Play all audios:
ABSTRACT The field of plasmonics1 offers a route to control light fields with metallic nanostructures through the excitation of surface plasmon polaritons2. These surface waves, bound to a
metal dielectric interface, can tightly confine electromagnetic energy3. Active control over surface plasmon polaritons has potential for applications in sensing4, photovoltaics5, quantum
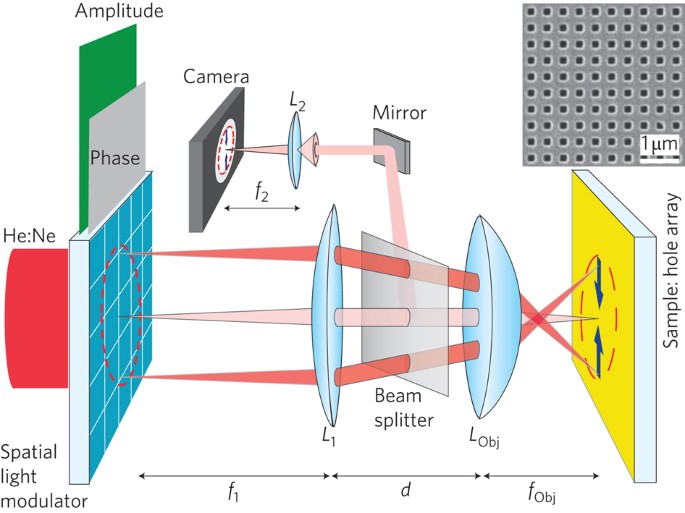
communication6,7, nanocircuitry8,9, metamaterials10,11 and super-resolution microscopy12. We achieve here active control of plasmonic fields using a digital spatial light modulator.
Optimizing the plasmonic phases through feedback, we focus surface plasmon polaritons at a freely prechosen point on the surface of a nanohole array. Digital addressing and scanning of
surface plasmon polaritons without mechanical motion may enable novel interdisciplinary applications of advanced plasmonic devices in cell microscopy, optical data storage and sensing.
Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this
journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer
support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS TUNABLE PHOTON-INDUCED SPATIAL MODULATION OF FREE ELECTRONS Article 26 January 2023 DYNAMIC CONTROL AND MANIPULATION OF NEAR-FIELDS USING
DIRECT FEEDBACK Article Open access 24 October 2024 DETECTION OF A PLASMON-POLARITON QUANTUM WAVE PACKET Article 13 February 2023 REFERENCES * Barnes, W. L., Dereux, A. & Ebbesen, T. W.
Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. _Nature_ 424, 824–830 (2003). Article ADS Google Scholar * Polman, A. Applied physics: plasmonics applied. _Science_ 322, 5903, 868–869 (2008).
Article Google Scholar * Schuller, J. A. et al. Plasmonics for extreme light concentration and manipulation. _Nature Mater._ 9, 193–204 (2010). Article ADS Google Scholar * Prodan, E.,
Radloff, C., Halas, N. J. & Nordlander, P. A hybridization model for the plasmon response of complex nanostructures. _Science_ 302, 419–422 (2003). Article ADS Google Scholar *
Atwater, H. A. & Polman, A. Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices. _Nature Mater._ 9, 205–213 (2010). Article ADS Google Scholar * Altewischer, E., van Exter, M. P. &
Woerdman, J. P. Plasmon-assisted transmission of entangled photons. _Nature_ 418, 304–306 (2002). Article ADS Google Scholar * Akimov, A. V. _et al._ Generation of single optical plasmons
in metallic nanowires coupled to quantum dots. _Nature_ 450, 402–406 (2007). Article ADS Google Scholar * Ebbesen, T. W., Genet, C. & Bozhevolnyi, S. I. Surface-plasmon circuitry.
_Phys. Today_ 61, 44–50 (2008). Article ADS Google Scholar * Engheta, N. Circuits with light at nanoscales: optical nanocircuits inspired by metamaterials. _Science_ 317, 1698–1702
(2007). Article ADS Google Scholar * Liu, N. _et al._ Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. _Nature Mater._ 8, 758–762 (2009). Article
ADS Google Scholar * Ergin, T., Stenger, N., Brenner, P., Pendry, J. B. & Wegener, M. Three-dimensional invisibility cloak at optical wavelengths. _Science_ 328, 337–339 (2010).
Article ADS Google Scholar * Fang, N., Lee, H., Sun, C. & Zhang, X. Sub-diffraction-limited optical imaging with a silver superlens. _Science_ 308, 534–537 (2005). Article ADS
Google Scholar * Derode, A., Roux, P. & Fink, M. Robust acoustic time reversal with high-order multiple scattering. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 75, 4206–4209 (1995). Article ADS Google Scholar
* Vellekoop, I. M., van Putten, E. G., Lagendijk, A. & Mosk, A. P. Demixing light paths inside disordered metamaterials. _Opt. Express_ 16, 67–80 (2008). Article ADS Google Scholar
* Cizmar, T., Mazilu, M. & Dholakia, K. In situ wavefront correction and its application to micromanipulation. _Nature Photon._ 4, 388–394 (2010). Article ADS Google Scholar * Dionne,
J. A., Diest, K., Sweatlock, L. A. & Atwater, H. A. PlasMOStor: a metal-oxide-Si field effect plasmonic modulator. _Nano Lett._ 9, 897–902 (2009). Article ADS Google Scholar *
MacDonald, K. F., Samson, Z. L., Stockman, M. I. & Zheludev, N. I. Ultrafast active plasmonics. _Nature Photon._ 3, 55–58 (2009). Article ADS Google Scholar * Utikal, T., Stockman, M.
I., Heberle, A. P., Lippitz, M. & Giessen, H. All-optical control of the ultrafast dynamics of a hybrid plasmonic system. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 104, 113903 (2010). Article ADS Google
Scholar * Temnov, V. V. _et al._ Active magneto-plasmonics in hybrid metal-ferromagnet structures. _Nature Photon._ 4, 107–111 (2010). Article ADS Google Scholar * Durach, M., Rusina,
A., Stockman, M. I. & Nelson, K. Toward full spatiotemporal control on the nanoscale. _Nano Lett._ 7, 3145–3149 (2007). Article ADS Google Scholar * Aeschlimann, M. _et al._ Adaptive
subwavelength control of nano-optical fields. _Nature_ 446, 301–304 (2007). Article ADS Google Scholar * Li, X. & Stockman, M. I. Highly efficient spatiotemporal coherent control in
nanoplasmonics on a nanometer-femtosecond scale by time reversal. _Phys. Rev. B_ 77, 195109 (2008). Article ADS Google Scholar * Volpe, G., Cherukulappurath, S., Parramon, R. J.,
Molina-Terriza, G. & Quidant, R. Controlling the optical near field of nanoantennas with spatial phase-shaped beams. _Nano Lett._ 9, 3608–3611 (2009). Article ADS Google Scholar *
Garcia-Vidal, F. J., Martin-Moreno, L., Ebbesen, T. W. & Kuipers, L. Light passing through subwavelength apertures. _Rev. Mod. Phys._ 82, 729–787 (2010). Article ADS Google Scholar *
Sentenac, A. & Chaumet, P. C. Subdiffraction light focusing on a grating substrate. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 101, 013901 (2008). Article ADS Google Scholar * Bartal, G., Lerosey, G. &
Zhang, X. Subwavelength dynamic focusing in plasmonic nanostructures using time reversal. _Phys. Rev. B_, 79, 201103 (2009). Article ADS Google Scholar * Johnson, P. B. & Christy, R.
W. Optical constants of the noble metals. _Phys. Rev. B_ 6, 4370–4379 (1972). Article ADS Google Scholar * Lalanne, P. & Hugonin, J. P. Interaction between optical nano-objects at
metallo-dielectric interfaces. _Nature Phys._ 2, 551–556 (2006). Article ADS Google Scholar * Devaux, E., Ebbesen, T. W., Weeber, J. C. & Dereux, A. Launching and decoupling surface
plasmons via micro gratings. _Appl. Phys. Lett._, 83, 4936–4938 (2003). Article ADS Google Scholar * Popoff, S. M. _et al._ Measuring the transmission matrix in optics: an approach to the
study and control of light propagation in disordered media. _Phys. Rev. Lett._ 104, 100601 (2010). Article ADS Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors thank E.
van Putten and J. Cesario for stimulating and helpful discussions, and H. Zeijlermaker for sample fabrication. This work is part of the research programme of the ‘Stichting voor Fundamenteel
Onderzoek der Materie’, which is financially supported by the Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * FOM-Institute for Atomic
and Molecular Physics AMOLF, Science Park 104, Amsterdam, 1098 XG, The Netherlands Bergin Gjonaj, Jochen Aulbach, Patrick M. Johnson, L. Kuipers & Ad Lagendijk * Complex Photonic
Systems, Faculty of Science and Technology, and MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology, University of Twente, PO Box 217, 7500 AE Enschede, The Netherlands Allard P. Mosk Authors * Bergin Gjonaj
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Jochen Aulbach View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar *
Patrick M. Johnson View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Allard P. Mosk View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * L. Kuipers View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Ad Lagendijk View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS B.G. was the primary researcher on this project, developing and building the set-up, carrying out all experiments and analysis, and writing the paper.
All authors made essential contributions to the project and take full responsibility for the results presented. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Bergin Gjonaj. ETHICS DECLARATIONS
COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing financial interests. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary information (PDF 287 kb) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS
Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Gjonaj, B., Aulbach, J., Johnson, P. _et al._ Active spatial control of plasmonic fields. _Nature Photon_ 5, 360–363 (2011).
https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2011.57 Download citation * Received: 21 November 2010 * Accepted: 01 April 2011 * Published: 22 May 2011 * Issue Date: June 2011 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2011.57 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative