Play all audios:
ABSTRACT Recent studies have suggested that lincRNA-ROR is involved in the tumorigenesis of different types of cancers. However, the role of lincRNA-ROR in retinoblastoma has not been
determined. We investigated lincRNA-ROR levels in 58 retinoblastoma and adjacent non-tumor tissues by quantitative reverse transcription PCR. Recurrence-free survival was analyzed using Cox
regression analyses. Cell migration and invasion abilities were detected by wound-healing, Transwell invasion, and bioluminescence imaging assays. Western blotting was performed to detect
epithelial–mesenchymal transition markers. Interactions between lincRNA-ROR, miR-32-5p, and Notch1 were confirmed by Luciferase, RNA pull-down, and RIP assays. Histone acetylation was
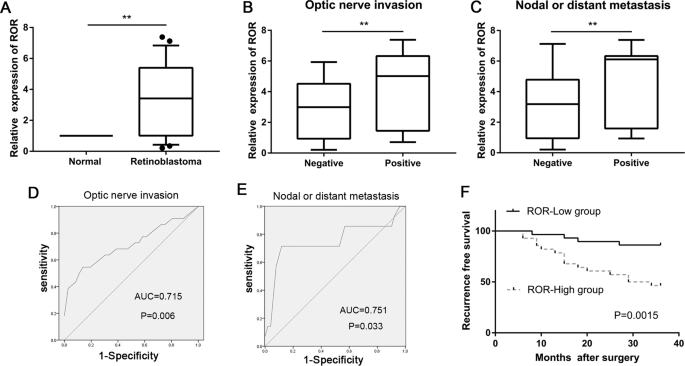
detected by chromatin immunoprecipitation assays. We showed that lincRNA-ROR was significantly upregulated in retinoblastoma tissues, and overexpression of lincRNA-ROR was significantly
correlated with optic nerve invasion, nodal or distant metastasis, and recurrence. We also showed that lincRNA-ROR is a critical promoter of retinoblastoma cell metastasis, both in vivo and
in vitro. Further, we demonstrated that lincRNA-ROR activates the Notch signaling pathway by acting as a sponge of miR-32-5p. Upregulation of lincRNA-ROR was attributed to the CBP-mediated
H3K27 acetylation at the promoter region. Our results reveal a potential competing endogenous RNA regulatory pathway, in which lincRNA-ROR modulates the epithelial–mesenchymal transition
program by competitively binding to endogenous miR-32-5p and regulating Notch signaling pathway activity in retinoblastoma cells, which may provide new insights into novel molecular
therapeutic targets for retinoblastoma. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through
your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant
access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions *
Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS MIR-889-3P TARGETING BMPR2 PROMOTES THE DEVELOPMENT OF RETINOBLASTOMA VIA JNK/MAPK/ERK SIGNALING Article Open
access 27 March 2024 LINC01152 UPREGULATES MAML2 EXPRESSION TO MODULATE THE PROGRESSION OF GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME VIA NOTCH SIGNALING PATHWAY Article Open access 22 January 2021 LNCRNA
LINC00998 INHIBITS THE MALIGNANT GLIOMA PHENOTYPE VIA THE CBX3-MEDIATED C-MET/AKT/MTOR AXIS Article Open access 02 December 2020 REFERENCES * Ghassemi F, Khodabande A. Risk definition and
management strategies in retinoblastoma:current perspectives. Clin Ophthalmol. 2015;9:985–94. Article Google Scholar * Cassoux N, Lumbroso L, Levy-Gabriel C, Aerts I, Doz F, Desjardins L.
Retinoblastoma: update on current management. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol. 2017;6:290–5. Google Scholar * Pritchard EM, Dyer M, Guy R. Progress in small molecule therapeutics for the treatment of
retinoblastoma. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016;16:430–54. Article CAS Google Scholar * Stenzel E, Göricke S, Temming P, Biewald E, Zülow S, Göbel J, et al. Feasibility of intra-arterial
chemotherapy for retinoblastoma: experiences in a large single center cohort study. Neuroradiology. 2019;61:351–7. Article Google Scholar * Horita K, Kurosaki H, Nakatake M, Kuwano N,
Oishi T, Itamochi H, et al. lncRNA UCA1-mediated Cdc42 signaling promotes oncolytic vaccinia virus cell-to-cell spread in ovarian cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2019;13:35–48. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Zhang J, Lin Z, Gao Y, Yao T. Downregulation of long noncoding RNA MEG3 is associated with poor prognosis and promoter hypermethylation in cervical cancer. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 2017;36:5. Article Google Scholar * Zhang J, Yao T, Lin Z, Gao Y. Aberrant methylation of MEG3 functions as a potential plasma-based biomarker for cervical cancer. Sci Rep.
2017;7:6271. Article Google Scholar * Zhang J, Gao Y. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits cervical cancer cell growth by promoting degradation of P-STAT3 protein via ubiquitination. Cancer
Cell Int. 2019;19:175. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhang L, Peng D, Sood AK, Dang CV, Zhong X. Shedding light on the dark cancer genomes: long noncoding RNAs as novel biomarkers and
potential therapeutic targets for cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018;17:1816–23. Article CAS Google Scholar * Loewer S, Cabili MN, Guttman M, Loh YH, Thomas K, Park IH, et al. Large intergenic
non-coding RNA-ROR modulates reprogramming of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Genet. 2010;42:1113–7. Article CAS Google Scholar * Li L, Gu M, You B, Shi S, Shan Y, Bao L, et
al. Long non-coding RNA ROR promotes proliferation, migration and chemoresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2016;107:1215–22. Article CAS Google Scholar * Fei D, Sui G, Lu
Y, Tan L, Dongxu Z, Zhang K. The long non-coding RNA-ROR promotes osteosarcoma progression by targeting miR-206. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23:1865–72. Article CAS Google Scholar * Feng S, Yao
J, Chen Y, Geng P, Zhang H, Ma X, et al. Expression and functional role of reprogramming-related long noncoding RNA (lincRNA-ROR) in glioma. J Mol Neurosci. 2015;56:623–30. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Gao Y, Lu X. Decreased expression of MEG3 contributes to retinoblastoma progression and affects retinoblastoma cell growth by regulating the activity of Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:1461–9. Article CAS Google Scholar * Gao Y, Huang P, Zhang J. Hypermethylation of MEG3 promoter correlates with inactivation of MEG3 and poor prognosis in
patients with retinoblastoma. J Transl Med. 2017;15:268. Article CAS Google Scholar * Salehi B, Varoni EM, Sharifi-Rad M, Rajabi S, Zucca P, Iriti M, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition as a target for botanicals in cancer metastasis. Phytomedicine. 2019;55:125–36. Article CAS Google Scholar * Abdollahzadeh R, Daraei A, Mansoori Y, Sepahvand M, Amoli MM,
Tavakkoly-Bazzaz J. Competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) cross talk and language in ceRNA regulatory networks: a new look at hallmarks of breast cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:10080–100.
Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhang J, Yao T, Wang Y, Yu J, Liu Y, Lin Z. Long noncoding RNA MEG3 is downregulated in cervical cancer and affects cell proliferation and apoptosis by
regulating miR-21. Cancer Biol Ther. 2016;17:104–13. Article Google Scholar * Zhang L, Xue Z, Yan J, Wang J, Liu Q, Jiang H. LncRNA Riken-201 and Riken-203 modulates neural development by
regulating the Sox6 through sequestering miRNAs. Cell Prolif. 2019;52:e12573. Article Google Scholar * Eades G, Wolfson B, Zhang Y, Li Q, Yao Y, Zhou Q. lincRNA-RoR and miR-145 regulate
invasion in triple-negative breast cancer via targeting ARF6. Mol Cancer Res. 2015;13:330–8. Article CAS Google Scholar * Dong C, Liu S, Lv Y, Zhang C, Gao H, Tan L, et al. Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR regulates proliferation and invasion via activating Notch signalling pathway in retinoblastoma. J Biosci. 2016;41:677–87. Article CAS Google Scholar * Li X, Yang L,
Shuai T, Piao T, Wang R. MiR-433 inhibits retinoblastoma malignancy by suppressing Notch1 and PAX6 expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;82:247–55. Article CAS Google Scholar * Chen X,
Xiao W, Liu X, Zeng M, Luo L, Wu M, et al. Blockade of Jagged/Notch pathway abrogates transforming growth factor β2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human retinal pigment
epithelium cells. Curr Mol Med. 2014;14:523–34. Article CAS Google Scholar * Li L, Wu D. miR-32 inhibits proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and metastasis by targeting
TWIST1 in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:1489–98. Article CAS Google Scholar * Wang M, Sun Y, Xu J, Lu J, Wang K, Yang DR, et al. Preclinical studies using
miR-32-5p to suppress clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis via altering the miR-32-5p/TR4/HGF/Met signaling. Int J Cancer. 2018;143:100–12. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhou B, Yuan
W, Li X. Long intergenic noncoding RNA 319 (linc00319) promotes cell proliferation and invasion in lung cancer cells by directly downregulating the tumor suppressor MiR-32. Oncol Res. 2017
[Epub ahead of print]. * Ding G, Li W, Liu J, Zeng Y, Mao C, Kang Y, et al. LncRNA GHET1 activated by H3K27 acetylation promotes cell tumorigenesis through regulating ATF1 in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;94:326–31. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zhang E, Han L, Yin D, He X, Hong L, Si X, et al. H3K27 acetylation activated-long non-coding RNA CCAT1
affects cell proliferation and migration by regulating SPRY4 and HOXB13 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:3086–101. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Chen F, Qi S, Zhang X, Wu J, Yang X, Wang R. lncRNA PLAC2 activated by H3K27 acetylation promotes cell proliferation and invasion via the activation of Wnt/β‑catenin pathway in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2019;54:1183–94. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Download references FUNDING The Project Supported by Shenzhen Science and Technology Plan
Project (Grant no. JCYJ20170307095222274), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant no. 2019A1515010412), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 81902751).
AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Ophthalmology, The Second Clinical Medical College (Shenzhen People’s Hospital), Jinan University, Shenzhen, China Yali Gao &
Xiaoling Luo * Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Second Clinical Medical College (Shenzhen People’s Hospital), Jinan University, Shenzhen, China Jun Zhang Authors * Yali Gao View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Xiaoling Luo View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Jun
Zhang View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Jun Zhang. ETHICS DECLARATIONS CONFLICT OF INTEREST The
authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. ETHICS STATEMENT All procedures performed in studies involving human participants and animals were in accordance with the ethical
standards of the ethic committee of the Shenzhen People’s Hospital. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PUBLISHER’S NOTE Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published
maps and institutional affiliations. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION TABLE S1 TABLE S2 RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Gao, Y., Luo, X. &
Zhang, J. LincRNA-ROR is activated by H3K27 acetylation and induces EMT in retinoblastoma by acting as a sponge of miR-32 to activate the Notch signaling pathway. _Cancer Gene Ther_ 28,
42–54 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-0181-z Download citation * Received: 23 February 2020 * Revised: 06 May 2020 * Accepted: 07 May 2020 * Published: 22 May 2020 * Issue Date:
February 2021 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-0181-z SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a
shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative