Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Secondary acute lymphoblastic leukemia (s-ALL) comprises up to 10% of ALL patients. However, data regarding s-ALL outcomes is limited. To answer what is the role of allogeneic
hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) in s-ALL, a matched-pair analysis in a 1:2 ratio was conducted to compare outcomes between s-ALL and de novo ALL (_dn_-ALL) patients reported between
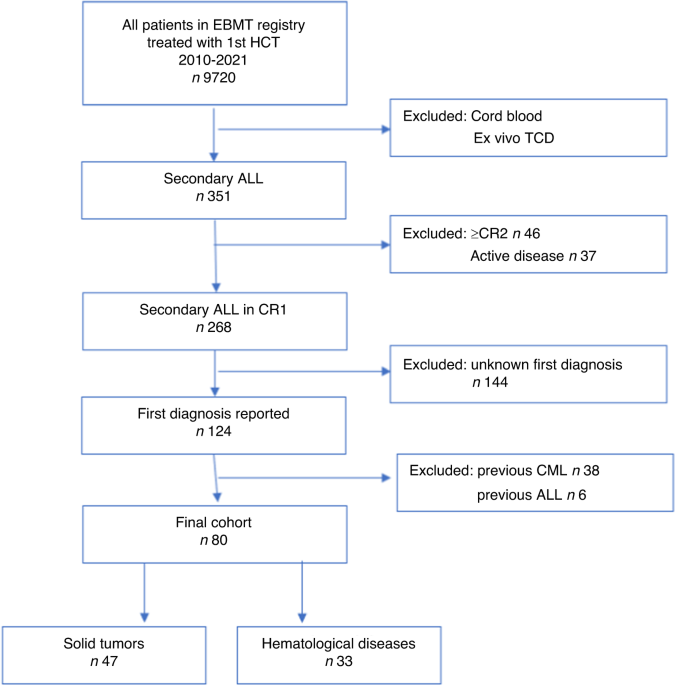
2000–2021 to the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation registry. Among 9720 ALL patients, 351 (3.6%) were s-ALL, of which 80 were in first complete remission (CR1) with a
known precedent primary diagnosis 58.8% solid tumor (ST), 41.2% hematological diseases (HD). The estimated 2-year relapse incidence (RI) was 19.1% (95%CI: 11–28.9), leukemia-free survival
(LFS) 52.1% (95%CI: 39.6–63.2), non-relapse mortality (NRM) 28.8% (95%CI: 18.4–40), GvHD-free, relapse-free survival (GRFS) 39.4% (95%CI: 27.8–50.7), and overall survival (OS) 60.8% (95%CI:
47.9–71.4), and did not differ between ST and HD patients. In a matched-pair analysis, there was no difference in RI, GRFS, NRM, LFS, or OS between s-ALL and _dn_-ALL except for a higher
incidence of chronic GvHD (51.9% vs. 31.4%) in s-ALL. To conclude, patients with s-ALL who received HCT in CR1 have comparable outcomes to patients with _dn_-ALL. Access through your
institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print
issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to
local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT
BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS CONTINUOUSLY IMPROVING OUTCOME OVER TIME AFTER SECOND ALLOGENEIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION IN RELAPSED ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA: AN EBMT REGISTRY ANALYSIS OF 1540
PATIENTS Article Open access 02 May 2024 ALLOGENEIC HEMATOPOIETIC CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR PATIENTS WITH ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA NOT IN REMISSION Article 21 December 2023 RELAPSE OF ACUTE
MYELOID LEUKEMIA AFTER ALLOGENEIC HEMATOPOIETIC CELL TRANSPLANTATION: CLINICAL FEATURES AND OUTCOMES Article 02 December 2020 DATA AVAILABILITY ASK, JMZ, ML, and MM had full access to all
study data (available upon data-specific request). REFERENCES * Giri S, Chi M, Johnson B, McCormick D, Jamy O, Bhatt VR, et al. Secondary acute lymphoblastic leukemia is an independent
predictor of poor prognosis. Leuk Res. 2015;39:1342–6. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Rosenberg AS, Brunson A, Paulus JK, Tuscano J, Wun T, Keegan THM, et al. Secondary acute
lymphoblastic leukemia is a distinct clinical entity with prognostic significance. Blood Cancer J. 2017;7:e605. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Aldoss I, Stiller T,
Tsai NC, Song JY, Cao T, Bandara NA, et al. Therapy-related acute lymphoblastic leukemia has distinct clinical and cytogenetic features compared to de novo acute lymphoblastic leukemia, but
outcomes are comparable in transplanted patients. Haematologica 2018;103:1662–8. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * McNerney ME, Godley LA, Le Beau MM. Therapy-related
myeloid neoplasms: when genetics and environment collide. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2017;17:513–27. * Khoury JD, Solary E, Abla O, Akkari Y, Alaggio R, Apperley JF, et al. The 5th edition of the
World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia. 2022;36:1703–19. * Alaggio R, Amador C, Anagnostopoulos I,
Attygalle AD, Araujo IB de O, Berti E, et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia. 2022;36:1720–48. *
Saygin C, Kishtagari A, Cassaday RD, Reizine N, Yurkiewicz I, Liedtke M, et al. Therapy-related acute lymphoblastic leukemia is a distinct entity with adverse genetic features and clinical
outcomes. Blood Adv. 2019;3:4228–37. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Barnea Slonim L, Gao J, Burkart M, Odetola OE, Kocherginsky M, Dinner SN, et al. Therapy-related
B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults has unique genetic profile with frequent loss of TP53 and inferior outcome. Leukemia 2021;35:2097–101. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Aldoss
I, Douer D, Pullarkat V. Therapy-related acute lymphoblastic leukemia: where do we stand with regards to its definition and characterization? Blood Rev. 2019;37:100584. * Pagano L, Pulsoni
A, Elena Tosti M, Annino L, Mele A, Camera A, et al. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia occurring as second malignancy: report of the GIMEMA archive of adult acute leukaemia. Br J Haematol.
1999;106:1037–40. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Swaika A, Frank RD, Yang D, Finn LE, Jiang L, Advani P, et al. Second primary acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults: a SEER
analysis of incidence and outcomes. Cancer Med. 2018;7:499–507. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Abdel Rahman ZH, Parrondo RD, Heckman MG, Wieczorek M, Miller KC, Alkhateeb H, et al.
Comparative study of therapy-related and de novo adult b-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2022;196:963–8. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Parrondo RD, Rahman ZA,
Heckman MG, Wieczorek M, Jiang L, Alkhateeb HB, et al. Unique characteristics and outcomes of therapy-related acute lymphoblastic leukemia following treatment for multiple myeloma. Blood
Cancer J. 2022;12:87. * Ferraro F, Gao F, Stockerl-Goldstein K, Westervelt P, DiPersio JF, Ghobadi A. Secondary acute lymphoblastic leukemia, a retrospective analysis from Washington
University and meta-analysis of published data. Leuk Res. 2018;72:86–91. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Meyer C, Burmeister T, Gröger D, Tsaur G, Fechina L, Renneville A,
et al. The MLL recombinome of acute leukemias in 2017. Leukemia 2018;32:273–84. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Nagler A, Ngoya M, Galimard JE, Labopin M, Kröger N, Socié G, et al.
Trends in outcome of transplantation in patients with secondary acute myeloid leukemia: an analysis from the Acute Leukemia Working Party (ALWP) of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transpl.
2022;57:1788–96. Article Google Scholar * Abdel Rahman ZH, Heckman MG, Miller K, Alkhateeb H, Patnaik MS, Sproat LZ, et al. Impact of novel targeted therapies and cytogenetic risk groups
on outcome after allogeneic transplantation for adult all. Transpl Cell Ther. 2021;27:165.e1–11. Article CAS Google Scholar * Vasudevan Nampoothiri R, Law AD, Lam W, Chen C, Al-Shaibani
Z, Loach D, et al. Outcomes of therapy-related acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Eur J Haematol. 2020;105:24–9. Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Aldoss I, Dagis A, Palmer J, Forman S, Pullarkat V. Therapy-related ALL: cytogenetic features and hematopoietic cell transplantation outcome. Bone Marrow Transplant.
2015;50:746–8. * Vasudevan Nampoothiri R, Pasic I, Law AD, Lam W, Chen C, Michelis FV, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with therapy-related hematologic
malignancies developing after multiple myeloma. Eur J Haematol. 2022;108:430–6. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Abdulwahab A, Sykes J, Kamel-Reid S, Chang H, Brandwein JM.
Therapy-related acute lymphoblastic leukemia is more frequent than previously recognized and has a poor prognosis. Cancer 2012;118:3962–7. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Tang G, Zuo Z,
Thomas DA, Lin P, Liu D, Hu Y, et al. Precursor B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia occurring in patients with a history of prior malignancies: Is it therapy-related? Haematologica
2012;97:919–25. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ganzel C, Devlin S, Douer D, Rowe JM, Stein EM, Tallman MS. Secondary acute lymphoblastic leukaemia is constitutional and
probably not related to prior therapy. Br J Haematol. 2015;170:50–5. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kelleher N, Gallardo D, González-Campos J, Hernández-Rivas JM, Montesinos P,
Sarrá J, et al. Incidence, clinical and biological characteristics and outcome of secondary acute lymphoblastic leukemia after solid organ or hematologic malignancy. Leuk Lymphoma.
2016;57:86–91. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kook HW, Kim JJ, Park MR, Jang JE, Min YH, Lee ST, et al. Therapy-related acute lymphoblastic leukaemia has a unique genetic profile
compared to de novo acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. J Cancer. 2022;13:3326–32. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Geyer MB, Shaffer BC, Bhatnagar B, Mims AS, Klein V,
Dilip D, Glass JL, et al. Lenalidomide-associated B-cell ALL: clinical and pathologic correlates and sensitivity to lenalidomide withdrawal. Blood Adv. 2023;7:3087–98. * Riazat-Kesh YJRA,
Mascarenhas J, Bar-Natan M. ‘Secondary’ acute lymphoblastic/lymphocytic leukemia-done playing second fiddle? Blood Rev. 2023;60:101070. * Aldoss I, Capelletti M, Park J, Pistofidis RS,
Pillai R, Stiller T, et al. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia as a clonally unrelated second primary malignancy after multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2019;33:266–70. Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Barnell EK, Skidmore ZL, Newcomer KF, Chavez M, Campbell KM, Cotto KC, et al. Distinct clonal identities of B-ALLs arising after lenolidomide therapy for multiple myeloma. Blood
Adv. 2023;7:236–45. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Sadowska-Klasa A, Abba M, Gajkowska-Kulik J, Zaucha JM. Therapy-related acute lymphoblastic leukemia following treatment for
multiple myeloma–diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma. Acta Oncol. 2022;61:1126–31. * Styczyński J, Tridello G, Koster L, Iacobelli S, van Biezen A, van der Werf S, et al. Death after
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: changes over calendar year time, infections and associated factors. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2020;55:126–36. Article Google Scholar * Pourhassan H,
Yang D, Afkhami M, Pillai R, Ball B, Al Malki M, et al. High prevalence and inferior long-term outcomes for TP53 mutations in therapy-related acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Hematol.
2022;97:E171–3. Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Hematology and Transplantology, Medical University of Gdańsk, Gdańsk, Poland A. Sadowska-Klasa
& J. M. Zaucha * Department of Hematology, Sorbonne University, Hopital Saint Antoine, Paris, France M. Labopin & M. Mohty * Department of Hematology, Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus,
BMT Service, Villejuif, France J. H. Bourhis * Programme de Transplantation & Therapie Cellulaire, Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie de Marseille, Institut Paoli Calmettes, Marseille,
France D. Blaise * CHU de Lille, LIRIC, INSERM U995, Université de Lille, Lille, France I. Yakoub-Agha * HUCH Comprehensive Cancer Center, Stem Cell Transplantation Unit, Helsinki, Finland
U. Salmenniemi * University Hospital, Hematology, Basel, Switzerland J. Passweg * CHU Lapeyronie, Département d’Hématologie Clinique, Montpellier, France N. Fegueux * Department of Bone
Marrow Transplantation, University Hospital, Essen, Germany T. Schroeder * Department of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Onco-Hematology, Maria Sklodowska-Curie National Research Institute
of Oncology, Gliwice Branch, Gliwice, Poland S. Giebel * Service d’Hématologie Clinique et Thérapie Cellulaire, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, AP-HP, Sorbonne University, and INSERM UMRs 938, Paris,
France E. Brissot * Ospedale San Raffaele, Haematology and BMT, Milan, Italy F. Ciceri Authors * A. Sadowska-Klasa View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * J. M. Zaucha View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M. Labopin View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * J. H. Bourhis View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * D. Blaise View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * I. Yakoub-Agha View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * U. Salmenniemi View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * J. Passweg View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * N. Fegueux View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * T. Schroeder View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * S. Giebel View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * E. Brissot View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * F. Ciceri View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M. Mohty View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS ASK
wrote the manuscript, designed the study, and interpreted the data. JMZ and MM designed the study, interpreted the data, and edited the manuscript. ML designed the study, performed the
statistical analyses, interpreted the data, and edited the manuscript. JHB, DB, IYA, US, JP, NF, TS, SG, EB, and FC reviewed the manuscript and provided clinical data. All authors approved
the final version of the manuscript. CORRESPONDING AUTHORS Correspondence to A. Sadowska-Klasa or J. M. Zaucha. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing
interests. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PUBLISHER’S NOTE Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. RIGHTS AND
PERMISSIONS Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s);
author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law. Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS
ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Sadowska-Klasa, A., Zaucha, J.M., Labopin, M. _et al._ Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation is equally effective in secondary acute lymphoblastic leukemia
(ALL) compared to de-novo ALL—a report from the EBMT registry. _Bone Marrow Transplant_ 59, 387–394 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-023-02192-0 Download citation * Received: 10
October 2023 * Revised: 16 December 2023 * Accepted: 20 December 2023 * Published: 09 January 2024 * Issue Date: March 2024 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-023-02192-0 SHARE THIS
ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative