance and dysglycemia in South Asians remain relatively unknown. The objective of this study was to detect
subcutaneous (SAT) vs. visceral (VAT) adipose tissue characteristics and adipocytokines associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and dysglycemia in South Asian women. SUBJECTS/METHODS
This was a hospital-based cross-sectional study conducted in Sri Lanka. Subjects comprised of 58 adult women who underwent routine abdominal surgeries. SAT and VAT were obtained from
anterior abdominal wall and omentum, respectively. Measures of adiposity, serum insulin and glucose, SAT and VAT crown-like structures (CLS), macrophages, resistin by immunohistochemistry,
mean adipocyte area (MAA), and serum adipocytokines were examined. RESULTS The homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) score significantly correlated with age and waist
circumference (WC), but not with body mass index (BMI). Although the number of CLS positively correlated with BMI, there were no significant differences between the number of CLS in women
with normal fasting glucose (NFG) vs. those with impaired fasting glucose (IFG), indicating that adipose tissue macrophage infiltration is unlikely to be related to dysglycemia. In contrast,
serum resistin level was on average 60% higher in women with IFG compared to ones with NFG (_p_ < 0.05). Serum resistin levels correlated with age (_r_ = 0.36, _p_ < 0.05) and WC (_r_
= 0.27, _p_ < 0.05). There were no associations in serum levels of other adipocytokines with IFG. Adipose immunohistochemistry showed that women with IFG had a higher percentage of
resistin positive adipocytes in SAT compared to ones with NFG. MAA of VAT, but not SAT, correlated with both BMI and WC. CONCLUSIONS Resistin may be an important adipokine linking central
adiposity and insulin resistance in South Asian women. Both systemic and adipose tissue resistin are linked to dysglycemia in these individuals and may be a potential biomarker for diabetes
in this population. SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS ENLARGED ADIPOCYTES FROM SUBCUTANEOUS VS. VISCERAL ADIPOSE TISSUE DIFFERENTIALLY CONTRIBUTE TO METABOLIC DYSFUNCTION AND
ATHEROGENIC RISK OF PATIENTS WITH OBESITY Article Open access 19 January 2021 ANALYSIS OF AN INDIAN DIABETES PREVENTION PROGRAMME ON ASSOCIATION OF ADIPOKINES AND A HEPATOKINE WITH INCIDENT
DIABETES Article Open access 13 October 2021 SEX-SPECIFIC ASSOCIATION OF VISCERAL AND SUBCUTANEOUS ADIPOSE TISSUE VOLUMES WITH SYSTEMIC INFLAMMATION AND INNATE IMMUNE CELLS IN PEOPLE LIVING
WITH OBESITY Article 22 December 2023 INTRODUCTION Type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a major health problem in the world as well as in South Asia1. A combination of insulin resistance and
pancreatic beta cell dysfunction are mechanistically responsible for the pathogenesis of T2DM2. Obesity, especially visceral adiposity, is a major risk factor for insulin resistance and
T2DM3. Obese individuals develop insulin resistance, which is attributed to (A) a chronic low-grade inflammation in white adipose tissue, (B) dysregulation of adipocytokine secretion, and
(C) ectopic lipid deposition and lipotoxicity4. Adipose tissue inflammation can lead to dysregulation of adipocytokine secretion that can induce insulin resistance in insulin-sensitive
tissues, such as skeletal muscle and liver. While mechanisms responsible for dysglycemia and insulin resistance have been studied in detail in western populations, these mechanisms have
hitherto been unexplored in detail in South Asians5. Indeed, individuals of South Asian descent have a higher risk of developing T2DM for a given body mass index (BMI) compared to
Caucasians. Therefore, it is likely that different mechanisms operate in the pathogenesis of obesity-associated insulin resistance and dysglycemia in South Asians5. It is especially
important to dissect these mechanisms given the recent escalation of obesity6 and its co-morbidities in this region7. Our aim in the current study was to understand the mechanisms leading to
insulin resistance and dysglycemia in South Asian women. We hypothesized that defective adipose tissue expansion during positive energy balance would give rise to dysregulated adipocytokine
secretion, which in turn leads to insulin resistance and dysglycemia in South Asian adults. To test this hypothesis, we studied metabolic markers, adipocytokines, and visceral (VAT), and
subcutaneous white adipose tissue (SAT) characteristics of adult women who were hospitalized for routine abdominal surgery. MATERIALS/SUBJECTS AND METHODS SUBJECTS The study group comprised
58 adult women who presented at Teaching Hospital, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka for a routine abdominal surgery (Age range 18–75; hysterectomy, _n_ = 23; laparoscopy, _n_ = 9; explorative
laparotomy, _n_ = 6; para-umbilical hernia repair, _n_ = 6; other, _n_ = 14). The Ethical Review Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, University of Peradeniya, approved this study. Patients
with T2DM, inflammatory conditions, cancer, or previous abdominal surgery were excluded. Demographic data, diet, and physical activity history were obtained using an
interviewer-administered questionnaire. Height was measured by a stadiometer to the nearest millimeter. Weight was measured by a digital scale to the nearest 100 g. Waist circumference was
measured midway between the lowest rib and the superior border of the iliac crest in the mid axillary line, with an inelastic measuring tape at the end of normal expiration to the nearest
millimeter. BMI was calculated [BMI = weight (kg)/height2 (m2)]. BMI cutoffs for Asians were used to classify different BMI categories. SERUM BIOMARKERS AND ADIPOCYTOKINES Following an
overnight fast, blood was collected into eppendorf tubes and allowed to clot on ice. Serum was separated via centrifugation. The supernatant was frozen and stored for subsequent analysis.
Serum glucose was measured by the glucose oxidase method. Serum insulin (EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA, Cat. #EZHI-14K), high-molecular weight (HMW) adiponectin (EMD Millipore, St.
Charles, Missouri, USA, Cat. #SPREZHMWADPN65K), Interleukin (IL)−8 (Bio-Techne Corporation, Minneapolis, MN, USA, Cat. #D8000C), IL-10 (RayBiotech, Inc., Norcross, GA, USA, Cat. #ELH-IL-10),
chemerin (BioVendor, Asheville, NC, USA, Cat. #RD191136200R), omentin-1 (BioVendor, Asheville, NC, USA, CAT. #RD191100200R), and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) (MP Biomedicals,
Solon, OH, USA; Cat. # 07BC-1119) were assayed using commercially available ELISA kits. Serum tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, total adiponectin and resistin were measured utilizing
Luminex XMAP technology Magpix™, Human Adipokine Magnetic Bead Panel I (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA; Cat. # HADK1MAG-61K). Milliplex® Human Adipokine Magnetic Bead Panel II (EMD Millipore,
Billerica, MA, USA; Cat. # HADK2MAG-61K) was used to measure IL-6, leptin, and monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)-1. Homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) score was
calculated as fasting glucose (mmol/L) x fasting insulin (mU/L) / 22.5. ADIPOSE TISSUE HISTOLOGY AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY During surgery, samples of greater omentum (VAT) and fat from the
anterior abdominal wall midway between the umbilicus and the pubic symphysis (SAT) were collected and fixed with formalin. Paraffin embedded and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained
tissue sections were prepared. The number of crown-like structures (CLS) per 25 fields of x10 objective (Olympus CX 31microscope) were calculated by a histopathologist blinded to the patient
details. Adipocyte size was measured using the ImageJ software (mean surface area of 100 adipocytes in each biopsy). Immunohistochemistry (IHC) for resistin and CD 68 was performed on
paraffin embedded sections using heat induced antigen retrieval method. The primary antibodies used were polyclonal rabbit anti resistin antibody (LS Bio, LS-B12981) and monoclonal mouse CD
68 (Dako, clone PG-M1, Code–Nr.M 0876). For visualization, a secondary antibody kit with peroxidase detection system was used (Dako REAL EnVision, detection system, Peroxidase/DAB,
rabbit/mouse). CD 68 was used to confirm the presence of macrophages in adipose tissue sections with or without forming CLS. Resistin expression in adipocytes was assessed and granular
cytoplasmic positivity was regarded as true positivity. The amount of resistin positive adipocytes in a given tissue section was expressed as a percentage of all adipocytes by visual
assessment. The strength and number of resistin positivity in macrophages when present in tissue sections were also documented. ULTRASOUND SCAN OF THE ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL The thickness
of anterior abdominal wall was measured in five places (left and right upper, left and right lower and midline around umbilicus) by ultrasound scanning and the recoding was obtained in
centimeters. Similar techniques have been employed previously to estimate the subcutaneous fat content in the abdominal wall8. DATA ANALYSIS Sample size was determined by a priori power
calculation, based on estimated detectable differences and standard deviations in adipocyte size and HOMA-IR score sufficient to achieve 80% statistical power for the detection of a
difference with _p_ < 0.05. Data were analyzed using Microsoft Excel (2013), SPSS (Statistical and Products Service Solutions, Chicago) version 20 and GraphPad Prism software. Pearson’s
correlations were calculated to examine relations between variables. Mean values of continuous variables between two groups were compared using the independent samples _t_-test. One-way
ANOVA followed by post hoc testing was used to compare more than two groups. RESULTS SUBJECT CHARACTERISTICS The mean age of women in the study group was 46.1 years (SD = 12.7) with a mean
BMI of 25.4 (SD = 5.9). Of the 58 women, 18 (31%) were overweight (BMI between 23 and 27.49) and 19 (33%) were obese (BMI ≥ 27.5) as per the south Asian BMI scale9, while 43 women (74%) had
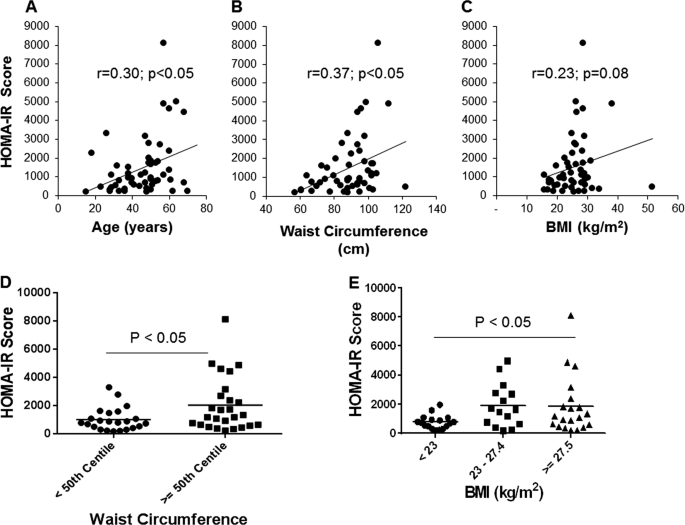
abdominal obesity (waist circumference ≥ 80 cm). VARIABLES ASSOCIATED WITH INSULIN RESISTANCE AND DYSGLYCEMIA First, we calculated the HOMA-IR score to assess the degree of insulin
resistance in these women. As illustrated in Fig. 1, HOMA-IR score exhibited significant positive correlations with age and waist circumference. Although the correlation between the HOMA-IR
score and BMI was not significant, obese (BMI ≥ 27.5) women had a significantly higher HOMA-IR score compared to normal weight women (BMI < 23). Women having a higher waist circumference
(≥50th centile in the group) also had a significantly higher HOMA-IR score compared to ones in the lower 50th centile, indicating that insulin resistance develops with increasing adiposity,
especially in the abdominal compartment. Next, we investigated potential mechanisms associated with insulin resistance and increasing visceral adiposity. A chronic low-grade inflammation
characterized by immune cell infiltration in the adipose tissue is causally linked to systemic insulin resistance10. These adipose tissue immune cell aggregates, which comprise macrophages
and other immune cell types such as T cells and B cells, can be identified as crown-like structures (CLS) under light microscopy11,12. Therefore, we next analyzed H&E stained sections of
VAT and SAT for CLS (_n_ = 38). As expected, the number of CLS per 25 fields of x10 objective positively correlated with BMI (Fig. 2). To better understand the association between increased
adiposity and adipose tissue inflammation, we measured the thickness of the anterior abdominal wall (AAWT) by ultrasound scanning in a subset of women (_n_ = 36) and found that this
thickness positively correlated with the number of CLS (_r_ = 0.57; _p_ < 0.05). Although the aforementioned associations provided evidence for adipose tissue inflammation, only 33% of
women had one or more CLS. Moreover, CLS were mainly found at higher levels of BMI (Fig. 2d, e). Finally, the number of CLS was not different between women with normal fasting glucose (NFG)
vs. impaired fasting glucose (IFG) (Fig. 2f). Therefore, adipose tissue macrophage infiltration per se is unlikely to be the major mechanism responsible for dysglycemia in these South Asian
women. CHARACTERISTICS OF WOMEN WITH NORMAL FASTING GLUCOSE VS. THOSE WITH IMPAIRED FASTING GLUCOSE White adipose tissue is an active endocrine organ. Adipose tissue hormones
(adipocytokines) can be dysregulated in obesity, which can lead to insulin resistance and dysglycemia10. Thus, we next analyzed the serum levels of major adipocytokines including leptin,
adiponectin, resistin, TNF-alpha, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, omentin-1, and chemerin, as well as the systemic inflammatory marker hsCRP in women with NFG vs. those with IFG (Table 1). As expected,
women with IFG had a higher waist circumference and HOMA-IR score compared to women with NFG. Of the studied adipocytokines, serum resistin was on average about 60% higher in the women with
IFG (_p_ < 0.05). SERUM AND ADIPOSE TISSUE RESISTIN Since resistin is known to be associated with insulin resistance13 and because we found that women with IFG have higher resistin levels
(Table 1), we next investigated factors associated with serum resistin. Figure 3 shows that serum resistin increases with age and waist circumference, and was trending significance with
increasing BMI. This potentially indicated that this adipokine is a potential link between increased visceral adiposity and dysglycemia. Since adipocyte size is linked to adipocyte function
and adipocytokine secretion14, next we investigated the relation between adipocyte size and resistin levels. While there was a trend for a positive correlation between mean VAT adipocyte
area and serum resistin level, this was not significant. There was no association between SAT adipocyte area and resistin (Fig. 3d, e). Finally, there was a positive correlation between
serum resistin and IL-6 levels (_r_ = 0.337, _p_ = 0.029), while none of the other studied adipocytokines correlated with resistin. It is well understood that resistin is primarily secreted
by adipocytes in rodents; however, the source of resistin in humans is controversial. Therefore, we performed immunohistochemistry of adipose tissue to study the resistin levels in this
tissue. We found that some, but not all adipocytes secrete resistin (Fig. 4). Moreover, adipocytes stained stronger for resistin than macrophages and the overall macrophage infiltration in
adipose tissue was sparse, suggesting that adipocytes may be the primary source of resistin in the adipose tissue in these women. SAT had a higher percentage of resistin positive adipocytes
compared to VAT, indicating depot-specific differences in resistin secretion (Fig. 4d). Importantly, women with IFG had a significantly higher percentage of resistin positive adipocytes in
the SAT compared with participants with NFG (Fig. 4e), suggesting that local resistin secretion in adipose tissue may be linked to dysglycemia. However, there was no correlation between
serum resistin level and the percentage of resistin positive cells in adipose tissue, suggesting that adipocyte resistin may not be the only contributor to serum resistin. ADIPOSITY,
ADIPOCYTE SIZE, AND INSULIN RESISTANCE Adipose tissue expansion in obesity occurs via adipocyte hyperplasia and hypertrophy15. The latter is characterized by increased adipocyte size and is
associated with insulin resistance15. To gain an understanding about the adipocyte expansion in these women, we compared the adipocyte area of different depots with adiposity measures.
Figure 5 shows that adipocytes were larger in the subcutaneous depot compared to the visceral depot. Adipocytes in the VAT became progressively larger when the BMI category increased. This
relationship was less marked in the SAT. VAT mean adipocyte area significantly correlated with BMI, waist circumference and mean anterior abdominal wall thickness (Fig. 5), suggesting that
visceral adipose tissue expands mainly by hypertrophy. In contrast, the mean adipocyte area of the SAT did not show correlations with BMI, waist circumference or anterior abdominal wall
thickness, suggesting that this adipose tissue depot mainly expands via adipocyte hyperplasia rather than hypertrophy. DISCUSSION The aim of the current study was to investigate the early
mechanistic derangements of glucose metabolism leading to type-2 diabetes (T2DM) in South Asian women. Therefore, we studied a sample of women with all categories of BMI and a spectrum of
age. We identified increasing body mass, especially visceral adiposity, and aging as possible factors associated with insulin resistance in these women. Serum level of the adipocytokine
resistin was significantly higher in women with IFG and positively correlated with waist circumference. Moreover, women with IFG had a higher percentage of resistin positive cells in adipose
tissue. To our knowledge, this is the first study to perform resistin immunohistochemistry in human adipose tissue and show that adipose tissue resistin expression is associated with
dysglycemia. Thus, it is plausible that both adipose tissue and systemic resistin are linked to dysglycemia in South Asian women. FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH INSULIN RESISTANCE The prevalence of
T2DM has increased alarmingly in the recent past and South Asia has not been spared of this heavy burden1. Insulin resistance and a decreased insulin secretory capacity of the pancreas are
the two key factors important in the pathogenesis of T2DM16,17. Therefore, identifying mechanisms responsible for insulin resistance is of interest. In the current study, we identified waist
circumference and age as two factors associated with insulin resistance. These findings are in agreement with previous studies which have shown that both waist circumference18 and visceral
adiposity19, as well as age20, are factors associated with insulin resistance and metabolic risk. While there was an association between HOMA-IR score and waist circumference, we did not
find a significant association between BMI and HOMA-IR score. This indicates that body fat distribution, rather than body mass per se may be linked to insulin resistance in South Asian
women. There are several mechanisms which link increased visceral adiposity with insulin resistance4,21. First, a chronic low-grade inflammation occurring in adipose tissue characterized by
immune cell infiltration is linked to insulin resistance12,22. Second, the dysregulated adipocytokine secretory patterns from adipose tissue leading to a pro-inflammatory state can lead to
insulin resistance in insulin-sensitive tissues12,23. Third, a “lipid-spillover” effect leading to ectopic fat deposition in liver and skeletal muscle can impair insulin signaling and
downstream metabolism culminating in insulin resistance21,24. To explore the aforementioned first mechanism, we examined H&E stained sections of VAT and SAT for crown-like structures and
for the presence of macrophages by immunostaining. While we did find a correlation between the number of CLS per 25 fields of x10 objective with both BMI and anterior abdominal wall
thickness, a significant number of CLS was found only at higher BMI levels. Moreover, there was no significant difference in the number of CLS between women with IFG vs. ones with NFG. In
contrast, some studies, especially in morbidly obese Caucasian subjects, have shown that adipose tissue macrophages are associated with systemic insulin resistance25. Taken together, this
suggests that adipose tissue immune cell infiltration is unlikely to be a major mechanism for dysglycemia in South Asian women. To assess the endocrine function of adipose tissue, we
measured the serum levels of several adipokines. We found that serum resistin was on average around 60% higher in women with IFG compared to those with NFG. Resistin is an adipokine secreted
by adipocytes, which is increased in obesity and induces insulin resistance in rodents13. Moreover, resistin knockout exerts metabolic benefits in rodents26. However, the link between
resistin, obesity and insulin resistance is inconsistent in humans, with some studies showing a positive association between serum resistin and insulin resistance27,28, while others report
no such relationship29,30. According to findings from the current study, it is likely that resistin is a key link between visceral adiposity and dysglycemia in South Asian women. RESISTIN
AND INSULIN RESISTANCE The source of serum resistin in humans is debatable. While resistin is considered to be an adipocytokine in rodents, resistin expression is highest in the bone marrow
immune cells in humans31. While human adipocytes express both resistin gene and protein32, some studies suggest that macrophages may be the major source of resistin in adipose tissue33. In
the current study, we performed immunohistochemistry to identify resistin protein expression in adipose tissue. Resistin expression in adipocytes was assessed and granular cytoplasmic
positivity was regarded as true positivity. The amount of resistin positive adipocytes in a given tissue section was expressed as a percentage of all adipocytes by microscopic assessment. We
did not use an automated method to quantify resistin because resistin positive cells were not uniformly distributed and there were many other non-specific peroxidase staining as found in
plasma in blood vessels. This type of analysis is recommended when there are only few positive cells for an immunostain34. We found that women with IFG had a higher percentage of resistin
positive cells, suggesting that local adipose tissue resistin may affect glucose homeostasis. Mechanistically, resistin induces insulin resistance by interfering with the insulin signaling
cascade, via activation of the serine kinases Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and via activating the Toll-like receptor 435. Indeed, resistin inhibits
glucose uptake by human adipocytes36 and rodent skeletal muscle cells37,38 in vitro. Since adipose tissue resistin secretion is not upregulated by lipopolysaccharide39, it cannot be
considered as a marker of adipose tissue inflammation. Therefore, it is likely that resistin is an adipocytokine, which has local as well as systemic effects on glucose homeostasis. While we
found that both serum and adipose tissue resistin were higher in women with IFG, there was no correlation between the serum and adipose tissue levels of this adipokine. Therefore, it is
unlikely that adipose tissue is the only source of resistin in these subjects. It is likely that in addition to immune cells, liver may also be a significant source of resistin in humans39.
INFLAMMATORY MARKERS, ADIPOCYTOKINES, AND DYSGLYCEMIA In the current study, we did not find any significant differences in serum adiponectin, leptin, TNF-alpha, MCP-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10,
chemerin, or omentin-1 levels between women with NFG vs. those with IFG. Previous studies have reported that South Asians have lower serum adiponectin levels compared to Caucasians40, which
has been pointed as a reason for the higher risk of T2DM among the former. Further, some studies have shown that adiponectin levels are inversely related to subsequent diabetes risk in
Asians41. There are some reports of other cytokines, such as TNF-alpha42, IL-6, MCP-1 and chemerin being increased12,30, and omentin-1 decreased in obesity and metabolic syndrome30. However,
we did not find such associations. ADIPOSE TISSUE EXPANSION IN OBESITY Adipocyte size is a strong determinant of the adipokine secretory patterns, with larger adipocytes producing more
pro-inflammatory adipokines43. Although we found that there was a trend for a positive correlation between serum resistin and mean adipocyte area in VAT, this was not significant. Further,
we did not find associations between adipocyte size and other serum adipokine levels. Previous studies have shown that South Asians have an increased visceral adipocyte area compared to
Caucasians40. The differences in insulin and adiponectin between these two populations are attributed to this difference in adipocyte size40. Adipocyte hypertrophy is a maladaptive response
to positive energy balance44. During positive energy balance, excess energy is stored in adipose tissue in the form of fat. The lipid storage capacity of the adipose tissue is increased by
either adipocyte hyperplasia or hypertrophy. When there is a defect in adipose tissue expansion, especially in adipogenesis and adipocyte hyperplasia, adipocytes can undergo hypertrophy and
ectopic fat deposition occurs in liver and skeletal muscle leading to insulin resistance21,24. In the current study, we found positive associations between VAT mean adipocyte area and all
indices of adiposity (BMI, waist circumference, and anterior abdominal wall thickness), while no such association was found in SAT. This potentially indicates: (A) a better ability of SAT to
expand without adipocyte hypertrophy, whereas VAT expands mainly by hypertrophy and (B) lipids being partitioned towards VAT, even with small increases in adiposity. In conclusion, insulin
resistance was associated with age and central adiposity in South Asian women. Serum and adipose tissue resistin may be an important adipocytokine linking central adiposity, insulin
resistance and dysglycemia in these women. REFERENCES * Chan, J. C. et al. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. _JAMA_ 301, 2129–340 (2009). Epub 2009/05/28.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Savage, D. B., Petersen, K. F. & Shulman, G. I. Disordered lipid metabolism and the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. _Physiol. Rev._ 87, 507–520
(2007). Epub 2007/04/13. Article CAS Google Scholar * Bogardus, C., Lillioja, S., Mott, D. M., Hollenbeck, C. & Reaven, G. Relationship between degree of obesity and in vivo insulin
action in man. _Am. J. Physiol._ 248(3 Pt 1), E286–E291 (1985). Epub 1985/03/01. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hardy, O. T., Czech, M. P. & Corvera, S. What causes the insulin
resistance underlying obesity? _Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes._ 19, 81–87 (2012). Epub 2012/02/14. Article CAS Google Scholar * Unnikrishnan, R., Anjana, R. M. & Mohan, V.
Diabetes in South Asians: is the phenotype different? _Diabetes_ 63, 53–55 (2014). Epub 2013/12/21. Article CAS Google Scholar * Jayawardana, N. W. et al. Lifestyle factors associated
with obesity in a cohort of males in the central province of Sri Lanka: a cross-sectional descriptive study. _BMC Public Health_ 17, 27 (2017). Epub 2017/01/07. Article CAS Google Scholar
* Jayawardana, N. et al. Aging and obesity are associated with undiagnosed hypertension in a cohort of males in the Central Province of Sri Lanka: a cross-sectional descriptive study. _BMC
Cardiovasc. Disord._ 17, 165 (2017). Epub 2017/06/24. Article CAS Google Scholar * Suzuki, R. et al. Abdominal wall fat index, estimated by ultrasonography, for assessment of the ratio
of visceral fat to subcutaneous fat in the abdomen. _Am. J. Med._ 95, 309–314 (1993). Epub 1993/09/01. Article CAS Google Scholar * Stegenga, H., Haines, A., Jones, K. & Wilding, J.
Identification, assessment, and management of overweight and obesity: summary of updated NICE guidance. _BMJ (Clinical research ed)._ 349, g6608 (2014). Epub 2014/11/29. Google Scholar *
Kalupahana, N. S., Moustaid-Moussa, N. & Claycombe, K. J. Immunity as a link between obesity and insulin resistance. _Mol. Asp. Med._ 33, 26–34 (2012). Epub 2011/11/02. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Apovian, C. M. et al. Adipose macrophage infiltration is associated with insulin resistance and vascular endothelial dysfunction in obese subjects. _Arterioscler. Thromb.
Vasc. Biol._ 28, 1654–1659 (2008). Epub 2008/06/21. Article CAS Google Scholar * Bremer, A. A., Devaraj, S., Afify, A. & Jialal, I. Adipose tissue dysregulation in patients with
metabolic syndrome. _J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab._ 96, E1782–E1788 (2011). Epub 2011/08/26. Article CAS Google Scholar * Steppan, C. M. et al. The hormone resistin links obesity to
diabetes. _Nature_ 409, 307–312 (2001). Epub 2001/02/24. Article CAS Google Scholar * Gustafson, B. et al. Inflammation and impaired adipogenesis in hypertrophic obesity in man. _Am. J.
Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab._ 297, E999–E1003 (2009). Epub 2009/07/23. Article CAS Google Scholar * Goossens, G. H. The role of adipose tissue dysfunction in the pathogenesis of
obesity-related insulin resistance. _Physiol. Behav._ 94, 206–218 (2008). Epub 2007/11/27. Article CAS Google Scholar * Lillioja, S. et al. Insulin resistance and insulin secretory
dysfunction as precursors of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Prospective studies of Pima Indians. _N. Eng. J. Med._ 329, 1988–1992 (1993). Epub 1993/12/30. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Haffner, S. M., Miettinen, H., Gaskill, S. P. & Stern, M. P. Decreased insulin secretion and increased insulin resistance are independently related to the 7-year risk of NIDDM
in Mexican-Americans. _Diabetes_ 44, 1386–1391 (1995). Epub 1995/12/01. Article CAS Google Scholar * Park, K. et al. Association of long-term change in waist circumference with insulin
resistance. _Obes. (Silver Spring, Md)._ 18, 370–376 (2010). Epub 2009/08/15. Article CAS Google Scholar * Ng, A. C., Wai, D. C., Tai, E. S., Ng, K. M. & Chan, L. L. Visceral adipose
tissue, but not waist circumference is a better measure of metabolic risk in Singaporean Chinese and Indian men. _Nutr. Diabetes_ 2, e38 (2012). Epub2012/01/01. Article CAS Google Scholar
* Ferrannini, E. et al. Insulin action and age. European Group for the Study of Insulin Resistance (EGIR). _Diabetes_ 45, 947–953 (1996). Epub 1996/07/01. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Grundy, S. M. Adipose tissue and metabolic syndrome: too much, too little or neither. _Eur. J. Clin. Invest._ 45, 1209–1217 (2015). Epub 2015/08/21. Article CAS Google Scholar * Lawler,
H. M. et al. Adipose tissue hypoxia, inflammation, and fibrosis in obese insulin-sensitive and obese insulin-resistant subjects. _J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab._ 101, 1422–1428 (2016). Epub
2016/02/13. Article CAS Google Scholar * Fain, J. N. Correlative studies on the effects of obesity, diabetes and hypertension on gene expression in omental adipose tissue of obese women.
_Nutr. Diabetes_ 1, e17 (2011). Epub2011/01/01. Article CAS Google Scholar * Smith, U. & Kahn, B. B. Adipose tissue regulates insulin sensitivity: role of adipogenesis, de novo
lipogenesis and novel lipids. _J. Intern. Med._ 280, 465–475 (2016). Epub 2016/10/21. Article CAS Google Scholar * Bigornia, S. J. et al. Relation of depot-specific adipose inflammation
to insulin resistance in human obesity. _Nutr. Diabetes_ 2, e30 (2012). Epub2012/01/01. Article CAS Google Scholar * Singhal, N. S., Patel, R. T., Qi, Y., Lee, Y. S. & Ahima, R. S.
Loss of resistin ameliorates hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis in leptin-deficient mice. _Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab._ 295, E331–E338 (2008). Epub 2008/05/29. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Hivert, M. F. et al. Associations of adiponectin, resistin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha with insulin resistance. _J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab._ 93, 3165–3172 (2008). Epub
2008/05/22. Article CAS Google Scholar * Parvaresh Rizi, E. et al. Ethnic differences in the role of adipocytokines linking abdominal adiposity and insulin sensitivity among asians. _J.
Clin. Endocrinol. Metab._ 100, 4249–4256 (2015). Epub 2015/08/27. Article Google Scholar * Heilbronn, L. K. et al. Relationship between serum resistin concentrations and insulin resistance
in nonobese, obese, and obese diabetic subjects. _J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab._ 89, 1844–1848 (2004). Epub 2004/04/09. Article CAS Google Scholar * Jialal, I., Devaraj, S., Kaur, H.,
Adams-Huet, B. & Bremer, A. A. Increased chemerin and decreased omentin-1 in both adipose tissue and plasma in nascent metabolic syndrome. _J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab._ 98, E514–E517
(2013). Epub 2013/01/11. Article CAS Google Scholar * Patel, L. et al. Resistin is expressed in human macrophages and directly regulated by PPAR gamma activators. _Biochem. Biophys. Res.
Commun._ 300, 472–476 (2003). Epub 2002/12/31. Article CAS Google Scholar * McTernan, P. G. et al. Increased resistin gene and protein expression in human abdominal adipose tissue. _J.
Clin. Endocrinol. Metab._ 87, 2407 (2002). Epub 2002/05/08. Article CAS Google Scholar * Savage, D. B. et al. Resistin / Fizz3 expression in relation to obesity and peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma action in humans. _Diabetes_ 50, 2199–2202 (2001). Epub 2001/09/28. Article CAS Google Scholar * Hammond, M. E. et al. American Society of Clinical
Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer (unabridged version). _Arch.
Pathol. Lab. Med._ 134, e48–e72 (2010). Epub 2010/07/01. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Benomar, Y. et al. Central resistin overexposure induces insulin resistance through Toll-like receptor
4. _Diabetes_ 62, 102–114 (2013). Epub 2012/09/11. Article CAS Google Scholar * McTernan, P. G. et al. Resistin and type 2 diabetes: regulation of resistin expression by insulin and
rosiglitazone and the effects of recombinant resistin on lipid and glucose metabolism in human differentiated adipocytes. _J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab._ 88, 6098–6106 (2003). Epub 2003/12/13.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Moon, B., Kwan, J. J., Duddy, N., Sweeney, G. & Begum, N. Resistin inhibits glucose uptake in L6 cells independently of changes in insulin signaling and
GLUT4 translocation. _Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab._ 285, E106–15 (2003). Epub 2003/03/06. Article CAS Google Scholar * Jorgensen, S. B. et al. Oligomeric resistin impairs insulin
and AICAR-stimulated glucose uptake in mouse skeletal muscle by inhibiting GLUT4 translocation. _Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab._ 297, E57–E66 (2009). Epub 2009/05/14. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Szalowska, E., Elferink, M. G., Hoek, A., Groothuis, G. M. & Vonk, R. J. Resistin is more abundant in liver than adipose tissue and is not up-regulated by
lipopolysaccharide. _J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab._ 94, 3051–3057 (2009). Epub 2009/05/21. Article CAS Google Scholar * Anand, S. S. et al. Adipocyte hypertrophy, fatty liver and metabolic
risk factors in South Asians: the Molecular Study of Health and Risk in Ethnic Groups (mol-SHARE). _PLoS. One._ 6, e22112 (2011). Epub2011/08/11. Article CAS Google Scholar * Yamamoto, S.
et al. Circulating adiponectin levels and risk of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese. _Nutr. Diabetes_ 4, e130 (2014). Epub2014/08/19. Article CAS Google Scholar * Olson, N. C. et al.
Circulating levels of TNF-alpha are associated with impaired glucose tolerance, increased insulin resistance, and ethnicity: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. _J. Clin.
Endocrinol. Metab._ 97, 1032–1040 (2012). Epub 2012/01/13. Article CAS Google Scholar * Skurk, T., Alberti-Huber, C., Herder, C. & Hauner, H. Relationship between adipocyte size and
adipokine expression and secretion. _J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab._ 92, 1023–1033 (2007). Epub 2006/12/14. Article CAS Google Scholar * Heilbronn, L., Smith, S. R. & Ravussin, E.
Failure of fat cell proliferation, mitochondrial function and fat oxidation results in ectopic fat storage, insulin resistance and type II diabetes mellitus. _Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab.
Disord.: J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes._ 28(Suppl 4), S12–S21 (2004).Epub 2004/12/14. Article CAS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We would like to acknowledge Mr. K.P.G.
Karunaratna, Mr. G.H.D.S. Chandraprabha and Mr. P.U.B. Harangala for their technical assistance. This research was funded by the International Research Center, University of Peradeniya, Sri
Lanka (InRC/2015/01), an International Research/Development Seed Grant from the Office of International Affairs at Texas Tech University, and an International Research Seed Grant from the
College of Human Sciences at Texas Tech University, and the Obesity Research Cluster at Texas Tech University. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Pathology, Faculty
of Medicine, University of Peradeniya, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka Sulochana Wijetunge * Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Peradeniya, Peradeniya, Sri
Lanka R. M. C. J. Ratnayake * Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, University of Peradeniya, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka H. M. S. R. B. Kotakadeniya * Department of Radiology, Faculty of
Medicine, University of Peradeniya, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka Shanthini Rosairo * Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Peradeniya, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka Kembra
Albracht-Schulte, Latha Ramalingam, Naima Moustaid-Moussa & Nishan Sudheera Kalupahana * Department of Nutritional Sciences and Obesity Research Cluster, Texas Tech University, Lubbock,
TX, USA Nishan Sudheera Kalupahana Authors * Sulochana Wijetunge View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * R. M. C. J. Ratnayake View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * H. M. S. R. B. Kotakadeniya View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Shanthini Rosairo View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Kembra Albracht-Schulte View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Latha Ramalingam View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Naima Moustaid-Moussa View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Nishan Sudheera Kalupahana View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHORS
Correspondence to Naima Moustaid-Moussa or Nishan Sudheera Kalupahana. ETHICS DECLARATIONS CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. ADDITIONAL
INFORMATION PUBLISHER’S NOTE: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS OPEN ACCESS This
article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as
you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party
material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s
Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Wijetunge, S., Ratnayake, R.M.C.J.,
Kotakadeniya, H.M.S.R.B. _et al._ Association between serum and adipose tissue resistin with dysglycemia in South Asian women. _Nutr & Diabetes_ 9, 5 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41387-019-0071-3 Download citation * Received: 30 March 2018 * Revised: 30 May 2018 * Accepted: 08 June 2018 * Published: 18 February 2019 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41387-019-0071-3 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative